Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |
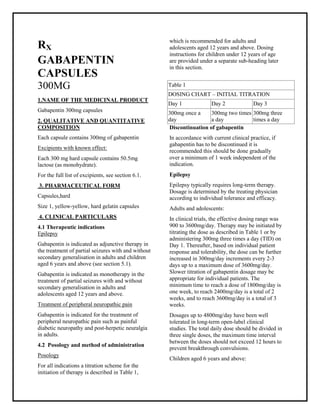
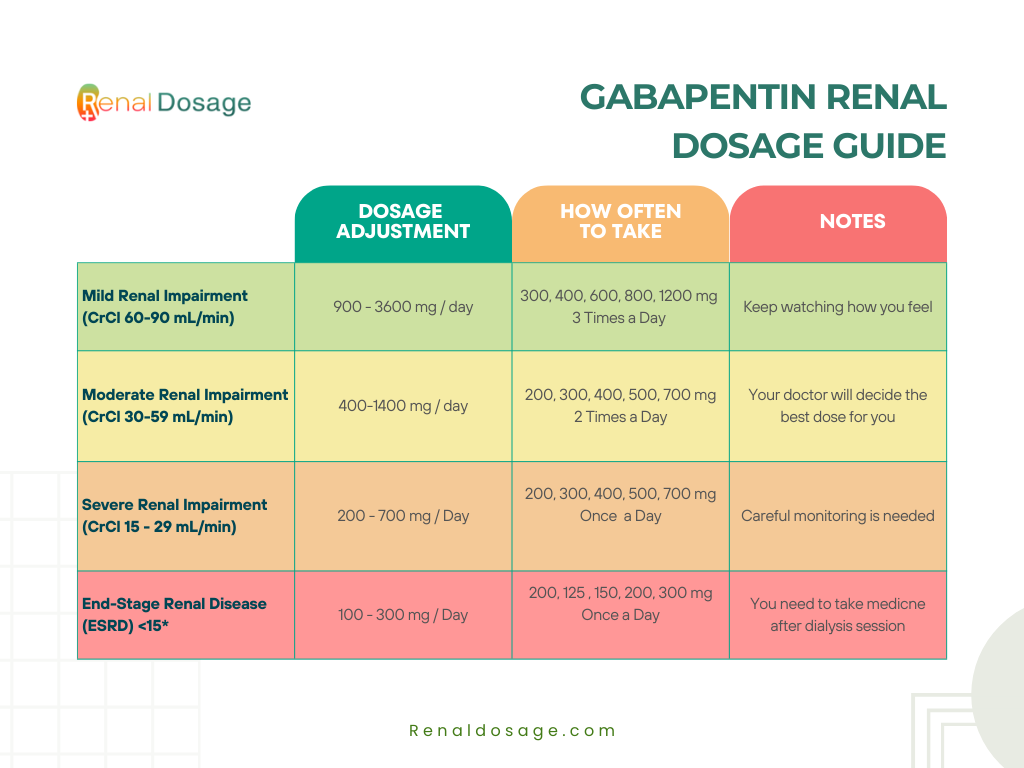
It may be reasonable to start older adults on a low dose of gabapentin, which can be effective to treat pain while exposing patients to a lower risk of adverse mental status side effects of gabapentin (dizziness, drowsiness and confusion) [7]. Gabapentin, widely used for treating various neurological conditions, plays a significant role in the health and well-being of elderly individuals. Although it can effectively manage symptoms of these ailments, recognizing the gabapentin side effects in the elderly is essential for caregivers and family members. These side effects can range from mild to severe, affecting each individual Prescribe gabapentin with caution to people with: A history of substance abuse. A history of psychotic illness. Low body weight (high doses of oral solution). Mixed seizures (including absences). Diabetes mellitus. Renal impairment – dose adjustments are necessary. Also prescribe gabapentin with caution to people who are: Elderly. At risk of suicide. [ABPI, 2020a; Joint Formulary Committee Explore the use of gabapentin in elderly patients, including its benefits for neuropathic pain and seizures, potential risks such as dizziness and cognitive effects, and important considerations for safe prescribing in this vulnerable population. Gabapentin’s side effects of altered mental status, dizziness, and unsteady gait lead to increased falls in the elderly, which increases the risk of hip fractures, and other life-threatening injuries. Gabapentin can help older adults manage nerve pain, seizures, or restless legs, but it brings risks worth comprehending. For seniors, this medication may spark dizziness, balance troubles, or fuzzy cognition—side effects that raise fall dangers in a group already vulnerable to injuries. Gabapentin Side Effects in Elderly: Discover the potential risks and solutions. Ensure senior health with our comprehensive guide on gabapentin side effects in elderly individuals. While gabapentin can be safe for many elderly patients, several factors require careful consideration: 1. Dosage Adjustments. Elderly patients often require lower doses of gabapentin due to age-related changes in kidney function. Find out the usual and maximum doses of gabapentin for different indications, such as epilepsy, postherpetic neuralgia, and restless legs syndrome. Learn how to adjust the dose based on renal function and age. The starting dose is 10 to 15 milligrams (mg) per kilogram (kg) of body weight per day and divided in 3 doses. Your doctor may adjust your dose as needed and tolerated. Children younger than 3 years of age—Use and dose must be determined by your doctor. For postherpetic neuralgia: Physical side effects of gabapentin in the elderly The biggest concern regarding the physical side effects of gabapentin in seniors involves reactions that pose a heightened risk of falls. Side effects, such as sweating, cardiac conduction abnormalities and high blood pressure are seen during the titration to the target dose. If a single-drug treatment is not effective for pain relief, adding venlafaxine to gabapentin may be more effective in the treatment of painful diabetic neuropathy [81]. Learn about common and serious gabapentin side effects in elderly patients. Understand risks, precautions, and when to seek medical help. Conclusion Gabapentin is commonly used for neuropathic pain relief in all stages of life. But how safe is gabapentin for older adults? What are the main gabapentin side effects in the elderly? Older adults have a higher prevalence of side effects due to overlapping health conditions and polypharmacy. Discover the potential side effects of gabapentin in elderly women, including common reactions, risks specific to older adults, and important considerations for safe use. Gabapentin needs to be gradually increased over a period of time until a maximum daily dose of 600mgs three times a day is reached. Follow the table below taking from 1 tablet a day to a maximum of 2 tablets three times a day: Stay on three capsules a day for about a week and if your pain relief is adequate, keep on this dose. For adults, your gabapentin dosage varies depending on your medical conditions and which form you’re taking. The maximum dosage is 3,600 mg per day. For children, the dosage is based on age and body weight. There are several ways to save on gabapentin. For instance, GoodRx can help you access Horizant at an exclusive cash price of about $170. ution should be taken for patients’ co-prescribed opioid and Pregabalin at doses exceeding 300mg a day. Patients co-prescribed an opioid with gabapentin and / pregabalin are at an increased risk of side effects such as sedation and respiratory depression4,5,6, The recommended maintenance dose of gabapentin capsules in patients 5 to 11 years of age is 25 mg/kg/day to 35 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses. Gabapentin may be administered as the oral solution, capsule, or tablet, or using combinations of these formulations. While gabapentin can be an effective treatment for many conditions, it’s essential to be aware of its potential side effects, especially in older adults who may be more susceptible to adverse reactions. Some of the most common side effects observed in elderly patients taking gabapentin include: 1.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |