Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
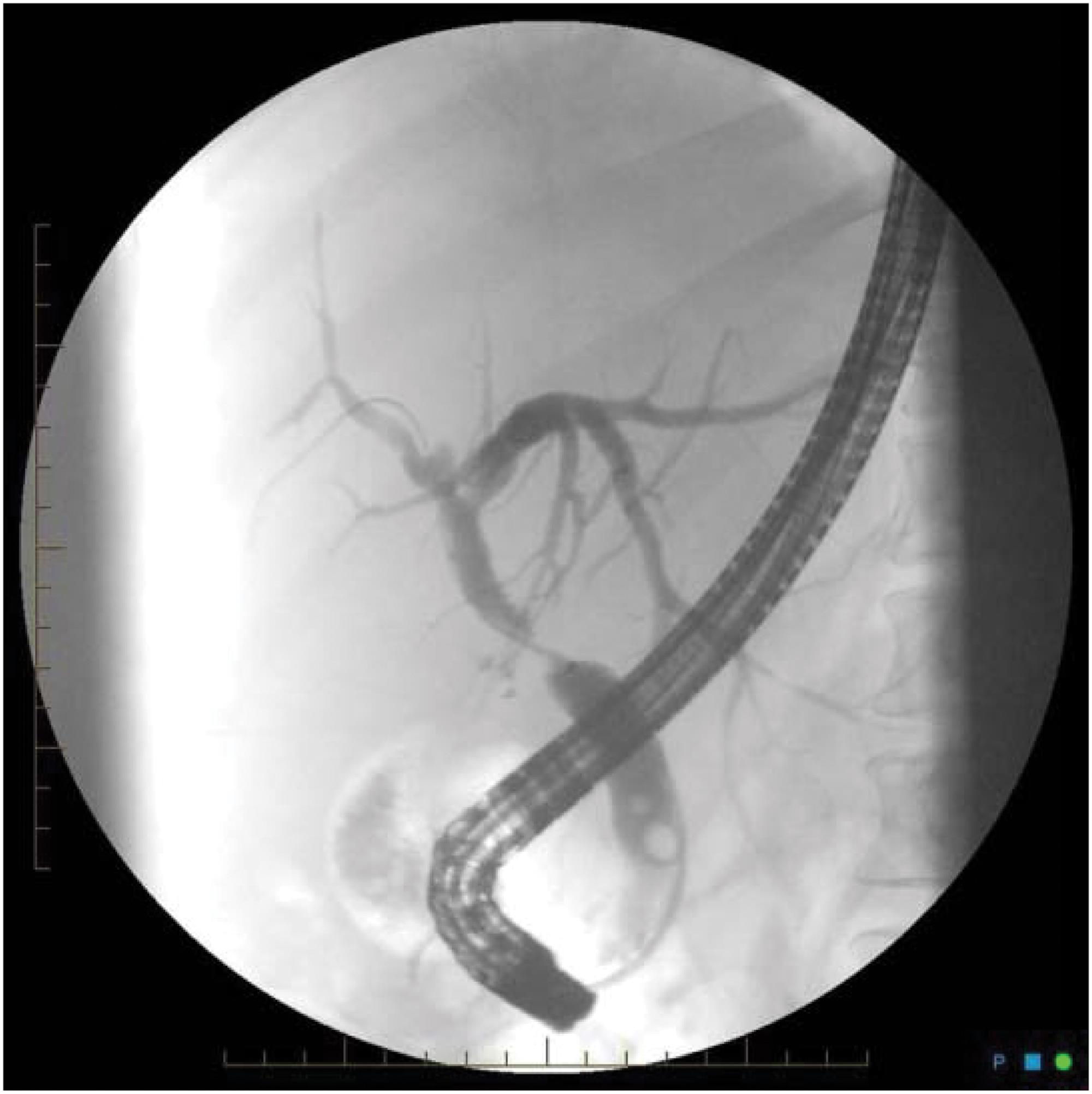
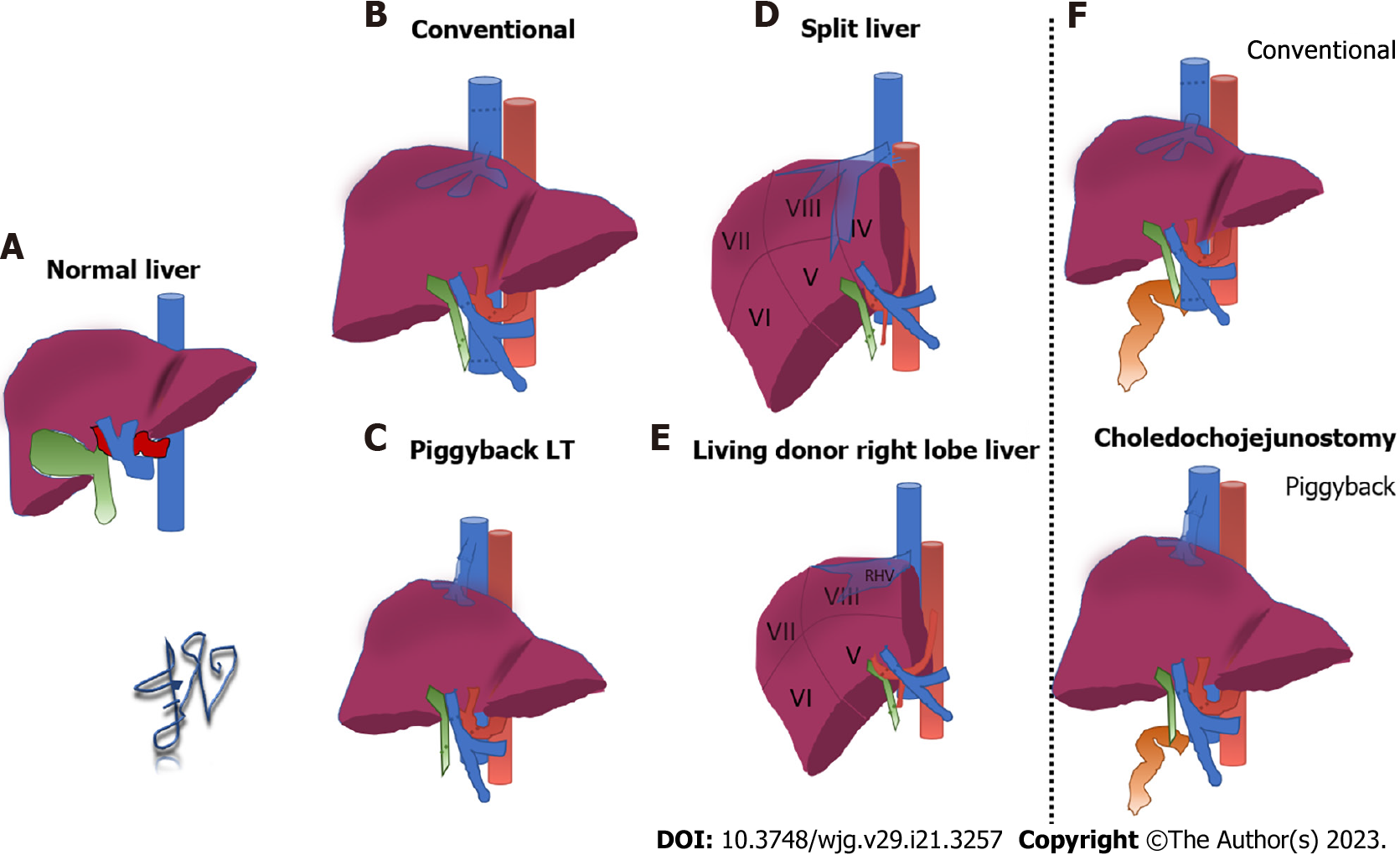
Gabapentin is a unique anticonvulsant that is used as adjunctive therapy in management of epilepsy and for neuropathic pain syndromes. Therapy with gabapentin is not associated with serum aminotransferase elevations, but several cases of clinically apparent liver injury from gabapentin have been reported. Liver transplantation (LT) is a life-saving treatment representing the only viable option for patients suffering from end-stage liver disease (ESLD) or acute liver failure. Patients who undergo LT require a multidisciplinary approach to postoperative pain management. However, pain management in this context is often inadequately explored. Limited options exist for proper pain control in Purpose: Trazodone and gabapentin are commonly used treatments. We report a rare case of trazodone and gabapentin-induced liver injury. Case: A 40-year-old woman with a history of depression presented jaundice. She had no other complaints. The patient denied risk factors for acute and chronic liver disease. This included eight patients with cirrhosis and recent use of opiates, benzodiazepines, gabapentin/Lyrica, and/or proton pump inhibitors as well as 14 providers (primary care, transplant surgery, transplant hepatology). Interviews explored opinions, behaviors, and understanding surrounding the risks and benefits of deprescribing. Results Quality care for patients living with alcohol-associated liver disease (ALD) includes identification and treatment of comorbid alcohol use disorder (AUD). 1 In addition to recommending behavioral interventions, providers caring for this population should feel comfortable prescribing AUD pharmacotherapy, which is safe, effective, and associated with reduced hepatic decompensation and mortality Antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) are a common cause of drug induced liver injury (DILI). Over the last few decades, several newer AEDs were approved for marketing in the United States, and they are increasingly prescribed for indications other than Post-Operative Liver Pain Protocol – Intraoperative Regional Blocks Background: Current pain management strategies for Liver Transplantation rely heavily upon post-extubation narcotic use in the intensive care unit (ICU) with little use of intraoperative strategies or multimodal analgesia. Levetiracetam, gabapentin, pregabalin, and lacosamide are drugs of choice for treatment of partial-onset seizures in post-transplant patients given their efficacy spectrum, generally excellent tolerability, and lack of drug interaction potential. Levetiracetam is the drug of choice for primary generalized seizures in post-transplant patients. A new study suggests that gabapentin could provide greater benefit than FDA-approved drugs for patients with alcohol-associated liver disease. Specifically, postliver transplantation, patients follow up at least weekly with a transplant surgeon for the first month and at least monthly with a transplant hepatologist for the first 6 mo. Neuropraxia-specific therapy was defined as initiation of gabapentin or amitriptyline for symptoms or targeted physical or occupational therapy. The removal of gabapentin and the administration of steroids resulted in the normalization of liver test abnormalities. Another case reported a 26-year-old patient taking 1500 mg of gabapentin with associated hepatocellular injury [4]. Neurologic complications are relatively common after solid organ transplantation and affect 15%-30% of liver transplant recipients. Etiology is often related to immunosuppressant neurotoxicity and opportunistic infections. Most common complications Discussion: Gabapentin induced liver injury is rare with few reported cases, many of which did not exclude other etiologies. In this case, the key elements of diagnosing DILI were met including gabapentin initiation closely preceding liver injury, other etiologies excluded, and discontinuation of gabapentin leading to improvement. Pain management is important to your recovery after liver transplant. By reducing your pain, the goal is for you to be able to move around more easily and do therapy exercises. This will help prevent complications like blood clots and help you recover and gain strength. These guidelines are intended to provide a bridge between transplant centers and pri-mary care physicians in the long-term management of the liver transplant patient. Key words: Immunosuppression, liver, long-term, management, transplantation Your mom is not alone. This post transplant time is challenging with all of the changes and transitioning. I am leaving the medication decisions up to Mayo team. We need to provide the team with good information of when, where, and what level of the various side effects of meds. With their experience and expertise, our team can decide to change or lower meds- or add meds such as Gabapentin for No official document has been published for primary care physicians regarding the management of liver transplant patients. With no official source of reference, primary care physicians often question their care of these patients. The following guidelines have been approved by the American Society of Transplantation and represent the position of the association. The data presented are based on This chapter aims to address and discuss in detail the analgesic issues in liver transplantation and liver resection. The goals of analgesia during liver transplantation are similar to other types of surgery, but unique considerations found in patients with end-stage liver disease impact the overall approach to pain management. A 41-year-old male with a previous orthotopic liver transplant began experiencing insomnia, anxiety, diaphoresis, headaches, and palpitations that progressed over a 2-day period. As part of his home medication regimen, the patient was taking gabapentin for peripheral neuropathy. His acute onset of i The prevalence of substance use disorder in the liver transplantation (LT) population makes postoperative pain management challenging. We report our initial experience with a novel, comprehensive, multidisciplinary opioid avoidance pathway in 13 LT recipients between January 2018 and September 2019.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |