Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
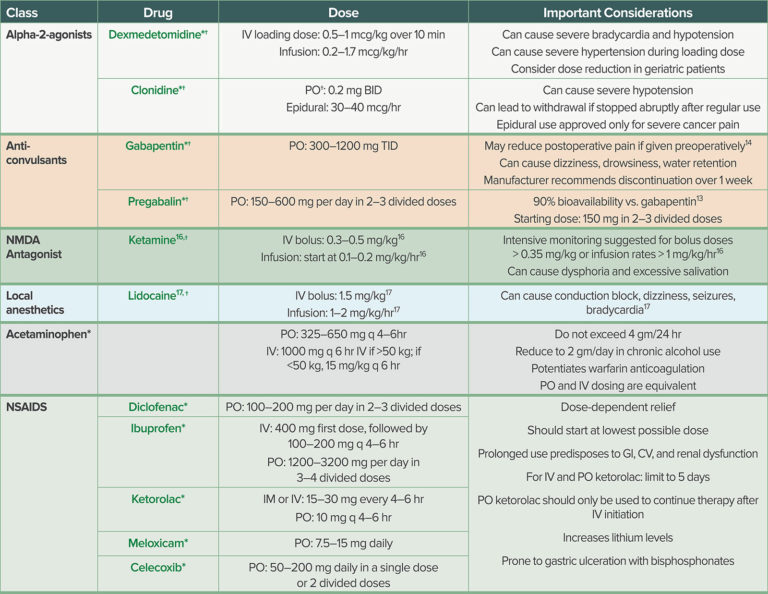 |  |
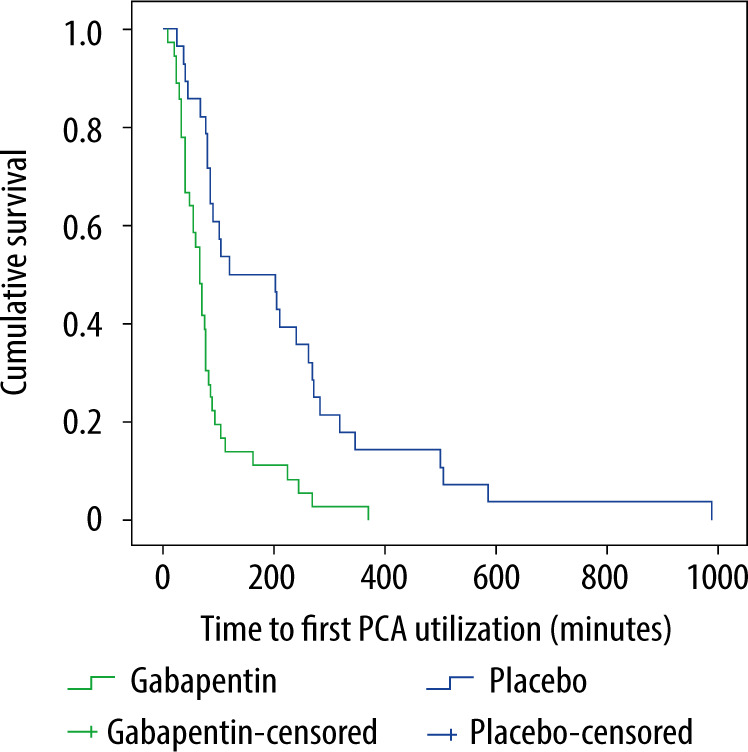
Conclusion Gabapentin, pregabalin, and duloxetine have potential to further decrease post-operative pain and lower opioid dependency. This review creates an opening for further research in hand surgery to assess an updated protocol for pain management to reduce opioid dependency. Outcomes and Data Analyses The primary outcome is prolonged use of gabapentin in the postoperative period, defined as a prescription refilled at 90-180 days after discharge from surgery, a time period based on definitions of prolonged use of opioids after surgical procedures. 20, 25, 26 We calculated the days’ supply and average daily dose. The most common dose of gabapentin assessed was 1200 mg daily (12 studies), with some studies using doses as low as 300 mg daily (Table 1). Eleven studies (25, 28 – 33, 36, 38 – 40) administered gabapentin as a single dose within 1 h to 2 h before surgery; the remainder involved initiating therapy on the day before surgery or continuing it for up to 10 days after surgery (Table 1). With This cohort study examines whether perioperative gabapentin use among older adults after major surgery is associated with in-hospital adverse clinical events. SUMMARY Gabapentin (NeurontinTM) has gained significant interest as part of a multi-modal pain management strategy for the control of acute pain. There has been considerable variation in both the dose and the regimen used in recent clinical trials. Most have relied on pre-operative dosing and have utilized a single dose of 300 to 1200 mg. Higher doses seem to show a decrease in postoperative Conclusions The use of gabapentin is effective in the management of postoperative pain in bariatric surgery. However, there is limited data regarding the opioid-sparing effect and adverse effect profiles of gabapentin in the bariatric surgical population. The results from this study demonstrate that gabapentin is more beneficial in mastectomy and spinal, abdominal, and thyroid surgeries. Gabapentin is an effective analgesic adjunct, and clinicians should consider its use in multimodal treatment plans among patients undergoing elective surgery. Gabapentin may be prescribed either before or after surgery to help with postsurgical pain. However, it should be used with caution due to the high risk of abuse. SUMMARY Gabapentin (NeurontinTM) has gained significant interest as part of a multi-modal pain management strategy for the control of acute pain. There has been considerable variation in both the dose and the regimen used in recent clinical trials. Most have relied on pre-operative dosing and have utilized a single dose of 300 to 1200 mg. Higher doses seem to show a decrease in postoperative 1.2 A single 300 mg dose of gabapentin should be given be should be given preoperatively in open and laparoscopic colorectal surgical procedures (Level of evidence: Moderate) This review evaluated the efficacy and tolerability of peri-operative gabapentin administration to control acute post-operative pain. Peri-operative gabapentin administration was found to be effective in reducing pain scores, opioid requirements and opioid-related adverse effects in the first 24 hours after surgery. Given the significant differences between the studies and the possibility of Conclusion Gabapentin, pregabalin, and duloxetine have potential to further decrease post-operative pain and lower opioid dependency. This review creates an opening for further research in hand surgery to assess an updated protocol for pain management to reduce opioid dependency. This randomized clinical trial evaluates the effects of perioperative administration of gabapentin on postoperative pain resolution and time to cessation of opioid use. Consider the following when using gabapentinoids in the perioperative period The evidence supports the use of gabapentinoids in the perioperative period. A typical dose range for perioperative gabapentin is 200-300 mg and 25-50 mg for pregabalin. Given the opioid-sparing effect of gabapentinoids, lower doses of perioperative narcotics may be used. After your surgery, begin taking 1 pill (300 mg) 3 times a day for the next 5 days Depending on what time your surgery ends, start taking the Gabapentin at lunch or dinner This medication may make you feel a little dizzy the first time you take it but this effect usually stops after the first dose or two Understanding Gabapentin Dosage Dosage can vary significantly from one patient to another. Typically, gabapentin is started at a low dose and gradually increased until effective pain relief is achieved or side effects become intolerable. The standard starting dose after surgery might range from 300 mg to 600 mg per day, divided into three doses. It’s crucial to monitor how each person Pain management after total knee arthroplasty (TKA) varies and has been widely studied in recent years. Some randomized controlled studies have carried out to evaluate the effects of gabapentin on pain relief after TKA. However, no solid result was For example, a gabapentin dose of 1.2 grams per day 1 hour before surgery and for 2 days after CABG surgery showed that postoperative pain scores at 1, 2, and 3 days as well as the consumption of tramadol given as a rescue analgesic were significantly lower in the gabapentin group when compared to the placebo group [41]. They used a gabapentin dose of 1.2 g per day treatment 1 hour before surgery and for 2 days after surgery and investigated its effect on postoperative acute pain.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |