Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
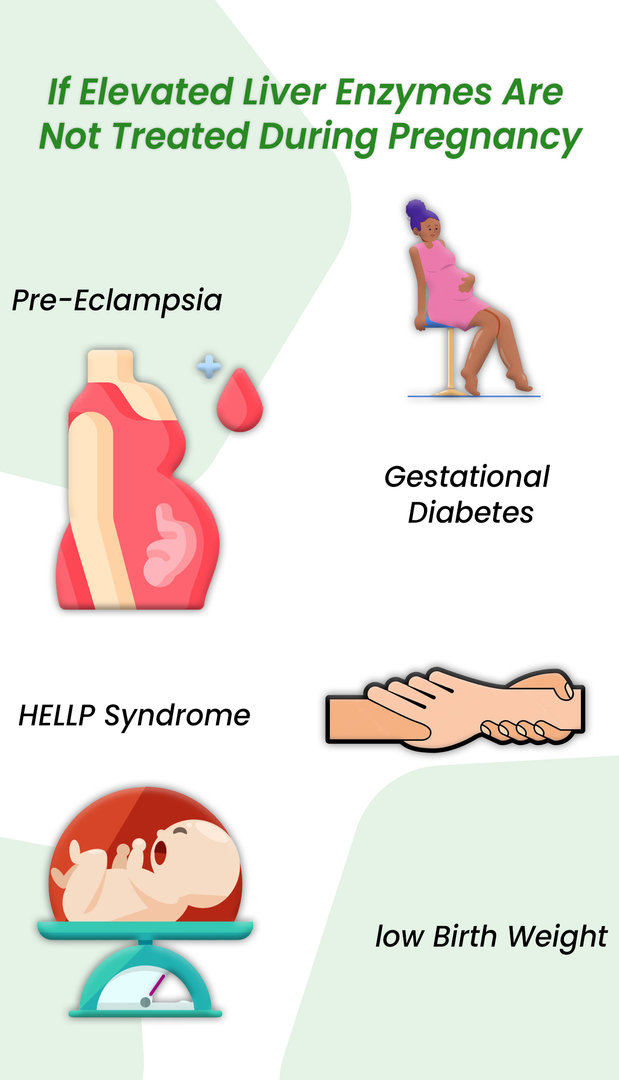 |  |
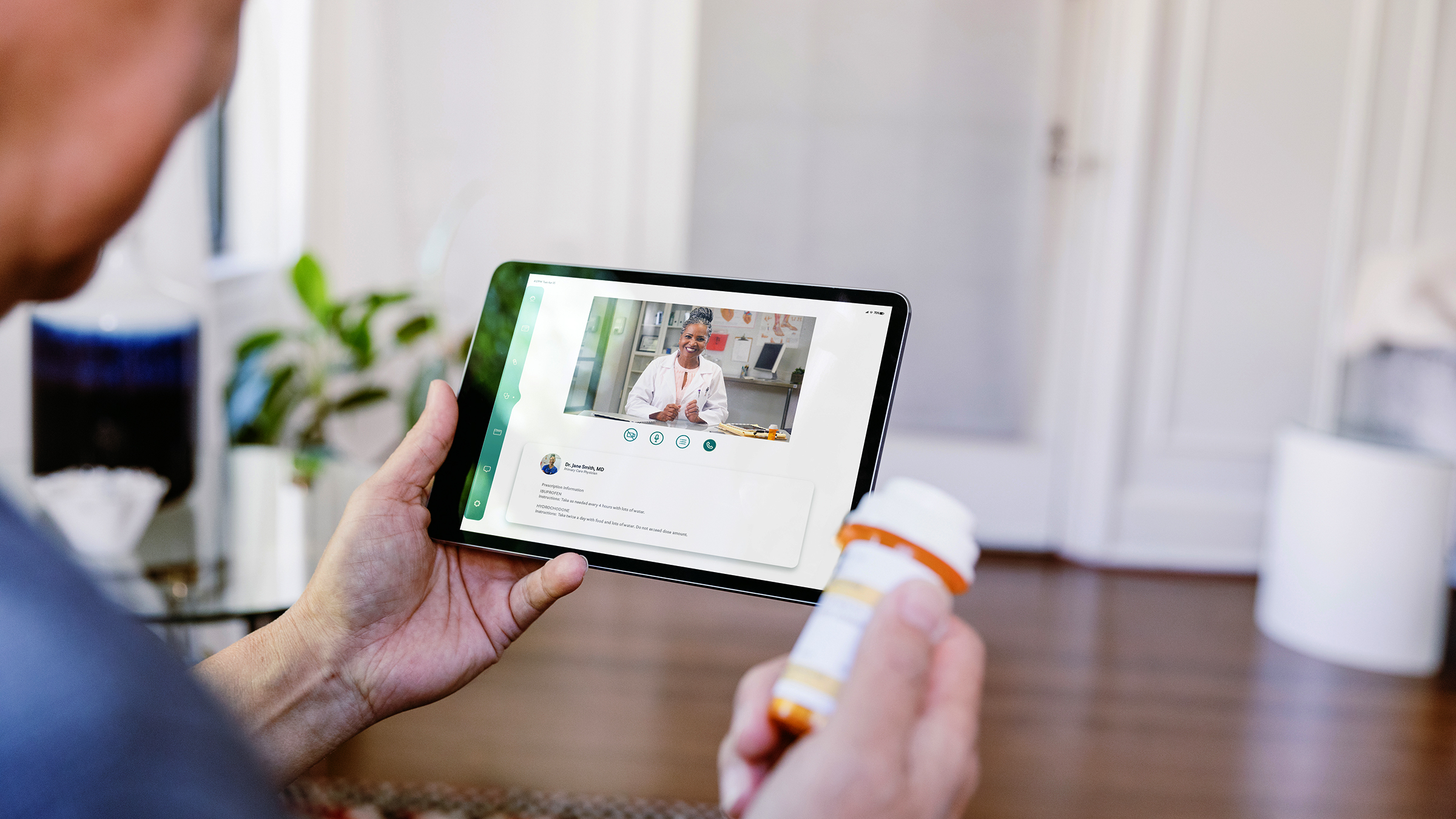
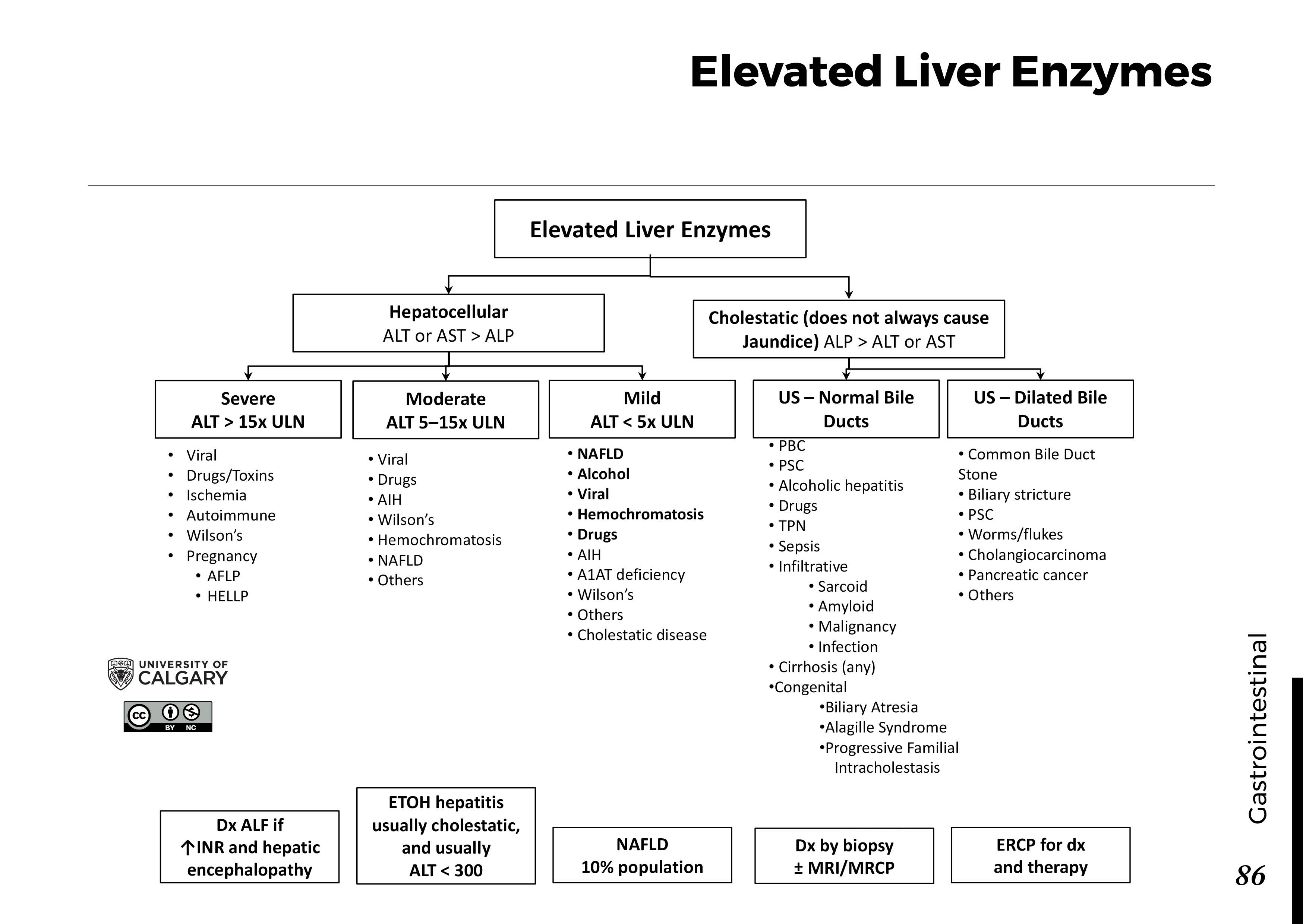
Gabapentin (Neurontin) is generally not harmful to the liver or kidneys, but in rare cases, it can cause DRESS syndrome. It is not metabolized by the liver and is excreted unchanged in the kidneys after circulation. Key takeaways: Gabapentin (Neurontin, Horizant, Gralise) usually isn’t bad for your liver or kidneys. In most cases, it has no harmful effect on these organs. In rare instances, gabapentin can cause DRESS (drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms) syndrome. Gabapentin has infrequently been reported to cause liver injury, but the causality in previous reports is contested. Different reports suggest that gabapentin has a low profile of interaction with other drugs, hepatic enzymes, and plasma proteins. It is recommended for controlling seizures, treating nerve pain after having had shingles, and treating restless legs syndrome. Gabapentin use isn’t known to affect enzyme or bilirubin levels, but it may rarely cause an allergic reaction characterized by elevated eosinophil levels. This is a condition called eosinophilia, which may cause liver damage. Gapentin is not metabolized by the liver, and its effects on the liver and kidneys are similar to previous studies. In rare cases, gabapentin can cause DRESS (drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms). High liver enzyme levels may indicate inflammation within the liver, which can be a sign of a medical condition like hepatitis or other conditions. Elevated liver enzymes might be found during routine blood testing and are usually mildly raised for a short time. Therapy with gabapentin is not associated with serum aminotransferase elevations, but several cases of clinically apparent liver Gabapentin is an uncommon cause of DILI reported to cause a hepatocellular, cholestatic, or mixed picture of liver injury. Given the limitations of prior cases, we feel our report most closely ties gabapentin use to the resultant transaminase elevation. Medications like Tylenol and Aleve are hepatotoxic, meaning they could raise liver enzymes and damage your liver over time. See the list of medications to avoid. After gabapentin was discontinued, liver enzymes began to downtrend with discharge values of AST 16, ALT 35, ALP 413, Tbili 9.3 and INR 1.1 (Figure). Gabapentin induced liver injury is rare with few reported cases, many of which did not exclude other etiologies. Gabapentin, a medication frequently prescribed for neuropathic pain and seizures, undergoes metabolic processing primarily by the kidneys, yet concerns persist about its potential impact on other organs. The liver, responsible for detoxification and drug Therapy with gabapentin is not associated with serum aminotransferase elevations, but several cases of clinically apparent liver injury from gabapentin have been reported. In conclusion, gabapentin and magnesium long-term treatments proved better tolerability than valproate on liver; however, they may adversely affect the kidney, to different magnitudes. Gabapentin is not metabolized by the liver. Instead, it is excreted unchanged in your kidneys after circulating in your blood. Gabapentin affects nerves and chemicals in your body that are involved in some types of pain and in seizures. Unlike many other medications that undergo extensive hepatic metabolism, gabapentin is primarily excreted unchanged through the kidneys. This characteristic reduces the likelihood of direct liver toxicity compared to drugs that require significant metabolic processing by the liver. Can administration of gabapentin for trigeminal neuralgia dramatically increase liver function tests? There are several liver enzymes, but the ones that show liver damage from medications are aspartate transaminase (AST) and alanine transaminase (ALT). Medications may cause liver enzymes to be elevated without serious liver damage until they reach 3 to 5 times the normal levels. Possible: Many medications can exhibit mild adverse effects on the liver, and not unusual to see slight elevations of liver enzymes. No need to stop med unless the elevation is more than 3 times normal, in most cases. Can gabapentin cause liver enzymes to be elevated? Gabapentin is a unique anticonvulsant used as an adjunctive therapy in managing epilepsy and neuropathic pain syndromes. It is a structural analogue of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and has been approved for use in the United States in 1993. It is used as an anticonvulsant and neuropathy agent, with over 18 million prescriptions filled Find out whether gabapentin can cause elevated liver enzyme levels and learn about the potential risks and side effects of this medication.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |