Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
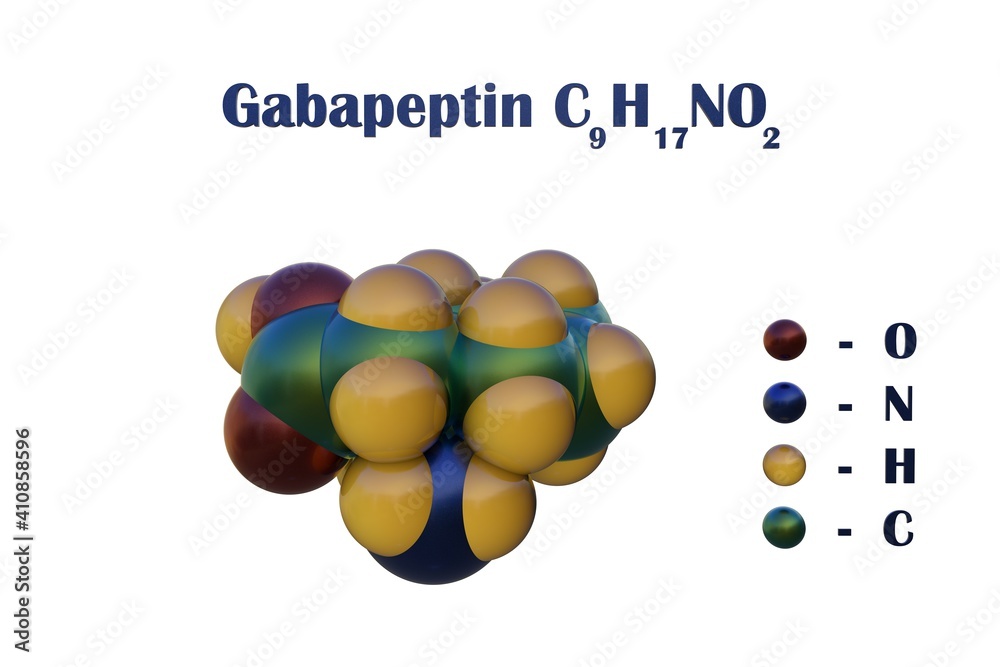
What is gabapentin and what is it used for? Gabapentin is used to control seizures, to treat nerve pain that can happen after having had shingles, and to treat a condition called restless legs syndrome. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication used in the management of peripheral neuropathic pains, postherpetic neuralgia, and partial-onset seizures. Gabapentin was originally used as a muscle relaxant and an anti-spasmodic. However, it was later discovered that gabapentin has the potential of an anticonvulsive medication and can be used as an adjunct to more potent anticonvulsants. Gabapentin is primarily utilized for the following conditions: Treat partial seizures. Alleviate nerve pain stemming from shingles. Manage restless leg syndrome. Combined with another antibiotic like clarithromycin (Biaxin) to address stomach ulcers caused by Helicobacter pylori infection. Gabapentin tablet contains gabapentin, a gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) analogue, as the active pharmaceutical ingredient. Gabapentin's chemical name is 1- (aminomethyl)cyclohexaneacetic acid The use of Gabapentin capsules in patients less than 12 years of age with compromised renal function has not been studied. 2.4 Dosage in Elderly Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and dose should be adjusted based on creatinine clearance values in these patients. Gabapentin is a gamma-amino acid that is cyclohexane substituted at position 1 by aminomethyl and carboxymethyl groups. Used for treatment of neuropathic pain and restless legs syndrome. It has a role as an anticonvulsant, a calcium channel blocker, an environmental contaminant and a xenobiotic. Gabarone package insert / prescribing information for healthcare professionals. Includes: indications, dosage, adverse reactions and pharmacology. The chemical structure of gabapentin is derived from the addition of a lipophilic cyclohexyl group to the backbone of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Gabapentin is a crystalline substance and freely soluble in water, alkaline and acidic solutions. The chemical structures for gabapentin, GABA, and pregabalin are shown below: O O O OH NH2 OH NH2 Gabapentin Chemical Properties, Uses, Production Description Gabapentin is a second- generation antiepileptic drug (AED) known under the proprietary brand name of Neurontin® (Pfizer, New York, NY) in the UK and USA. Generic formulation MHRA/ CHM advice to minimize risk when switching patients with epilepsy between different manufacturers’ products (including generic products): It is usually The anti-seizure drug gabapentin is used to treat epilepsy, nerve pain after shingles and restless legs syndrome by affecting chemical messengers in the brain and nerves. Common side effects Gabapentin, sold under the brand name Neurontin among others, is an anticonvulsant medication primarily used to treat neuropathic pain and also for partial seizures [10][7] of epilepsy. It is a commonly used medication for the treatment of neuropathic pain caused by diabetic neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia, and central pain. [11] . ChemicalBook provide Chemical industry users with Gabapentin Boiling point Melting point,Gabapentin Density MSDS Formula Use,If You also need to Gabapentin Other information,welcome to contact us. Patients taking gabapentin should not drive until they have gained sufficient experience to assess whether gabapentin impairs their ability to drive. Driving performance studies conducted with a prodrug of gabapentin (gabapentin enacarbil tablet, extended-release) indicate that gabapentin may cause significant driving impairment. Gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant) is a medicine used to treat partial seizures, nerve pain from shingles and restless leg syndrome. It works on the chemical messengers in your brain and nerves. Some of the uses of gabapentin include the following; 1. Treat nerve pain in adults. Patients suffering from diabetes are at a higher risk of suffering from nerve pain. Gabapentin is used in treating nerve pain in adults, which is related to diabetes and lumbar spine disc disease. 2. Treat herpes virus. The drug information on GABAPENTIN include structure, IUPAC, physiochemical properties, synthesis, SAR, MOA, therapeutic uses, side effects and MCQs for GPAT and other exam preparations. Gabapentin extended-release tablets (Horizant) are used to treat restless legs syndrome (RLS; a condition that causes discomfort in the legs and a strong urge to move the legs, especially at night and when sitting or lying down). Gabapentin is in a class of medications called anticonvulsants. Gabapentin is approved to prevent and control partial seizures, relieve postherpetic neuralgia after shingles and moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome. Learn what side effects to watch for, drugs to avoid while taking gabapentin, how to take gabapentin and other important questions and answers. Gabapentin (CAS 60142-96-3) information, including chemical properties, structure, melting point, boiling point, density, formula, molecular weight, uses, prices
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |