Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
/GettyImages-1132248020-a3646ab44b7e42d9b6a267edfbead4b1.jpg) |  |
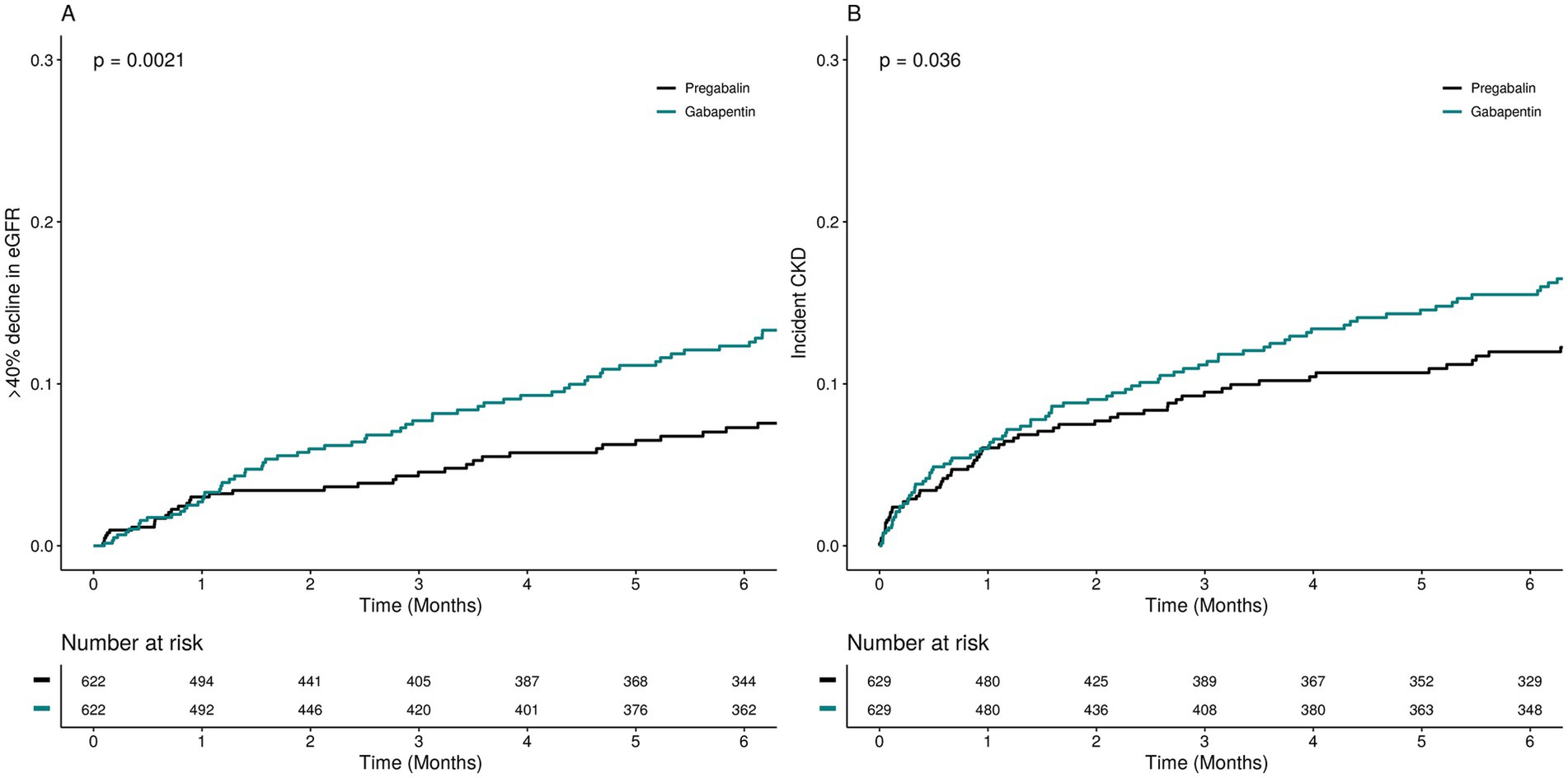
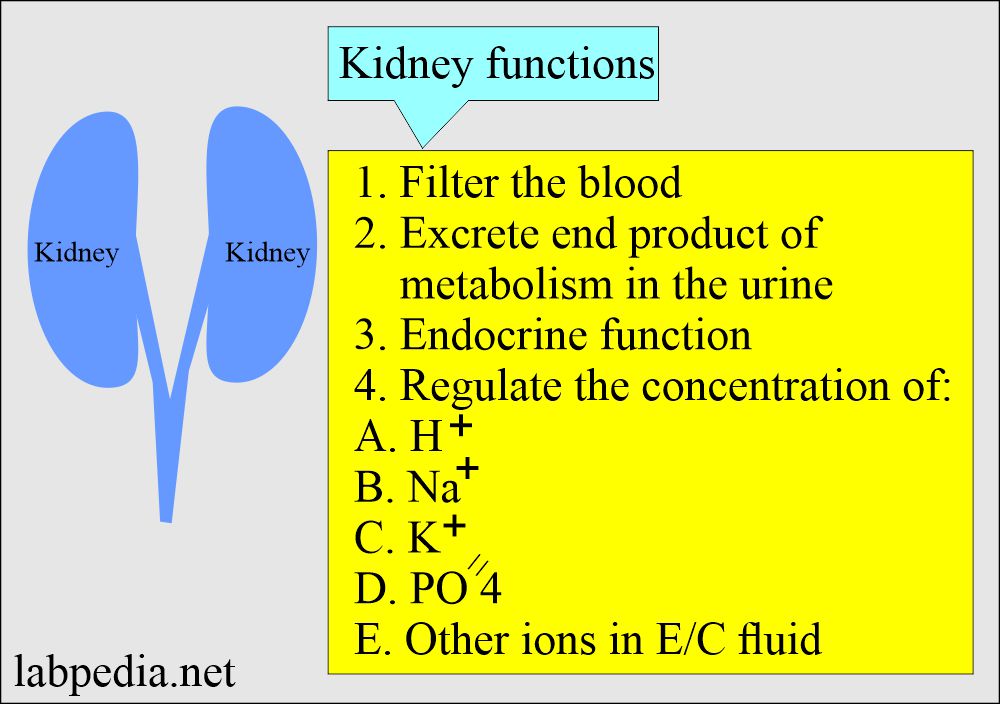
For people with kidney disease, aspirin can increase the risk of bleeding. And in those with reduced kidney function, aspirin is not recommended unless prescribed by a physician. Here’s a scenario of using gabapentin in chronic kidney disease. A 42 year old African American man with a history of coronary artery disease and decompensated heart failure s/p heart transplant and chronic kidney disease presented to a hospital on 9/29/16 complaining of shortness of breath, dyspnea upon exertion and LE edema. Abstract Background: Gabapentin and pregabalin are well-tolerated medications primarily cleared by the kidney. Patients receiving higher gabapentinoid doses with decreased kidney function may be at an increased risk of adverse effects (AEs), but limited evidence exists evaluating gabapentinoid dosing and AEs in this population. Objective: To determine whether patients with decreased creatinine Gabapentin is a prescription drug for seizures and nerve pain. It usually doesn't harm the liver or kidneys, but it can cause a rare allergic reaction called DRESS syndrome. If you have kidney problems, you may need a lower dose of gabapentin. Gabapentin can be used by kidney disease patients, but dosage adjustments are critical. Learn how to safely use gabapentin with kidney issues and discover alternative medications. Gabapentin can be removed from plasma by hemodialysis. Gabapentin affects kidney function as it is primarily eliminated by the kidneys and its clearance is directly proportional to creatinine clearance. This means that patients with impaired renal function may have reduced gabapentin clearance, leading to increased drug levels and potential Gabapentin toxicity in patients with chronic kidney disease is underrecognized. Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive dangerously high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, which can lead to all sorts of problems. An alternative we recommend instead of Gabapentin is Alpha Lipoic Acid. How Does Gabapentin Affect Kidney Function Over Time? Long-term use of Gabapentin may impact kidney function, particularly in patients with pre-existing conditions. Gabapentin, a medication frequently prescribed for managing neuropathic pain and seizures, impacts kidney function, necessitating careful consideration of creatinine levels. Creatinine, a waste product generated by muscle metabolism, serves as a key indic Gabapentinoids, including gabapentin and pregabalin, are frequently prescribed as opioid alternatives. Given that gabapentinoids are eliminated from the body by the kidney, we sought to determine the risk of serious adverse events in patients with chronic kidney disease who started a gabapentinoid at a higher versus a lower dose. From the Research Gabapentin and Renal Function Gabapentin is primarily cleared by the kidney, and its elimination is reduced as kidney function declines 4, 5. Patients with decreased renal function may be at an increased risk of adverse effects due to higher gabapentin levels 6, 7, 5. Gabapentin is frequently used as an analgesic in patients with chronic kidney disease. Although gabapentin is well known for its favorable pharmacokinetics, it is exclusively eliminated renally, and patients with chronic kidney disease are at risk for toxicity. Existing literature on such risk is lacking. Conclusion Gabapentin toxicity in patients with chronic kidney disease is underrecognized. Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive inappropriately high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, occasioning overt toxicity; advanced age and comorbidity predispose these patients for toxicity. Medications are a very important part of staying healthy, especially if you have chronic kidney disease (CKD). But all medicines bring some level of risk for side effects and other safety concerns. Some medicines can damage your kidneys. Many more medicines leave your body through the kidneys - so, they can build up in more advanced stages of CKD. Abstract Background: Gabapentin is frequently used as an analgesic in patients with chronic kidney disease. Although gabapentin is well known for its favorable pharmacokinetics, it is exclusively eliminated renally, and patients with chronic kidney disease are at risk for toxicity. Existing literature on such risk is lacking. Gabapentin primarily affects the central nervous system, but it can also influence various other organs through its therapeutic actions. Gabapentin, a medication initially designed for epilepsy, has garnered attention for its wide-ranging applications in treating neuropathic pain and other conditions. Understanding what organs gabapentin affects is crucial for anyone considering or currently Abstract Gabapentin contains a cyclohexyl group and is a form of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Despite its name, gabapentin does not affect the inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA or its receptors. Instead, it acts as a ligand, binding strongly to the α2δ (Ca) channel subunit and interfering with its regulatory function and the release of excitatory neurotransmitters. Gabapentin is approved Gabapentin’s apparent total clearance is 100 mL/min in adults with normal renal function, which is essentially equivalent to CrCl and does not suggest the involvement of tubular reabsorption. 1 Some evidence suggest that active tubular secretion mediated by organic cation transporter-1 (OCT-1) may play a role in gabapentin’s renal clearance. CONCLUSION: Gabapentin toxicity in patients with chronic kidney disease is underrecognized. Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive inappropriately high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, occasioning overt toxicity; advanced age and comorbidity predispose these patients for toxicity. Discussion. Gabapentin is widely used in the management of pain. It is entirely excreted through the renal system so this needs to be considered in any patient becoming acutely ill and developing renal failure. We describe a patient who developed significant deterioration in her conscious level due to iatrogenic gabapentin overdose. Conclusion.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
/GettyImages-1132248020-a3646ab44b7e42d9b6a267edfbead4b1.jpg) |  |