Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
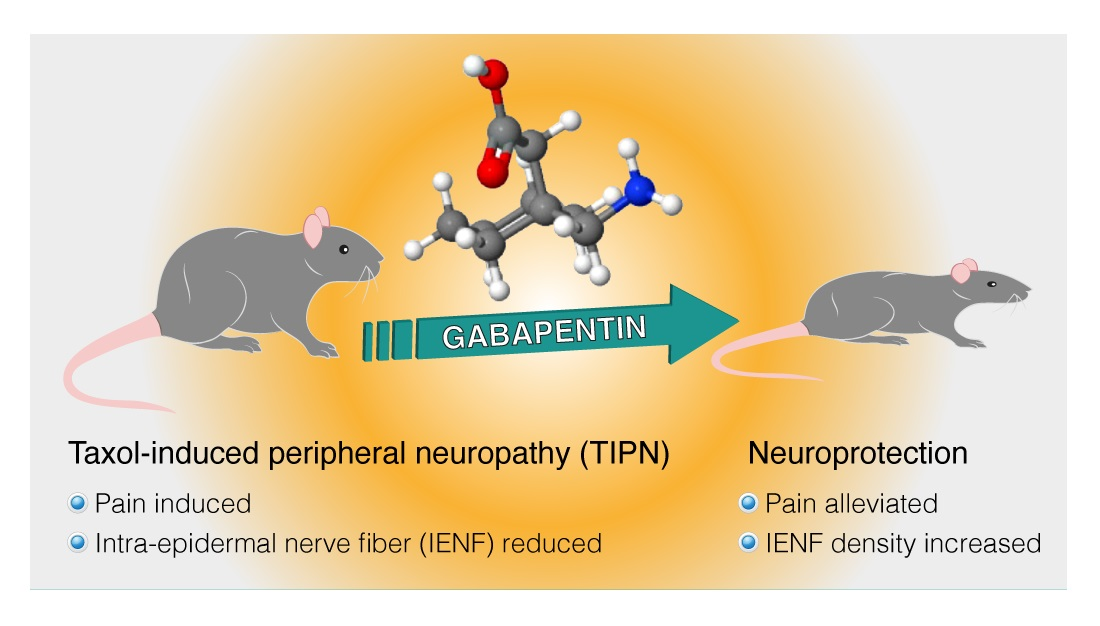 |  |
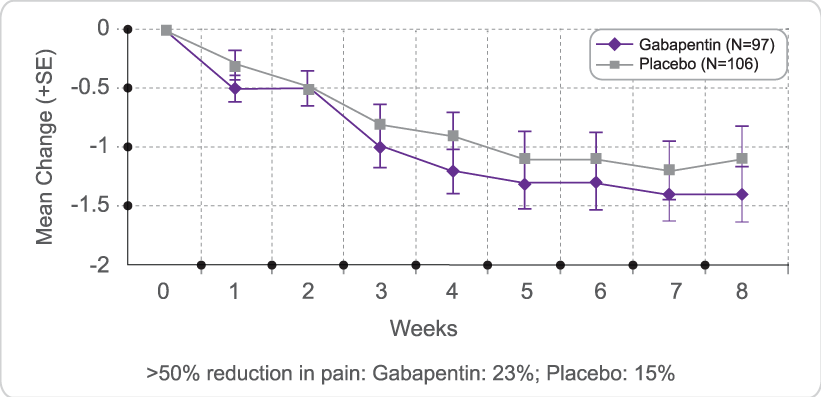
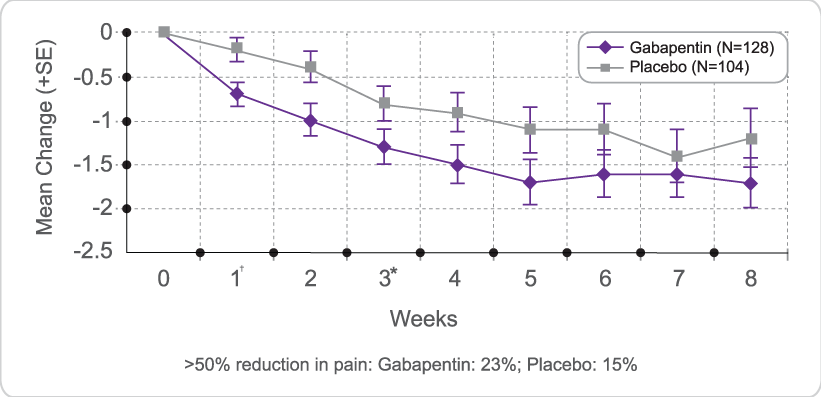
Gabapentin is commonly used to treat neuropathic pain (pain due to nerve damage). This review updates a review published in 2014, and previous reviews published in 2011, 2005 and 2000. To assess the analgesic efficacy and adverse effects of Pandey A, Sompura S, Pandey S, et al. Double-blind randomized placebo-controlled trial to compare the effects of gabapentin, pregabalin and tramadol plus acetaminophen combination in improvement of pain in patients with painful diabetic neuropathy. Gabapentin is a medication originally developed to treat seizures but has since become a go-to for nerve-related pain, including peripheral neuropathy. It works by inhibiting certain nerve signals, effectively reducing pain sensations. Gabapentin is approved to treat seizures and postherpetic neuralgia, a type of nerve pain following shingles. It is thought to work by changing how nerves send messages to your brain. It is also used off-label to treat other neuropathic pain conditions. Gabapentin for chronic neuropathic pain and fibromyalgia in adults Neuropathic pain is pain coming from damaged nerves. It differs from pain messages carried along healthy nerves from damaged tissue (a fall, cut, or arthritic knee). Neuropathic pain is treated by different medicines than pain from damaged tissue. Gabapentinoid drugs—specifically gabapentin (Neurontin) and pregabalin (Lyrica)—are increasingly being prescribed for pain because physicians and patients seek alternatives to opioids in the Discover why gabapentin isn't a cure-all for foot neuropathy. El Paso podiatrists can show you better options for nerve pain relief. Schedule your visit today! Indeed, gabapentin has been shown to be effective in the treatment of post-herpetic neuralgia, diabetic neuropathy, trigeminal neuralgia and pain syndromes following spinal cord injury, and also for deep tissue pain and hyperalgesia [26]. Gabapentin can help relieve nerve pain in some people with postherpetic neuralgia (nerve pain after shingles) and peripheral diabetic neuropathy (nerve pain in the feet in people with diabetes). The three systematic reviews summarized in this report examined the efficacy and safety of treatments for patients with any type of neuropathic pain,8 painful diabetic neuropathy,9 or fibromyalgia.10 All the reviews included gabapentin, pregabalin, TCAs, and SNRIs. Neuropathic pain after spinal cord injury (SCI) has a significant negative impact on the patients’ quality of life. The objective of this systematic review is to examine the safety and efficacy of pregabalin (PGB) and gabapentin (GBP) in the Millions of people suffer from the burning, tingling, and numbness of a form of neuropathy called idiopathic sensory polyneuropathy. A recent study directly comparing four medications produced disappointing results, but is a step in the right direction. I now advocate for deprescribing gabapentin when patients do not achieve adequate pain relief for chronic neuropathic pain at a cumulative daily dose of 1800 mg. Instead, I consider pregabalin as a substitute for gabapentin in patients with inadequate pain control rather than further dose escalations. Both gabapentin and pregabalin are particularly effective in the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia, diabetic neuropathy and pain caused by a spinal cord injury. Pregabalin may also be used to treat fibromyalgia. Pain expert offers clinical guidance to a commonly asked question about the proper, safe, and effective dose of gabapentin when treating neuropathic pain. Key Findings The findings from four systematic reviews and one RCT for gabapentin (GBP) compared to placebo or active comparators is limited by quantity and quality of evidence for studies on neuropathic pain associated with conditions including chronic lower back pain, fibromyalgia, mixed neuropathic pain, and nerve injury pain. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant drug that has been used for a number of off-label indications, including neuropathic pain. It is thought to act by binding to calcium channels and modulating calcium influx, or by blocking new synapse formation. Neuropathic pain tends to be chronic, is complex, and can be difficult to treat effectively. Treatment often involves pharmacologic and physical A Doctor’s Insight into Nerve Pain Management If you’re dealing with nerve pain from conditions like peripheral neuropathy, sciatica, or diabetic nerve damage, you may have been prescribed gabapentin to manage your symptoms. But a question that frequently comes up among patients is: Does gabapentin help heal nerve damage, or does it just mask the pain? As a doctor specializing in treating Narrative: Neuropathic pain, when the pain generator is the nerve itself, occurs in a variety of conditions including diabetes mellitus and postherpetic neuropathy. The exact mechanism of action Gabapentin at doses of 1800 mg to 3600 mg daily (1200 mg to 3600 mg gabapentin encarbil) can provide good levels of pain relief to some people with postherpetic neuralgia and peripheral diabetic neuropathy. Evidence for other types of neuropathic pain is very limited. The outcome of at least 50% pai
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |