Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
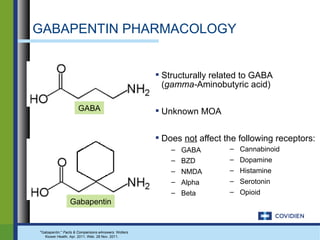 |  |
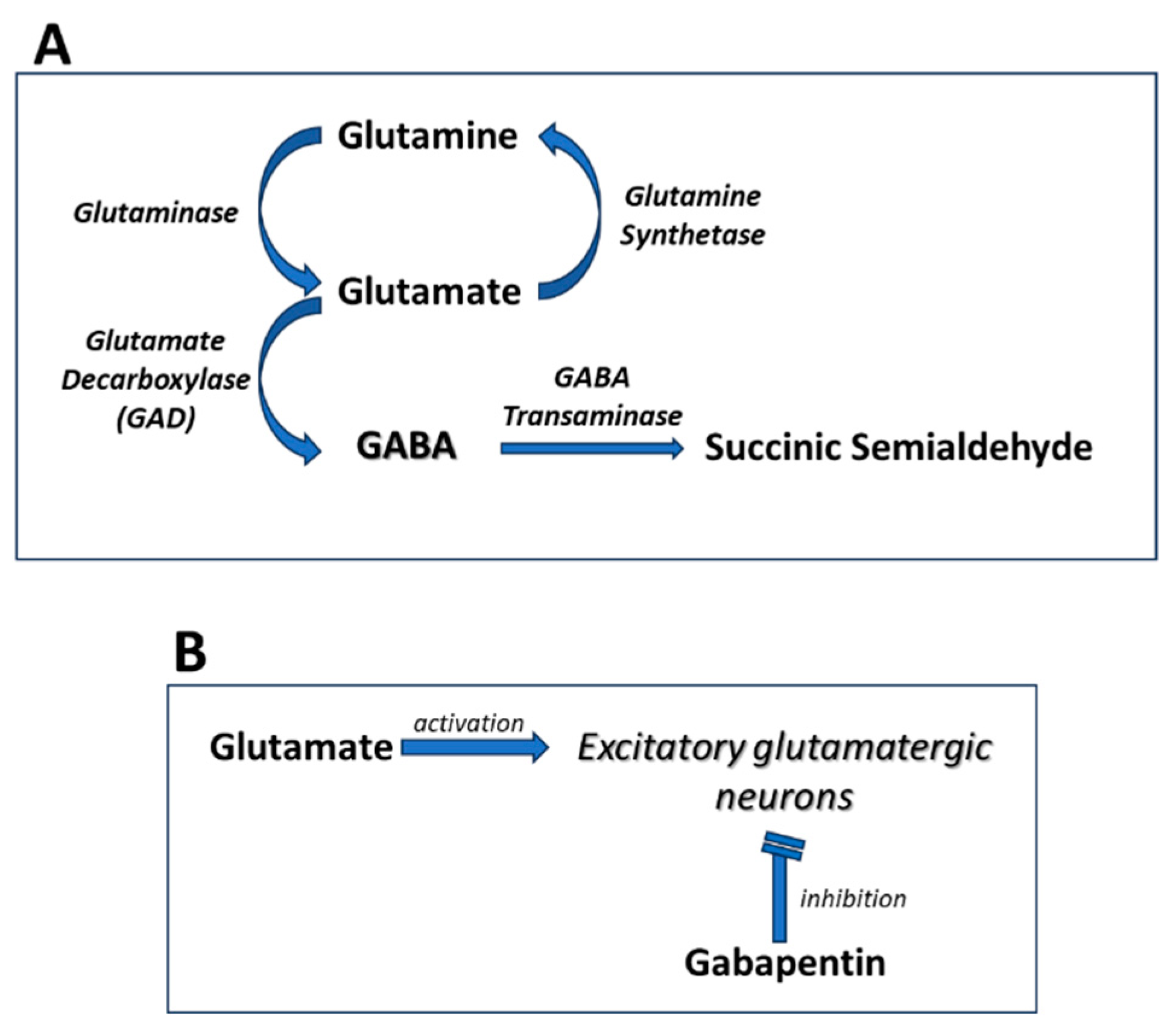
Research has shown that gabapentin exerts a modulating effect at neuronal receptor sites, inhib- iting the release of the neurotransmitters dopamine (5), serotonin and norepinephrine (6) and resulting in in- creased GABA concentrations in various locations throughout the brain (7). It is concluded that gabapentin is not an agonist at GABA (B) receptors that are functional in baclofen-induced antiallodynia in the postoperative pain model in vivo and in GIRK channel activation in ventrolateral PAG neurons in vitro. GABA is a naturally occurring neurotransmitter in the brain that inhibits or slows down nerve activity, helping to reduce anxiety and promote relaxation. On the other hand, Gabapentin is a medication that is structurally similar to GABA but does not directly bind to GABA receptors. Methods: Seventeen healthy adults were randomly assigned to receive topiramate, gabapentin, and lamotrigine and underwent GABA measurements using a 4.1-T magnet from a 13.5-mL volume over the occipital region. GABA concentrations and serum levels were measured at 3 and 6 hours following administration of an acute single dose of one of the drugs. Gabapentin: Gabapentin is indicated for postherpetic neuralgia and serves as adjunctive therapy for managing partial seizures (with or without secondary generalization) in adults and pediatric patients aged 3 or older. Gabapentin was designed as a GABA analog, and some studies have suggested that it modulates the action of the GABA synthetic enzyme, glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) and the glutamate synthesizing enzyme, branched-chain amino acid transaminase, resulting in increased GABA synthesis. 139 Gabapentin increases non-synaptic GABA responses from Gabapentin is a structural analog of the inhibitory neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Its anticonvulsant, analgesic and anxiolytic properties suggest that it increases GABAergic inhibition; however, the molecular basis for these effects is unknown as gabapentin does not directly modify GABA type A (GABAA) receptor function, nor does it modify synaptic inhibition. Here, we An intrathecal injection of gabapentin or baclofen, a GABA (B) receptor agonist, induced antiallodynia in this postoperative pain model. Intrathecal injection of GABA (B) receptor antagonists CGP 35348 and CGP 55845 antagonized baclofen- but not gabapentin-induced antiallodynia. Gabapentin has no direct GABAergic action and does not block GABA uptake or metabolism. Gabapentin blocks the tonic phase of nociception induced by formalin and carrageenan, and exerts a potent inhibitory effect in neuropathic pain models of mechanical hyperalgesia and mechanical/thermal allodynia. Gabapentin robustly increases cell-surface expression of δGABA A receptors and increases a tonic inhibitory conductance in neurons. This enhanced δGABA A receptor function contributes to the ataxic and anxiolytic but not antinociceptive properties of gabapentin. Gabapentin is approved to prevent and control partial seizures, relieve postherpetic neuralgia after shingles and moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome. Learn what side effects to watch for, drugs to avoid while taking gabapentin, how to take gabapentin and other important questions and answers. However, gabapentin was shown to increase expression of δGABAA receptors, inhibitory tone in the cerebellum, and brain GABA concentration in patients, 3,4 while pregabalin enabled a larger neuronal calcium influx for facilitating neurotransmission. 2 These findings substantiate a GABAergic effect of gabapentin and pregabalin. GABAPENTIN (NEURONTIN) One of the most extensively used anticonvulsants in the management of neuropathic pain, gabapentin has proven efficacy in the management of diabetic polyneuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia, phantom limb pain, and pain following spinal cord injury (Fig. 346-4). An analogue of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), gabapentin is thought to exert its analgesic effect by modulating Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and glutamate are implicated in numerous neuropsychiatric and substance abuse conditions, but their spectral overlap with other resonances makes them a challenge to quantify in humans. Gabapentin, marketed for the treatment of seizures and neuropathic pain, has been sh Explore the complex relationship between gabapentin and dopamine, including effects on neurotransmitters and implications for various disorders. Gabapentin has no direct GABAergic action and does not block GABA uptake or metabolism. Gabapentin blocks the tonic phase of nociception induced by formalin and carrageenan, and exerts a potent inhibitory effect in neuropathic pain models of mechanical hyperalgesia and mechanical/thermal allodynia. GABA vs. Gabapentin What's the Difference? GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) and Gabapentin are both substances that affect the central nervous system, but they have different mechanisms of action and uses. GABA is a naturally occurring neurotransmitter in the brain that inhibits or slows down nerve activity, helping to reduce anxiety and promote relaxation. On the other hand, Gabapentin is a Gabapentin can be an effective treatment for brain damage symptoms such as neuropathy, seizures, and autonomic dysfunction. However, it is not without side effects or risks. Research regarding gabapentin's effects on GABA and glutamate synthetic and metabolizing enzymes reveals a complex pattern of activity and provides an incomplete explanation for its anticonvulsant effects. Gabapentin is a structural analog of the inhibitory neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Its anticonvulsant, analgesic and anxiolytic properties suggest that it increases GABAergic inhibition; however, the molecular basis for these effects is unknown as gabapentin does not directly modify GABA type A (GABA A) receptor function, nor does it modify synaptic inhibition. Here, we
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |