Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
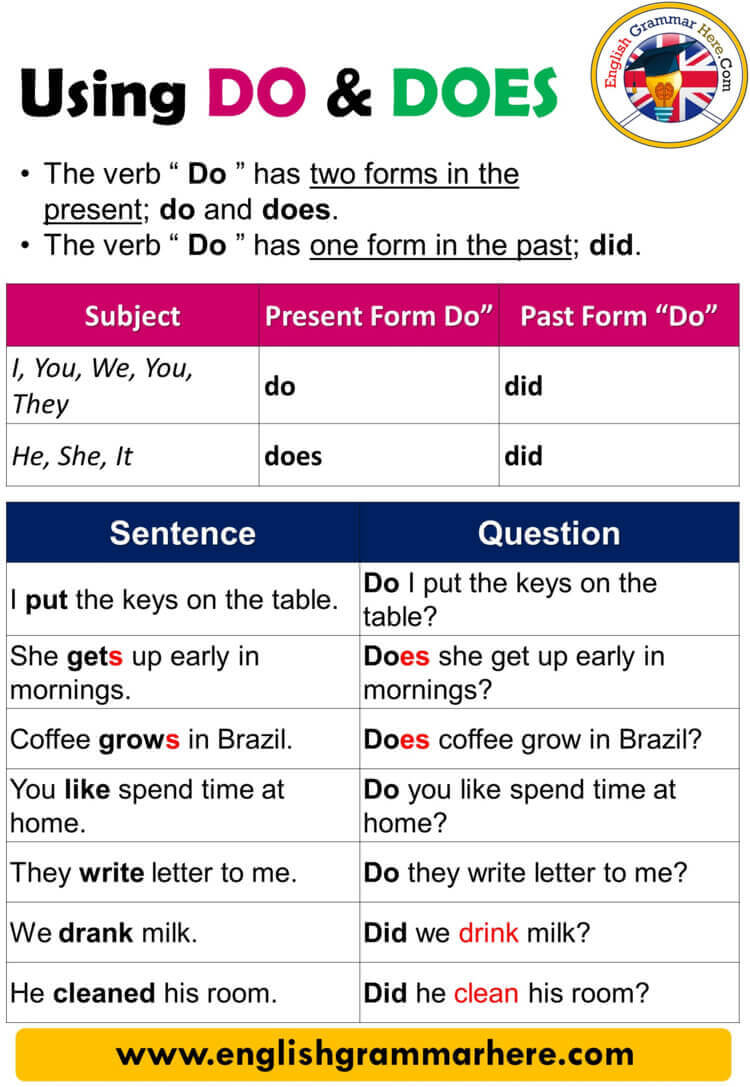
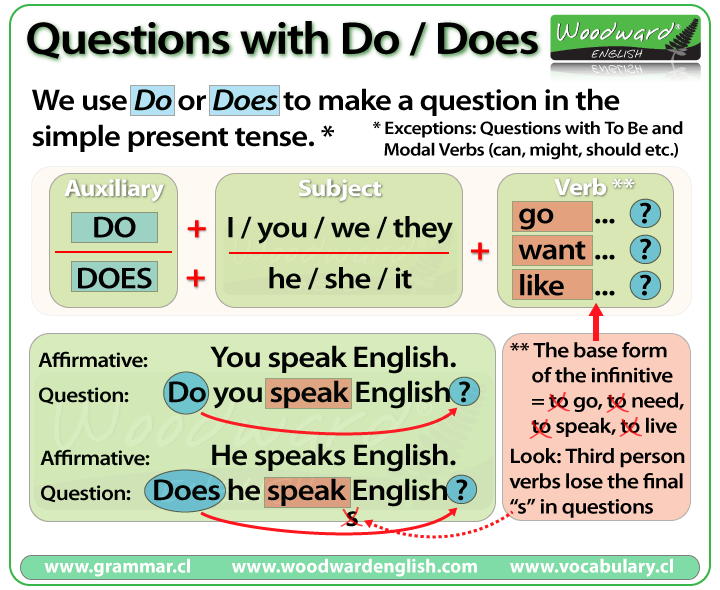
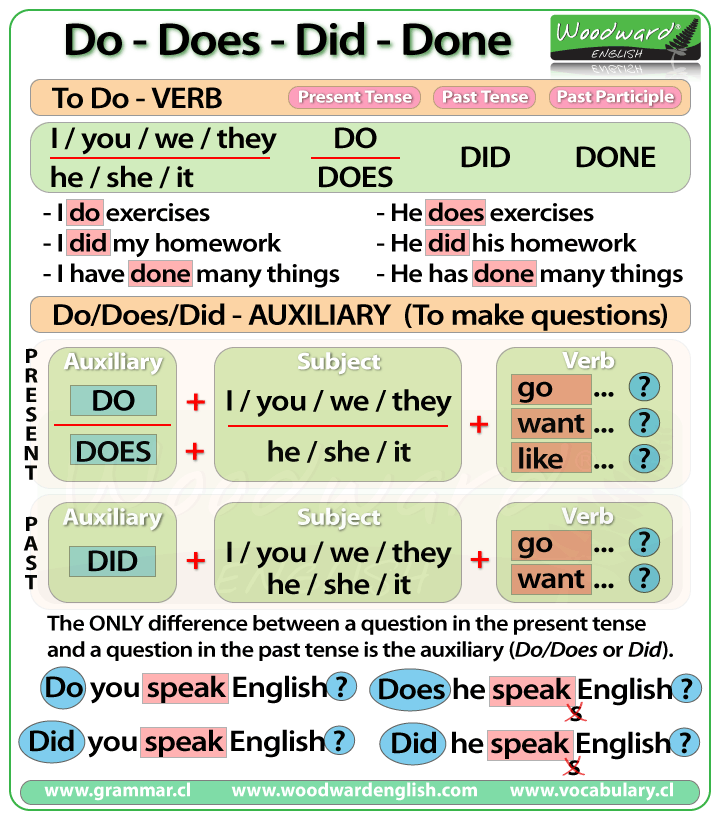
Gabapentin is an anti-seizure medication that can also ease alcohol withdrawal symptoms and help reduce alcohol consumption. Learn more about how it works. When discontinuing gabapentin (Neurontin), withdrawal symptoms can occur, so a gradual dose reduction is recommended. Read here for side effects, timeline, and treatment for gabapentin withdrawal. Gabapentin is a medication that can sometimes help opioid addicts cope with their withdrawal symptoms, but there are risks involved. Is Gabapentin Used to Treat Alcoholism? Yes, gabapentin is used to treat alcohol addiction by helping manage withdrawal symptoms and reducing alcohol cravings. Gabapentin helps individuals recovering from alcohol use disorder by reducing anxiety and promoting better sleep. Recent studies have demonstrated that gabapentin can be helpful for treating withdrawal symptoms. Learn about gabapentin for withdrawal at Recovery First. QuestionIs gabapentin efficacious in the treatment of alcohol use disorder in adults with a history of alcohol withdrawal symptoms? FindingsIn this randomized clinical trial, gabapentin compared with placebo significantly increased the number of people with total abstinence and reduced drinking. A new study reports the nerve pain reliever gabapentin may be helpful in treating people with serious alcohol withdrawal symptoms. Some experts say gabapentin is most effective if used in We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Gabapentin, marketed under brand names like Neurontin, is a medication widely indicated to manage nerve pain, seizures, and mental health conditions. While it can offer relief and improve quality of life, prolonged or high-dose use of the medication can provoke physical dependence. When someone who is dependent moderates or discontinues use, they experience gabapentin withdrawal. This guide to Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant and pain-relieving medication that has several off-label uses, including the treatment of alcohol withdrawal syndrome. Learn more here. This randomized clinical trial examines the efficacy of gabapentin as pharmacotherapy for alchohol use disorder in adults with a history of alcohol withdrawal. For mild alcohol withdrawal that’s not at risk of worsening, your provider may prescribe carbamazepine or gabapentin to help with symptoms. For moderate alcohol withdrawal, benzodiazepines or barbiturates are the first-line therapy to reduce your risk of seizures and the development of delirium tremens. Q.2: What is the lowest starting dose for gabapentin on day 1 for withdrawal management? Q.3: Which patient population is less likely to respond to gabapentin protocol? Q.4: Does gabapentin have benefits other than reducing alcohol withdrawal symptoms: during treatment and post-treatment? The researchers enrolled 96 adults who met the DSM-5 diagnosis for AUD, including alcohol withdrawal symptoms. Following three days of alcohol abstinence, the participants were randomly assigned to receive either gabapentin (starting at 300 mg/day and titrated up to 1,200 mg/day over five days) or placebo pills for 16 weeks. A more personalized, symptom-specific, approach might improve efficacy and acceptance. Objective: To examine whether gabapentin would be useful in the treatment of AUD, especially in those with the most alcohol withdrawal symptoms. Approximately one-half of patients with alcohol use disorder who abruptly stop or reduce their alcohol use will develop signs or symptoms of alcohol withdrawal syndrome. The syndrome is due to Gabapentin is used off-label in alcohol withdrawal care. This guide covers clinical evidence, side effects, and treatment guidelines. Find out what you need to know about gabapentin for alcohol withdrawal and discover the pros, cons, risks, and benefits, and how it may affect health. Wondering about mixing gabapentin with your evening glass of wine? You're not alone! Many patients ask about this common concern when they're prescribed this medication. While the official answer isn't a strict "no," there are important things to consider before combining these two substances. Gabapentin and alcohol are both central The anticonvulsant drug gabapentin is used off-label to treat alcohol-related withdrawal, cravings, anxiety, and insomnia. Although it is well tolerated and has demonstrated efficacy for mild alcohol withdrawal and early abstinence, there is concern about its potential for abuse. Gabapentin should be prescribed only as a second-line alternative to standard therapies, and only after screening
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |