Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH_Illustration_What-to-Know-About-Gaba_Illustrator_Jessica-Olah_Final-ea5963205783442fa62455edbc5851ef.jpg) | 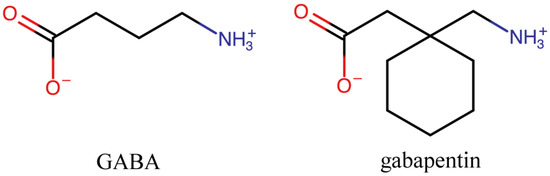 |
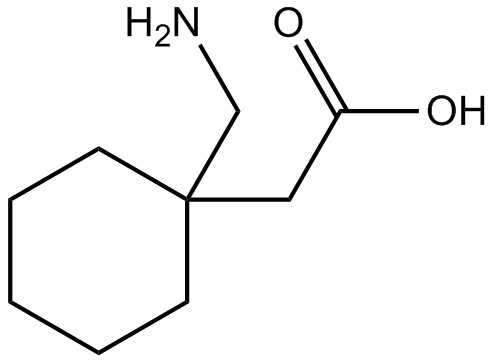
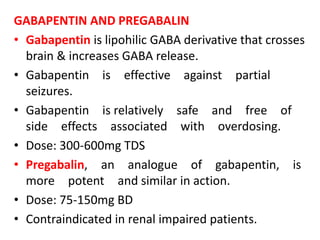
What's the Difference? GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) and Gabapentin are both substances that affect the central nervous system, but they have different mechanisms of action and uses. GABA is a naturally occurring neurotransmitter in the brain that inhibits or slows down nerve activity, helping to reduce anxiety and promote relaxation. GABA is not the same as gabapentin. GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) is an amino acid supplement; gabapentin is a prescription medication December 23, 2022 By Trudy Scott 53 Comments The key difference between GABA and gabapentin is that GABA is the major inhibitory neurotransmitter that helps in the development and maturation of the mammalian central nervous system, whereas gabapentin is a medication that can mimic the effect of GABA. GABA and gabapentin are chemically related, but there is a difference between them based on their structural make-up and applications GABA and Gabapentin, though distinct entities share a common goal: to promote calmness and regulate neuronal activity. While GABA is a natural neurotransmitter with diverse functions, Gabapentin is a synthetic medication mimicking some of its effects for specific therapeutic purposes. We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and glutamate are implicated in numerous neuropsychiatric and substance abuse conditions, but their spectral overlap with other resonances makes them a challenge to quantify in humans. Gabapentin, marketed for the GABA stimulates the release of the hormone prolactin by the pituitary gland, potentially alleviating issues related to prostate enlargement. Recommended doses range from 20 mg to 40 mg daily, preferably dissolved under the tongue. Explore the differences between Gamma Aminobutyric Acid (GABA), a neurotransmitter, and Gabapentin, a medication, despite their similar names. Gabapentin is a structural analog of the inhibitory neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Its anticonvulsant, analgesic and anxiolytic properties suggest that it increases GABAergic inhibition; however, the molecular basis for these effects GABA is a naturally occurring neurotransmitter in the brain, primarily responsible for inhibiting nerve transmission, which helps to reduce neuronal excitability. In contrast, gabapentin is a medication designed to mimic the effects of GABA, used primarily to treat conditions like epilepsy and neuropathic pain. Learn about the difference between GABA and gabapentin, a neurotransmitter and an inhibitory medication often used for seizures and neuropathic pain. Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is a neurotransmitter with a crucial role in the human brain and body. It's recognized for its calming and relaxing effects, and many people use GABA supplements to unwind, alleviate stress, and enhance sleep. Gabapentin, while structurally similar to GABA, is a medication with distinct effects and applications. Gabapentin Gabapentin is a structural analogue of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Gabapentin was originally introduced as an antiepileptic drug. Mechanism of Action • Although gabapentin is related to GABA, it does not appear to have any analgesic effect at GABA receptors. • GABA is known for its potential benefits in reducing anxiety and stress. By binding to GABA receptors in the brain, it can help inhibit the transmission of nerve signals, resulting in a calming effect. This is why GABA is often used as a natural remedy for anxiety and related conditions. GABA also has potential applications in pain management. It can help alleviate nerve pain by reducing the Gabapentin is a new chemical compound designed as a structural analog of GABA that is effective in the treatment of partial seizures. In contrast to GABA, gabapentin readily penetrates the blood–brain barrier. In man, gabapentin has been demonstrated to increase GABA concentrations [126]. Most probably the mechanism of action is related to events modulated through its interaction with a GABA and gabapentin are chemically related but have different structural make-ups and applications. Here is a table comparing the differences between GABA and gabapentin: Gaba vs. Gabapentin: side effect and effectiveness comparison (a real world drug study) Summary: We compare the side effects and drug effectiveness of Gaba and Gabapentin. The phase IV clinical study is created by eHealthMe based on reports (from sources including the FDA) of 428,095 people who take Gaba and Gabapentin, and is updated regularly. GABA may be able to help those with insomnia. Learn how best to try this supplement and how much to take. Gabapentin was developed for treating epilepsy by alleviating the excitability of a patient’s nervous system. This also helps with other disorders with neuropathic pain, for example fibromyalgia, insomnia, and bipolar disorder. Another name for gabapentin is Neurontin, and this medication has no effect on the amount of GABA in the brain.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH_Illustration_What-to-Know-About-Gaba_Illustrator_Jessica-Olah_Final-ea5963205783442fa62455edbc5851ef.jpg) |  |