Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
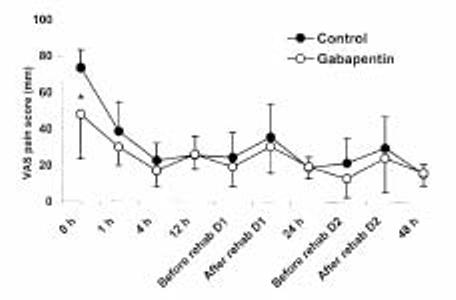
Gabapentin may be prescribed either before or after surgery to help with postsurgical pain. However, it should be used with caution due to the high risk of abuse. The knee flexion degree and treatment side effects were also compiled to evaluate the safety of gabapentin. After testing for the heterogeneity and publication bias among studies, data were aggregated for random-effects modeling when necessary. Background Postoperative pain after total knee arthroplasty (TKA) and total hip arthroplasty (THA) influence patients’ rehabilitation and life quality. Although gabapentin has been widely used for analgesia, its efficacy is still controversial in TKA and THA. This meta-analysis was performed to assess the efficacy and safety of gabapentin following TKA and THA. Method Electronic databases Perioperative gabapentin reduces 24 h opioid consumption and improves in-hospital rehabilitation but not post-discharge outcomes after total knee arthroplasty with peripheral nerve block This review evaluated the efficacy and tolerability of peri-operative gabapentin administration to control acute post-operative pain. Peri-operative gabapentin administration was found to be effective in reducing pain scores, opioid requirements and opioid-related adverse effects in the first 24 hours after surgery. Given the significant differences between the studies and the possibility of Outcomes and Data Analyses The primary outcome is prolonged use of gabapentin in the postoperative period, defined as a prescription refilled at 90-180 days after discharge from surgery, a time period based on definitions of prolonged use of opioids after surgical procedures. 20, 25, 26 We calculated the days’ supply and average daily dose. However, perioperative gabapentin had a significant effect on promoting opioid cessation after surgery. MeaningSeventy-two hours of perioperative gabapentin use may promote opioid cessation after surgery and decrease the duration of postoperative opioid use. This cohort study examines whether perioperative gabapentin use among older adults after major surgery is associated with in-hospital adverse clinical events. Gabapentin: A post-surgery pain relief option When it comes to post-surgery pain relief, gabapentin is a highly effective option. Many patients experience significant pain after undergoing surgery, and finding the right treatment to manage that pain is crucial for a successful recovery. Gabapentin has been proven to reduce post-operative pain and improve the overall recovery process. Reduced Abstract Purpose of review: Gabapentinoid use has increased substantially in the past several years after initial promising data with regard to acute perioperative pain control. The purpose of this review is to critically appraise the evidence for the use of gabapentinoids for acute pain management and its impact on the development of chronic pain after surgery. For example, a gabapentin dose of 1.2 grams per day 1 hour before surgery and for 2 days after CABG surgery showed that postoperative pain scores at 1, 2, and 3 days as well as the consumption of tramadol given as a rescue analgesic were significantly lower in the gabapentin group when compared to the placebo group [41]. Factors Influencing Duration of Gabapentin Use Several factors come into play when determining how long gabapentin should be taken after surgery. First off, the type and extent of the surgical procedure significantly influence recovery time and pain levels. The results from this study demonstrate that gabapentin is more beneficial in mastectomy and spinal, abdominal, and thyroid surgeries. Gabapentin is an effective analgesic adjunct, and clinicians should consider its use in multimodal treatment plans among patients undergoing elective surgery. The purpose of this systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and non-RCTs was to evaluate the efficacy and safety of gabapentin versus placebo for pain control after total knee arthroplasty (TKA). In December 2015, Gabapentin and other anticonvulsant medications have been established as an effective treatment for chronic neuropathic pain and are commonly used for such conditions as herpetic neuralgia, diabetic neuropathy, and phantom limb pain following amputation. Pain management after total knee arthroplasty (TKA) varies and has been widely studied in recent years. Some randomized controlled studies have carried out to evaluate the effects of gabapentin on pain relief after TKA. However, no solid result was We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Postoperative pain after total knee arthroplasty (TKA) and total hip arthroplasty (THA) influence patients’ rehabilitation and life quality. Although gabapentin has been widely used for analgesia, its efficacy is still controversial in TKA and THA. Gabapentin, a drug traditionally used for the relief of neuropathic pain, was compared in variable doses to placebo in relieving postoperative pain. Gabapentin resulted in less total patient-controlled analgesia (PCA) morphine use over 48 hours postoperatively (P <0.05), better active knee flexion on postoperative days (PODs) 2 and 3 (P <0.05 for both), and less pruritus (P <0.05) than placebo M, et al. Perioperative gabapentin reduces 24 h opioid consumption and improves in-hospital rehabilitation but not post-discharge outcomes after total knee arthroplasty with peripheral nerve block. Bja Br J Anaes
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |