Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
/male-kidney-anatomy--illustration-758313113-5a6bcd7bae9ab8003726d9d1.jpg) |  |
 |  |
 | :max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH_Illustration_Signs-and-Symptoms-of-End-Stage-Renal-Disease-ESRD_Laura-Porter_Final-d650ac51ed6d475cbad2532f772151bc.jpg) |
 |  |
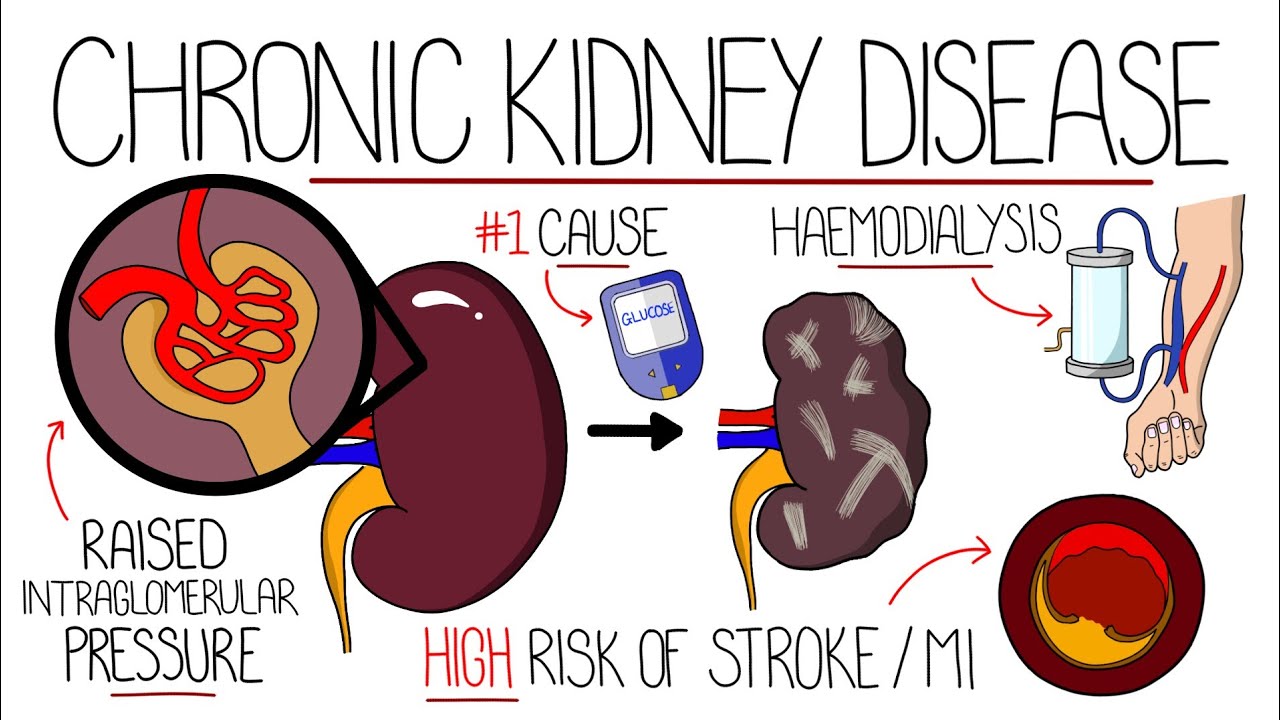 |  |
 |  |
Risk Factors for Kidney Issues While Using Gabapentin Several factors may increase the likelihood of developing kidney problems while on Gabapentin: Pre-existing Kidney Disease: Patients with chronic conditions such as diabetes or hypertension are more susceptible. Advanced Age: Older adults often have reduced renal function. Conclusion Gabapentin toxicity in patients with chronic kidney disease is underrecognized. Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive inappropriately high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, occasioning overt toxicity; advanced age and comorbidity predispose these patients for toxicity. Conclusion: Gabapentin toxicity in patients with chronic kidney disease is underrecognized. Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive inappropriately high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, occasioning overt toxicity; advanced age and comorbidity predispose these patients for toxicity. Although gabapentin is well known for its well recieved pharmacokinetics, it is exclusively eliminated renally, and patients with chronic kidney disease are at risk for toxicity. People with chronic kidney disease who take gabapentin should be very aware of this as to not cause further damage to their kidneys. Gabapentinoids, including gabapentin and pregabalin, are frequently prescribed as opioid alternatives. Given that gabapentinoids are eliminated from the body by the kidney, we sought to determine the risk of serious adverse events in patients with chronic kidney disease who started a gabapentinoid at a higher versus a lower dose. While gabapentin itself doesn't directly damage the kidneys, it can cause side effects like dizziness, somnolence, and peripheral edema that may be more pronounced in those with kidney disease. Regular monitoring of kidney function is advisable when using gabapentin in patients with renal impairment or other risk factors for kidney disease. Background Gabapentin and pregabalin are used to manage neuropathic pain, pruritus, and restless legs syndrome in patients on hemodialysis. These patients may be especially predisposed to complications related to these agents, which are renally As in the other 2 cases of gabapentin-induced acute renal failure and rhabdomyolysis, the patients involved had multiple illnesses and were affected by multiple medications or other factors that might lead to rhabdomyolysis and renal failure. Abstract Background: Gabapentinoids (GPs) are frequently prescribed in individuals with chronic kidney disease (CKD); however, their exclusive renal elimination warrants dose adjustments to decrease risk of toxicity. This study evaluated GP prescribing patterns and whether excessive dosing was associated with increased incidence of gabapentinoid-related adverse events (GRAEs). Conclusion Gabapentin toxicity in patients with chronic kidney disease is underrecognized. Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive inappropriately high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, occasioning overt toxicity; advanced age and comorbidity predispose these patients for toxicity. CONCLUSION: Gabapentin toxicity in patients with chronic kidney disease is underrecognized. Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive inappropriately high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, occasioning overt toxicity; advanced age and comorbidity predispose these patients for toxicity. The appropriate dosing based on the patient’s actual creatinine clearance is imperative to prevent severe adverse side effects and drug-related toxicity. We report a case of myoclonic activity developed in a patient with chronic kidney disease (CKD) shortly after a gabapentin dose increase. Case presentation Conclusion Gabapentin toxicity in patients with chronic kidney disease is underrecognized. Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive inappropriately high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, occasioning overt toxicity; advanced age and comorbidity predispose these patients for toxicity. Gabapentin is widely used in the management of pain. It is entirely excreted through the renal system so this needs to be considered in any patient becoming acutely ill and developing renal failure. Discussion: Gabapentin is widely used in the management of pain. It is entirely excreted through the renal system so this needs to be considered in any patient becoming acutely ill and developing renal failure. In rare instances, gabapentin can cause DRESS (drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms) syndrome. This is a severe allergic reaction that can cause damage to major organs, including the liver and kidneys. If you have existing kidney problems, you may need a lower dose of gabapentin. Gabapentin requires renal dosing in patients with chronic kidney disease and in patients at risk for developing AKI. In cases of symptomatic gabapentin-induced toxicity, dialysis should be instituted. Rational dosing of gabapentin and pregabalin in chronic kidney disease Mena Raouf 1, Timothy J Atkinson 1, , Meredith W Crumb Key takeaways Gabapentin is a medication used to treat seizures, postherpetic neuralgia pain associated with shingles, restless leg syndrome, and diabetic neuropathy. For people with normal kidney function, gabapentin is safe and doesn’t cause kidney complications or trigger kidney disease. Symptoms and laboratory findings were resolved after gabapentin discontinuation. Of note, as aforementioned, gabapentin toxicity has been reported in patients with chronic kidney disease or dialysis. The case reported by Bilgir et al had CKD stage 3 and the Italian case by Falconi et al had chronic renal failure on peritoneal dialysis.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
/male-kidney-anatomy--illustration-758313113-5a6bcd7bae9ab8003726d9d1.jpg) |  |
 |  |
 | :max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH_Illustration_Signs-and-Symptoms-of-End-Stage-Renal-Disease-ESRD_Laura-Porter_Final-d650ac51ed6d475cbad2532f772151bc.jpg) |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |