Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 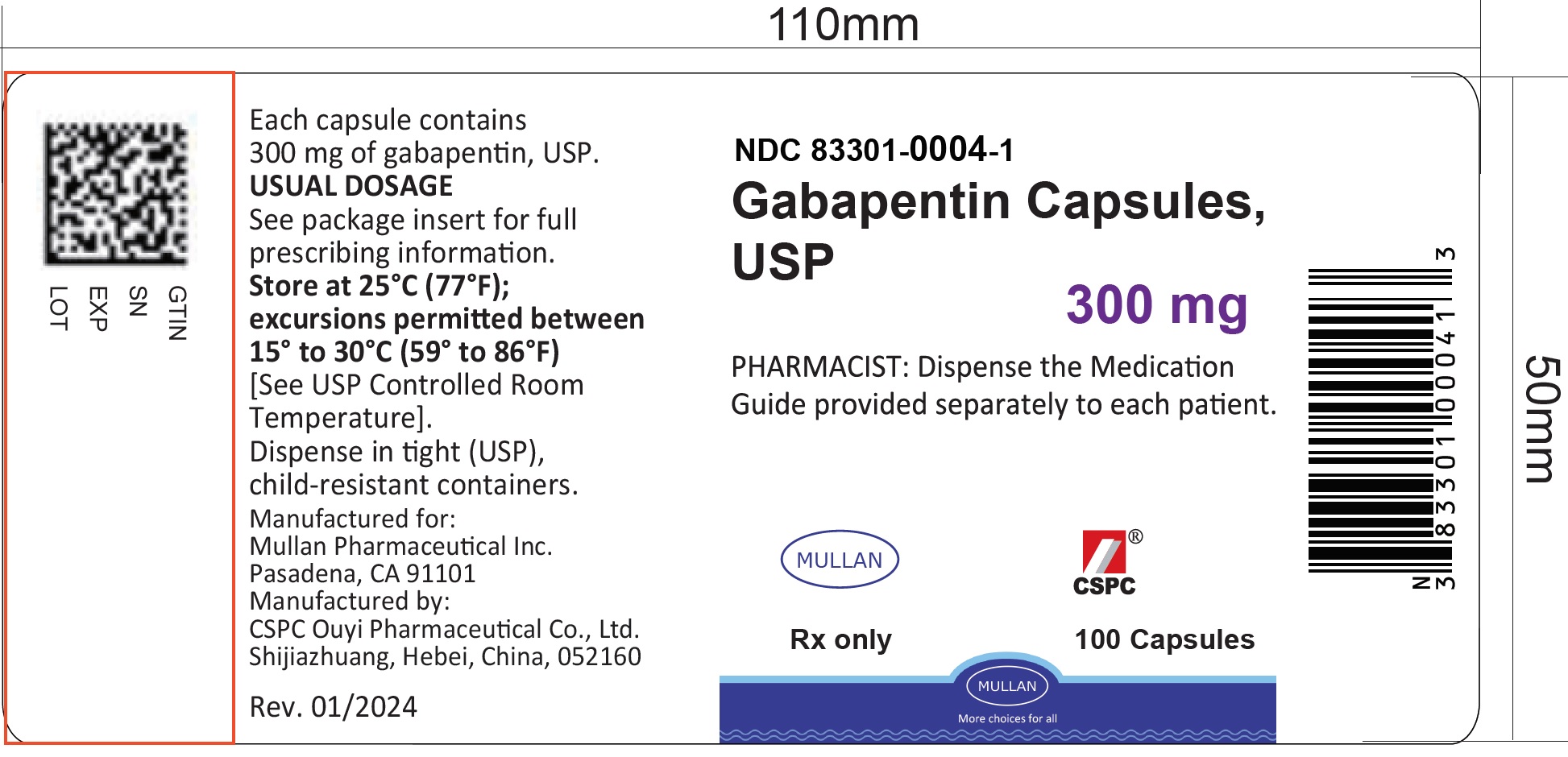 |
DESCRIPTION Neurontin® (gabapentin) Capsules, Neurontin (gabapentin) Tablets, and Neurontin (gabapentin) Oral Solution are supplied as imprinted hard shell capsules containing 100 mg, 300 mg, and 400 mg of gabapentin, elliptical film-coated tablets containing 600 mg and 800 mg of gabapentin or an oral solution containing 250 mg/5 mL of gabapentin. Dosage Forms Not Appropriate for Administration Through a Feeding Tube Mixing Medications With EN Formulations, Flushing Enteral Feeding Catheters, and Diluting Liquid Medications Column 1 lists the medication that was evaluated. Column 2 lists the dosage forms that were examined, and notes, in red print, those formulations deemed inappropriate for feeding tube administration. Column 3 lists the recommendations for feeding tube administration as well as rationale used in making that determination. Gabapentin Colonis 50mg/ml Oral Solution - Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC) by Colonis Pharma Ltd Key points Gabapentin capsules can safely be opened, and the contents of the capsule sprinkled onto food or dissolved in a drink for immediate consumption. Hard gelatin capsules - enteral tubes Prepare the capsule as follows: 1. Gently ease open the capsule to release the powder. 2. Tip the powder into a beaker - be sure to obtain all the powder. 3. Mix the powder with 15-30mL of water. 214,225 4. Draw up the solution in an enteral syringe. 5. Administer the solution through the enteral feeding tube. 6. Rinse the beaker with water, and administer This comparative-effectiveness study uses data from 2 clinical trials to evaluate whether the use of gabapentin for pain management is associated with less opioid use and feeding tube placement among adult patients with head and neck cancer receiving GABAPENTIN CAPSULES, USP - Rx only - Read the Medication Guide before you start taking gabapentin capsules, USP and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. Key Points Use of enteral feeding tubes for drug administration is increasing. Sizes of feeding tubes are decreasing. The range of healthcare professionals involved in drug administration via enteral feeding tubes is increasing. Collation of all available information is necessary. The key to managing medication use in patients who are receiving enteral tube feedings is to focus on prioritizing therapeutic goals. First, an in-depth review of the patient’s current medica-tion profile is essential to determine what medications may be crushed or are available in liquid dosage forms. It may be necessary to temporarily discontinue oral medications not suitable for EFT A total of 3686 tablets and 432 capsules that are frequently used in Japan were tested. Using SSM, 3377 (91.6%) tablets and 359 (83.1%) capsules disintegrated within 10 min and passed through the tube without clogging it in the tube passage test. With the conventional crushing method, 2117 tablets (57.4%) and 272 capsules (63.0%) could be crushed. the enteral feeding tube. Pulsatile flushing can create turbulence within the feeding tube. This can“clean” theinner walls and help keep thetube from clogging. Water is the best fluid to flush tubing. Sometimes, warm water may help prevent clogging. Anecdotally, soda and soda water have beenused to unclog enteral tubes. However, caution must be View gabapentin information, including dose, uses, side-effects, renal impairment, pregnancy, breast feeding, monitoring requirements and important safety information. Appendix 10: Administering drugs via feeding tubes Administering drugs via feeding tubes is generally an unlicensed activity. There is little published data and most recommendations are theoretical and/or based on local policy. An alternative licensed option may therefore be preferable, e.g. rectal or parenteral formulations. However, if given by tube, there is a range of possibilities (Figure A potential complication with pouring capsule contents through any enteral access device is that tube occlusions may occur, so large-bore feeding tubes (≥14 French) are preferred. Gabapentin Rosemont Oral Solution 50mg/mL Instructions for administration via nasogastric (NG) or percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) tubes. Gabapentin Rosemont Oral Solution is suitable for use with the following type of NG and PEG tubes: Ensure that the enteral feeding tube is free from obstruction before administration. These highlights do not include all the information needed to use GABAPENTIN CAPSULES safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for GABAPENTIN CAPSULES. GABAPENTIN capsules, for oral use Initial U.S. Approval: 1993 The following liquid medicines manufactured by Rosemont Pharmaceuticals have recently received UK licenses for administration via nasogastric (NG) or percutaneous endoscopic gastronomy (PEG) tube: Furosemide Oral Solution 20mg/5mL, 40mg/5mL and 50mg/5mL Ramipril Oral Solution 2.5mg/5mL Metoclopramide Hydrochloride Oral Solution 5mg/5mL Clonazepam Oral Solution 0.5mg/mL, 2mg/mL Gabapentin Oral For tubes terminating in the jejunum, sterile water should be used. Stop feed and/or flush enteral tube with 15-30mL of water prior to drug administration. Ensure the patient is sitting up at an angle of at least 30 degrees to avoid reflux of medication or water. Give medication via enteral tube as directed by the guidance within the table. Gabapentin Capsules package insert / prescribing information for healthcare professionals. Includes: indications, dosage, adverse reactions and pharmacology.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |