Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
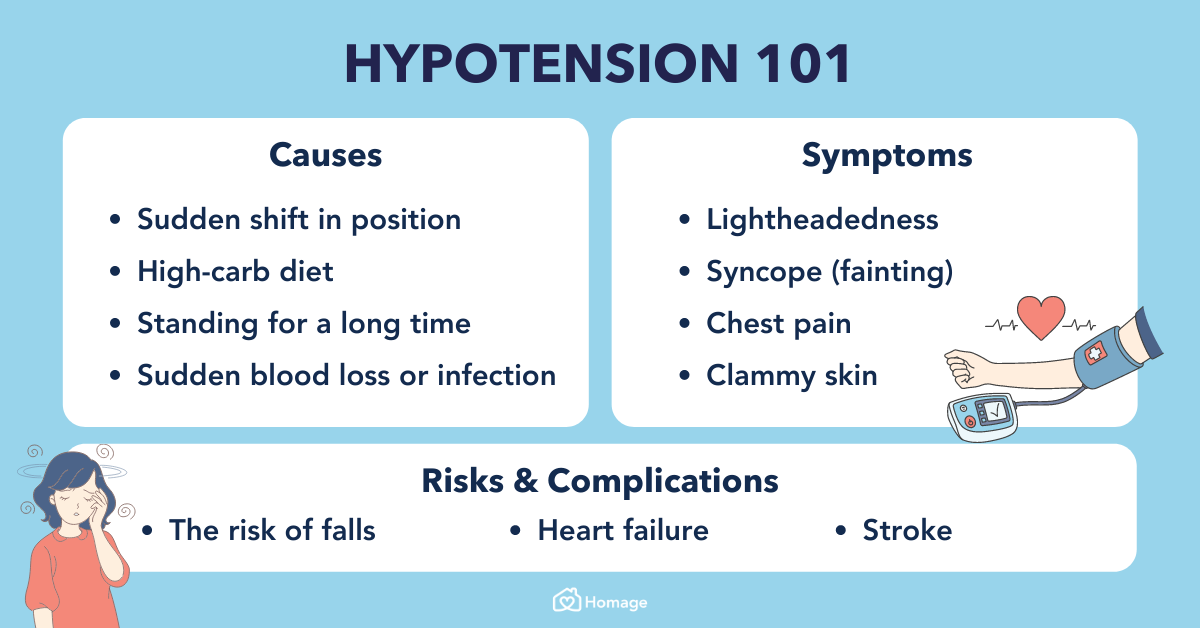
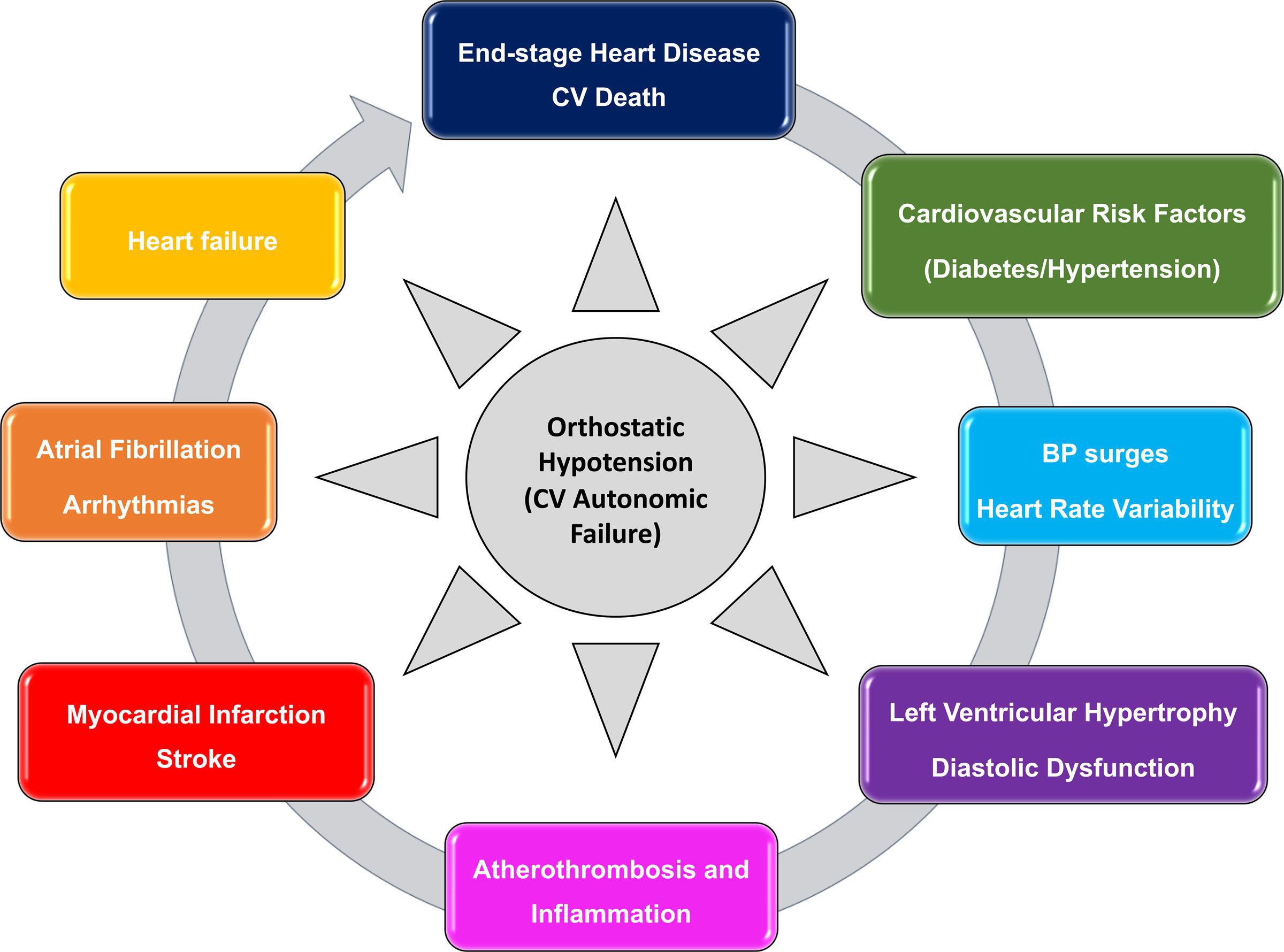
Abstract Drug-induced orthostatic hypotension is an important clinical problem. When symptomatic, it is poorly tolerated by the patient, and can be a cause for discontinuing treatment. It may have more serious consequences if it leads to syncope, falls and injury, or to sustained loss of perfusion of vital organs resulting in heart attack or stroke. Orthostatic hypotension is easily detected Data on chronic opioid treatment are limited, but hypotension, orthostatic hypotension, and syncope are commonly reported among potential adverse effects of most opioid analgesics, such as morphine, buprenorphine, fentanyl, oxycodone, and tapentadol [55 •]. Yet, the mechanism underlying opioid-mediated hypotension still remains a matter of This page includes the following topics and synonyms: Medication Causes of Orthostatic Hypotension, Orthostatic Hypotension due to Medication, Drug-Induced Orthostatic Hypotension, Drug-Induced Hypotension, Drug-Induced Syncope, Medication-Induced Syncope. Abstract Orthostatic hypotension (OH) is an abnormal blood pressure response to standing, which is associated with an increased risk of adverse outcomes such as syncope, falls, cognitive impairment, and mortality. Medical therapy is one the most common causes of OH, since numerous cardiovascular and psychoactive medications may interfere with the blood pressure response to standing, leading to Interestingly, although first-generation H1 antihistamines (e.g. diphenhydramine, hydroxyzine) are frequently implicated as a cause of orthostatic hypotension due to anticholinergic effect, antihistamines can also be used to treat orthostatic hypotension by reducing histamine-induced vasodilatation [24, 25]. Summary: Hypotension is reported as a side effect among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin), especially for people who are female, 60+ old, have been taking the drug for < 1 month also take Aspirin, and have High blood pressure. The phase IV clinical study analyzes which people have Hypotension when taking Gabapentin. The perioperative use of gabapentin is dis-cussed, previous reports of intraoperative hypotension re-lated to its use reviewed, and its potential role in periop-erative BP changes presented. Orthostatic hypotension is associated with a significant increase in cardiovascular risk and falls, and up to a 50% increase in relative risk of all-cause mortality. Many disorders can cause orthostatic hypotension, as can acute or chronic volume depletion and a side effect of medications (particularly antihypertensive agents). The symptom complex in orthostatic hypotension consisting of lightheadedness, dizziness, or faintness occurring with prolonged standing is called chronic orthostatic intolerance. Orthostatic hypotension (OH) is a common side effect of drugs. It causes a reduction in blood pressure (BP) on standing, which results in reduced cerebral blood flow that is linked to falls, strokes, cognitive impairment, and increased mortality. Orthostatic hypotension is a frequent cause of falls and syncope, impairing quality of life. It is an independent risk factor of mortality and a common cause of hospitalizations, which exponentially increases in the geriatric population. We present a management plan based on a systematic literature review and understanding of the underlying pathophysiology and relevant clinical pharmacology Key takeaways: Hypotension is when your blood pressure drops too low. It can have many causes, including dehydration, heart problems, and neurologic conditions like Parkinson’s disease. Some medications can also cause low blood pressure. Examples include blood pressure medications, nitrates, and opioids. Orthostatic hypotension is a frequent cause of falls and syncope, impairing quality of life. It is an independent risk factor of mortality and a common cause of hospitalizations, which exponentially increases in the geriatric population. We present a management plan based on a systematic literature review and understanding of the underlying pathophysiology and relevant clinical pharmacology Orthostatic hypotension is a chronic, debilitating illness that is difficult to treat. The therapeutic goal is to improve postural symptoms, standing time, and function rather than to achieve upright normotension, which can lead to supine Why was this study done? Orthostatic hypotension (OH) is a common side effect of drugs. It causes a reduction in blood pressure (BP) on standing, which results in reduced cerebral blood flow that is linked to falls, strokes, cognitive impairment, and increased mortality. Over 250 medications are associated with OH. However, there is conflicting evidence on the extent to which different drug We study how severe was Orthostatic hypotension, when it was recovered, drug effectiveness, race, and more among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin) - Oral and intravenous gabapentin can markedly attenuate blood pressure (BP) in hypertensive rats. The nucleus tractus solitarii (NTS) is the primary integrative center for cardiovascular control and other autonomic functions in the central nervous Summary: Orthostatic hypotension is reported as a side effect among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin), especially for people who are male, 60+ old, have been taking the drug for 1 - 6 months also take Aspirin, and have High blood pressure. The phase IV clinical study analyzes which people have Orthostatic hypotension when taking Gabapentin. Learn about the side effects of gabapentin, from common to rare, for consumers and healthcare professionals. Orthostatic hypotension (OH), a common, often overlooked, disorder with many causes, is associated with debilitating symptoms, falls, syncope, cognitive impairment, and risk of death. Chronic OH, a cardinal sign of autonomic dysfunction, increases with advancing age and is commonly associated with neurodegenerative and autoimmune diseases, diabetes, hypertension, heart failure, and kidney
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |