Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
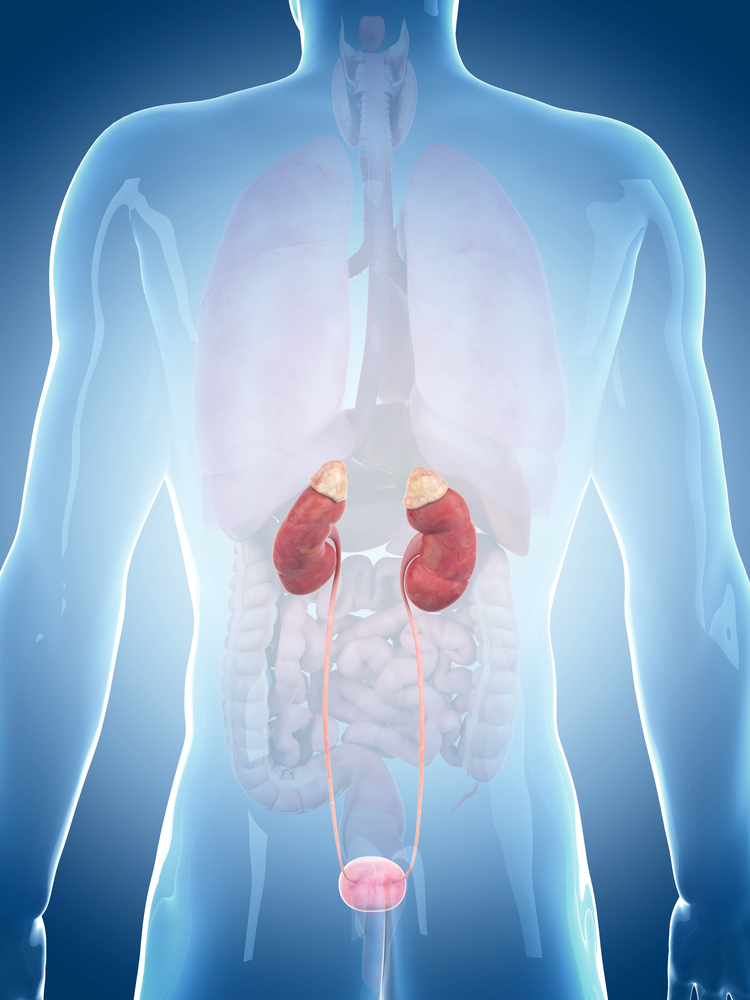
Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication commonly used to treat epilepsy and neuropathic pain. Rare cases of liver and kidney damage have been reported with Gabapentin use. Individuals with pre-existing liver or kidney conditions may be at a higher risk. Regular monitoring of liver and kidney function is essential while taking Gabapentin. Neurontin (gabapentin), generally prescribed for the treatment of nerve pain, is sometimes used to relieve severe pain caused by knee osteoarthritis (OA). Osteoarthritis, also known, as wear-and-tear arthritis, can often become so severe that joint replacement surgery is needed. Using gabapentin It does help with pain, but in one of my two cats it turns him into a total zombie. The good news is that within 48hrs of stopping the gabapentin, both my cats are back to normal. Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive inappropriately high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, occasioning overt toxicity; advanced age and comorbidity predispose these patients for toxicity. Get immediate medical help if you experience a rash, fever, trouble breathing, or facial swelling while taking gabapentin. Don't abruptly stop taking gabapentin because you may experience withdrawal symptoms such as anxiety, agitation, confusion, insomnia, nausea, pain, and sweating which may be severe. Key points: + Gabapentin is primarily renally excreted. + Patients with impaired renal function are at a greater risk of toxic reactions. + Dosage adjustment is necessary in adult patients with compromised renal function. + The label does not provide direct information on whether gabapentin worsens renal function. 3 Gabapentin’s apparent total clearance is 100 mL/min in adults with normal renal function, which is essentially equivalent to CrCl and does not suggest the involvement of tubular reabsorption. 1 Some evidence suggest that active tubular secretion mediated by organic cation transporter-1 (OCT-1) may play a role in gabapentin’s renal clearance. Impaired kidney function (reduced creatinine clearance) increases drug accumulation, raising side effects risk. So, it's important to change the dose if your kidneys aren't working right. 3. Standard Adult Dosage. For adults with normal kidneys: Nerve Pain/Restless Leg Syndrome: Start 300 mg once daily, increase to 300 mg 3 times a day. It can take one to two weeks to feel the full effects of Gabapentin for nerve pain. Some people use this medication long-term. Learn how long you should take Gabapentin for nerve pain. Gabapentin doesn’t hurt the liver or kidneys in most cases. However, taking a safe gabapentin dose is important to prevent potential side effects. Experiencing pain in your kidneys? Learn what causes kidney pain and how to treat mild to moderate kidney pain at home with these 15 simple solutions. Here are some options that are generally considered safer: Gabapentin: Gabapentin is often used for nerve pain and is safe for dogs with kidney disease. It is typically used to manage conditions like arthritis, spinal issues, and post-surgical pain. It does not have significant effects on kidney function, making it a reliable option. For most individuals without pre-existing kidney conditions, gabapentin remains a safe option for managing pain effectively. However, vigilance is key—both from healthcare providers and patients—to ensure optimal outcomes while safeguarding kidney health during treatment. In patients with normal renal function, the maximum dose of gabapentin is 3600mg daily in divided doses. However, gabapentin is renally cleared and so the dose needs to be adjusted according to the GFR. For patients on dialysis, the recommended dose is 100-300mg post dialysis on dialysis days only. Gabapentin is a medication used to treat seizures, postherpetic neuralgia pain associated with shingles, restless leg syndrome, and diabetic neuropathy. For people with normal kidney function, gabapentin is safe and doesn’t cause kidney complications or trigger kidney disease. Nonopioid analgesics, including acetaminophen, topical analgesics, gabapentinoids, serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors, and tricyclic antidepressants may be considered based on pain etiology and type, with careful dose considerations in kidney disease. NSAIDs may be used in CKD and ESKD for short durations with careful monitoring. Researchers at MIT and Massachusetts General Hospital have devised a potential new treatment that could make passing kidney stones faster and less painful, and eliminate surgery. They identified a combination of two drugs that relax the lining of the ureter and can be delivered directly with a catheter-like instrument. Gabapentin is also used off-label to treat conditions such as anxiety and nerve pain from diabetes. It may also be used to treat alcohol use disorder. Though gabapentin has many potential uses, it can cause side effects too. Knowing about gabapentin side effects in advance can help you manage them if they happen to you. Gabapentin is approved to prevent and control partial seizures, relieve postherpetic neuralgia after shingles and moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome. Learn what side effects to watch for, drugs to avoid while taking gabapentin, how to take gabapentin and other important questions and answers. Gabapentin is available in both branded and generic forms.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |