Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 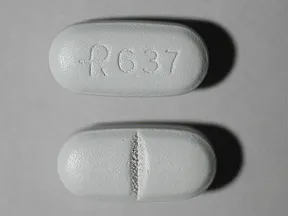 |
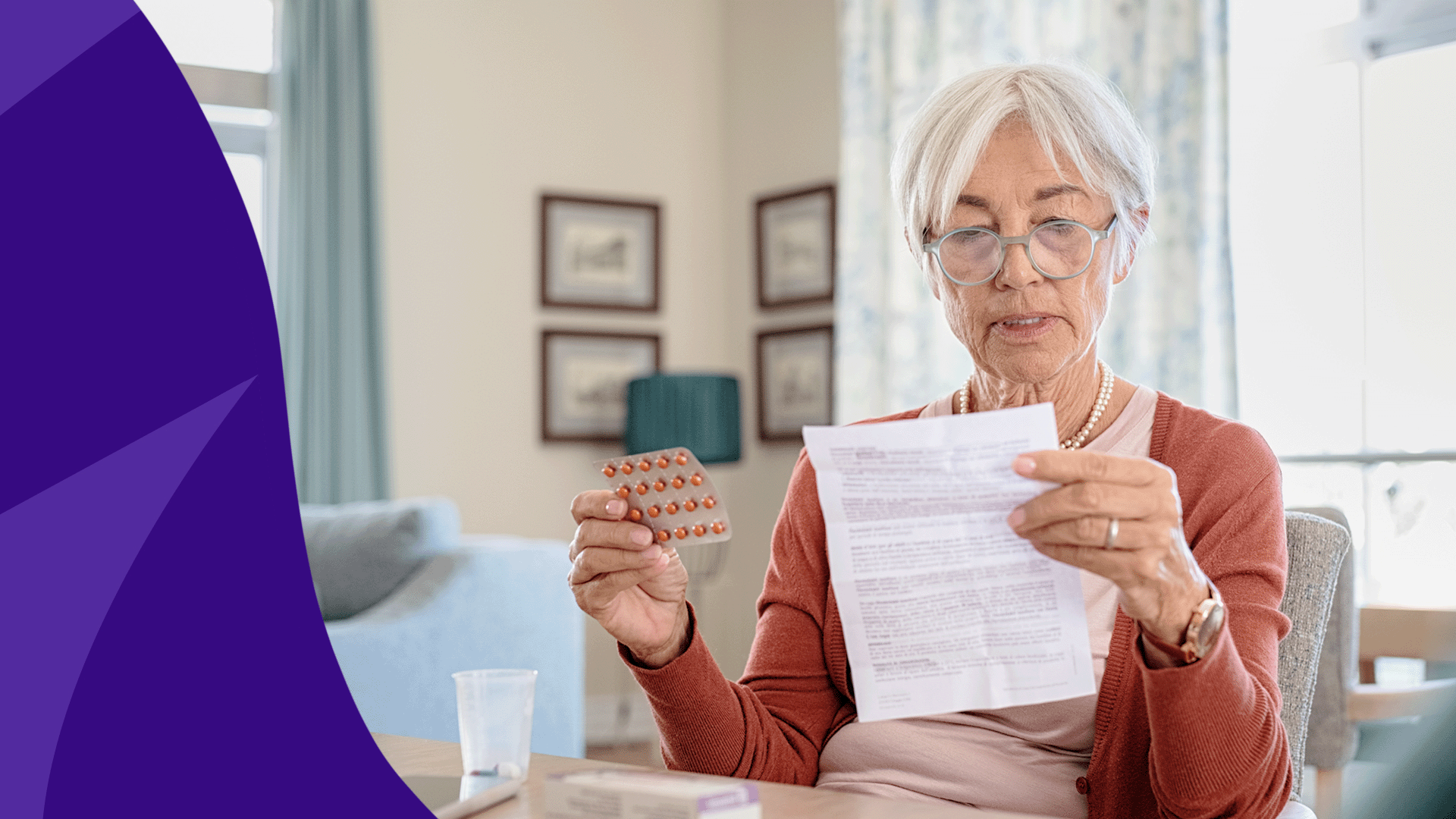
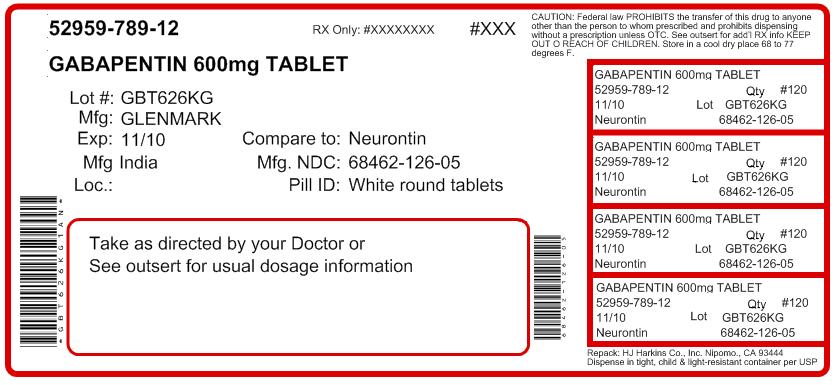
Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication prescribed for a variety of conditions. Learn about its uses, side effects, and what you should know if you've been prescribed this medication. Physical effects like dizziness and cognitive effects like confusion are common Gabapentin side effects in elderly patients. Gabapentin is approved to prevent and control partial seizures, relieve postherpetic neuralgia after shingles and moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome. Learn what side effects to watch for, drugs to avoid while taking gabapentin, how to take gabapentin and other important questions and answers. Gabapentin is available in both branded and generic forms. Discover the potential side effects of gabapentin in elderly women, including common reactions, risks specific to older adults, and important considerations for safe use. Conclusion Gabapentin is commonly used for neuropathic pain relief in all stages of life. But how safe is gabapentin for older adults? What are the main gabapentin side effects in the elderly? Older adults have a higher prevalence of side effects due to overlapping health conditions and polypharmacy. However, elderly patients are more likely to have unwanted effects (eg, problems with balance or walking, swelling in the feet or legs) and age-related kidney problems, which may require caution and an adjustment in the dose for patients receiving gabapentin. Though gabapentin has many potential uses, it can cause side effects. Read more about 13 gabapentin side effects here. Understanding Gabapentin Side Effects in Elderly Gabapentin is a medication commonly prescribed to manage various health conditions in elderly individuals. However, like any medication, it comes with potential side effects that can impact the well-being of senior citizens. Understanding these common gabapentin side effects in the elderly is essential for both patients and caregivers to ensure Discover the potential side effects of gabapentin in elderly patients, including risks of falls, cognitive impairment, and drug interactions. Learn how to manage these effects for safer treatment outcomes. Learn about common and serious gabapentin side effects in elderly patients. Understand risks, precautions, and when to seek medical help. Gabapentin can help control seizures as well as nerve pain from shingles. It may sometimes cause side effects, especially if you misuse it. Learn more. Gabapentin is an anti-epileptic drug, also called an anticonvulsant. It is used to treat some types of seizures and nerve pain caused by shingles. Learn about the common side effects of gabapentin in elderly patients, including dizziness, fatigue, cognitive impairment, and more. Explore the connection between gabapentin and depression, mechanisms behind gabapentin-related depression, and strategies to manage and mitigate side effects. Discover other significant concerns for elderly gabapentin users and the importance of personalized Gabapentin, widely used for treating various neurological conditions, plays a significant role in the health and well-being of elderly individuals. Although it can effectively manage symptoms of these ailments, recognizing the gabapentin side effects in the elderly is essential for caregivers and family members. These side effects can range from mild to severe, affecting each individual Key Takeaway While gabapentin can be safe and effective for many elderly patients, it requires careful consideration of individual health factors, potential side effects, and drug interactions to ensure its appropriate use in this population. When your older loved one is prescribed gabapentin, it is often to treat conditions like neuropathic pain or seizures. While the medication may bring relief, the side effects can present challenges, especially for the elderly. Gabapentin side effects in elderly individuals can affect not just their physical health, but also their emotional well-being and daily Gabapentin can help older adults manage nerve pain, seizures, or restless legs, but it brings risks worth comprehending. For seniors, this medication may spark dizziness, balance troubles, or fuzzy cognition—side effects that raise fall dangers in a group already vulnerable to injuries. Gabapentin is available as Gralise, Neurontin, and generic gabapentin in the following dosage forms that are taken by mouth. 100 mg, 300 mg, 400 mg oral capsules 250 mg/5 mL oral solution Learn about the side effects of gabapentin, from common to rare, for consumers and healthcare professionals.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |