Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
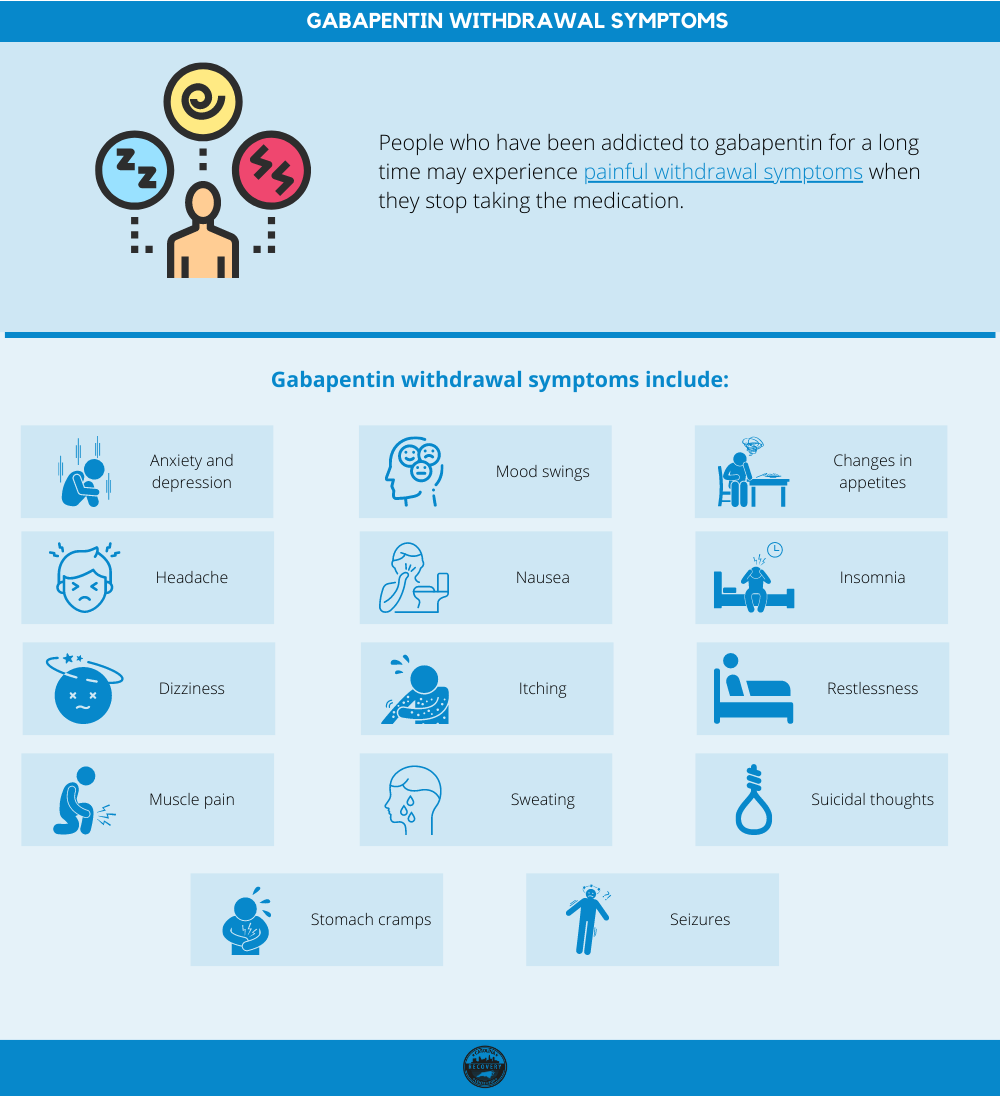
Thanks to its low addictive potential, gabapentin is usually seen as a safer option to opioids, however, the new findings raise concerns on its potential side effects on brain health. It can take one to two weeks to feel the full effects of Gabapentin for nerve pain. Some people use this medication long-term. Learn how long you should take Gabapentin for nerve pain. Gabapentin can be a valuable tool in managing various health conditions, but long-term use comes with potential risks. From physical side effects like weight gain and fatigue to cognitive and emotional challenges, it’s essential to be aware of how this medication may affect you over time. Gabapentin is fairly safe when you use it correctly. It does come with some possible side effects, though. People who misuse this drug are also at risk of additional side effects. People who’d received six or more gabapentin prescriptions were more likely to be diagnosed with dementia or mild cognitive impairment within 10 years of their initial pain diagnosis, results show. Looking at age groups, researchers found that 18- to 64-year-olds prescribed gabapentin were more than twice as likely to develop dementia or MCI. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication prescribed for a variety of conditions. Learn about its uses, side effects, and what you should know if you've been prescribed this medication. Learn about the side effects of gabapentin, from common to rare, for consumers and healthcare professionals. What is gabapentin used for? Gabapentin is commonly used to treat and prevent seizures in people with epilepsy or to treat nerve pain (postherpetic neuralgia) that can occur after a viral The brand-name drug Neurontin can treat one form of epilepsy in children as young as 3 years old. Some people take other medications with gabapentin to control epilepsy symptoms. Though gabapentin has many potential uses, it can cause side effects. Read more about 13 gabapentin side effects here. Gabapentin doesn’t hurt the liver or kidneys in most cases. However, taking a safe gabapentin dose is important to prevent potential side effects. Description Gabapentin is used to help control partial seizures (convulsions) in the treatment of epilepsy. This medicine cannot cure epilepsy and will only work to control seizures for as long as you continue to take it. Gabapentin is also used to manage a condition called postherpetic neuralgia, which is pain that occurs after shingles. Gabapentin works in the brain to prevent seizures and Gabapentin is an anti-epileptic drug, also called an anticonvulsant. It is used to treat some types of seizures and nerve pain caused by shingles. Making Informed Decisions About Gabapentin Given the discussions surrounding the dangers of Gabapentin, it is important for patients to engage in shared decision-making with their healthcare providers. Here are a few steps you can take: Educate Yourself: Read up on Gabapentin’s uses, side effects, and potential interactions. Conclusion Gabapentin is commonly used for neuropathic pain relief in all stages of life. But how safe is gabapentin for older adults? What are the main gabapentin side effects in the elderly? Older adults have a higher prevalence of side effects due to overlapping health conditions and polypharmacy. Like all medicines, gabapentin can cause side effects, although not everyone gets them. Common side effects These common side effects of gabapentin may happen in more than 1 in 100 people. They're usually mild and go away by themselves. There are things you can do to help cope with them: Feeling sleepy, tired or dizzy 7. Interactions Medicines that interact with gabapentin may either decrease its effect, affect how long it works, increase side effects, or have less of an effect when taken with gabapentin. An interaction between two medications does not always mean that you must stop taking one of the medications; however, sometimes it does. Gabapentin is approved to prevent and control partial seizures, relieve postherpetic neuralgia after shingles and moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome. Learn what side effects to watch for, drugs to avoid while taking gabapentin, how to take gabapentin and other important questions and answers. Gabapentin is available in both branded and generic forms. Receiving six or more prescriptions of the drug gabapentin for low back pain is associated with significantly increased risks of developing dementia and mild cognitive impairment (MCI)—29% and Gabapentin has been successfully used to treat some of the effects of brain damage. However, prolonged use can cause serious side effects. This article will summarize the use of gabapentin for brain damage and discuss which symptoms it can help relieve. What Is Gabapentin Used For? Gabapentin is most commonly prescribed for nerve pain such []
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |