Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 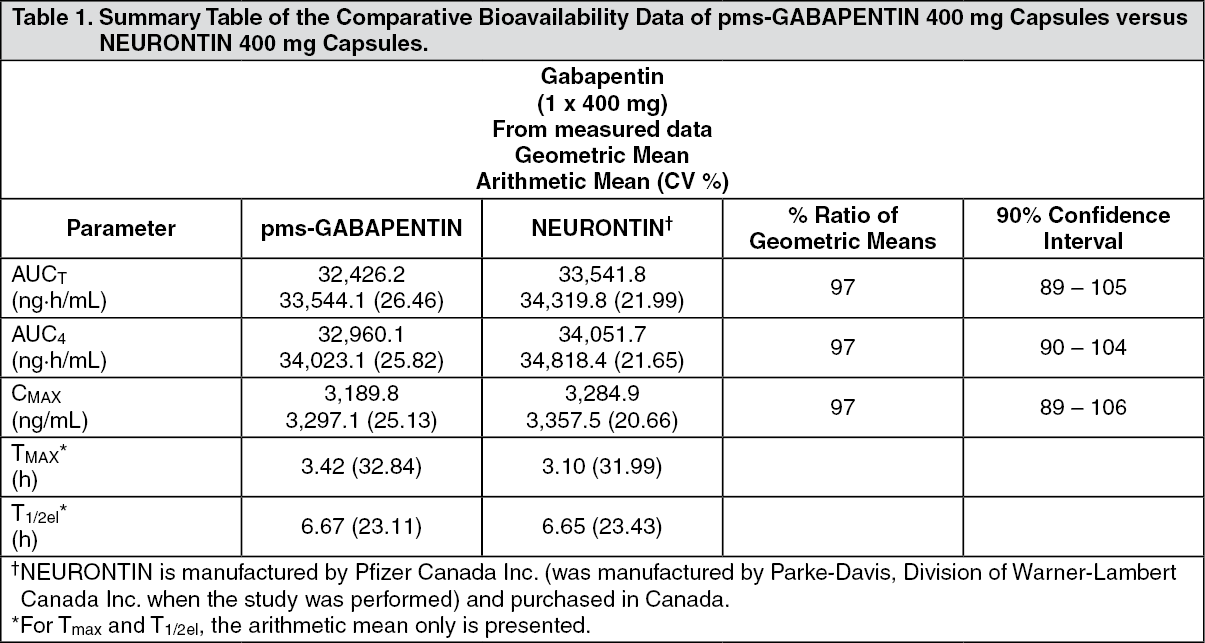 |
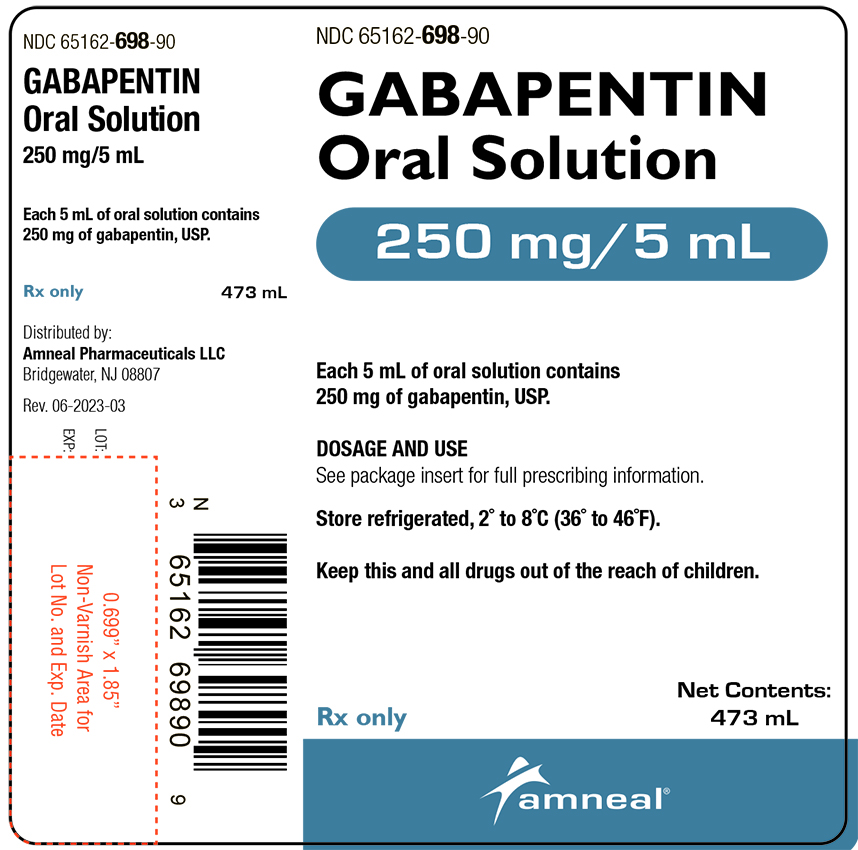
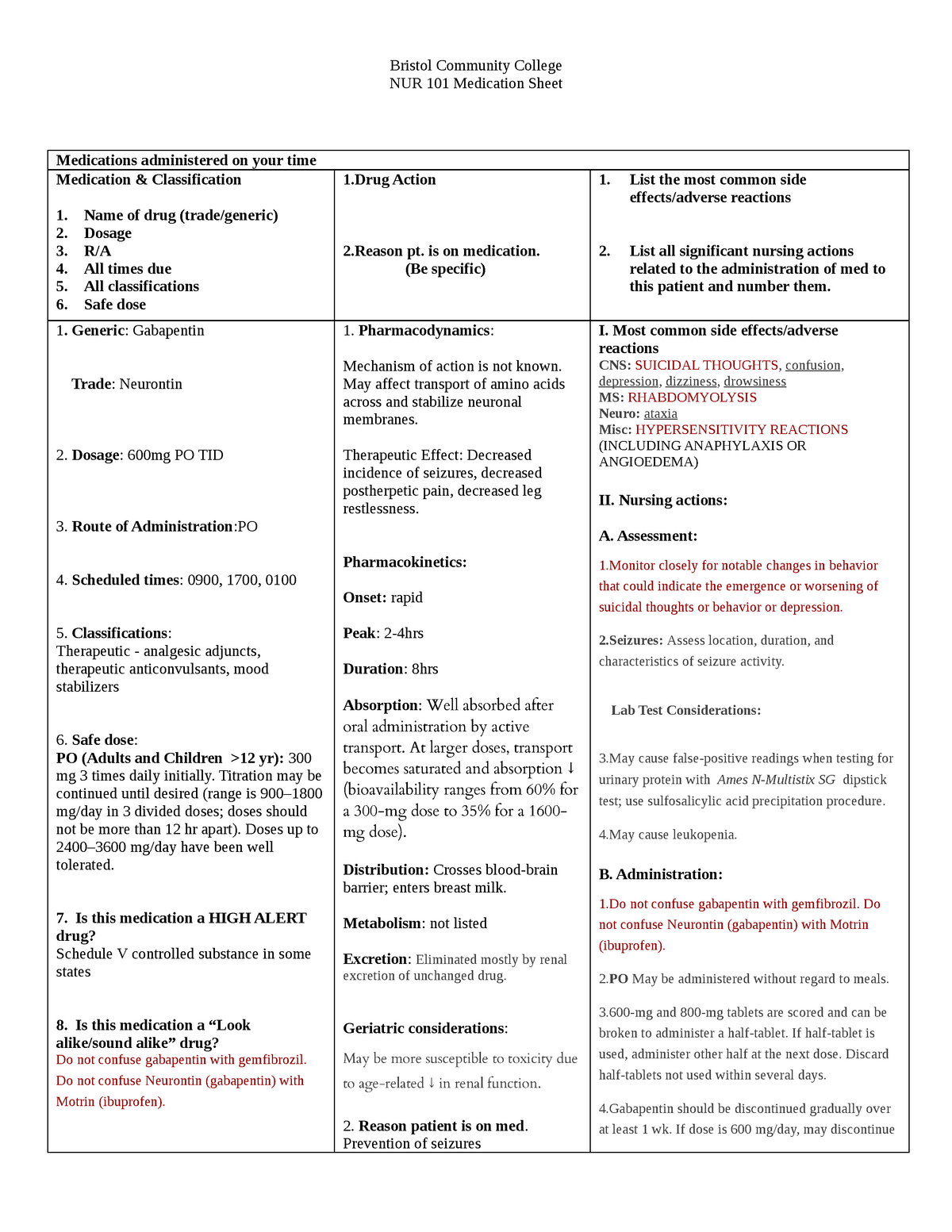
Gabapentin is an anticonvulsive medication that received approval from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1993 and has been available in generic form in the USA since 2004. Gabapentin was originally used as a muscle relaxant and an anti-spasmodic. However, it was later discovered that gaba Gabapentin is a relatively safe, readily available, and effective drug for alcohol-use disorder treatment, specifically for the abstinence maintenance phase. A study published in 2015 showed evidence for gabapentin use in treating alcohol withdrawal and dependence. Receiving six or more prescriptions of the drug gabapentin for low back pain is associated with significantly increased risks of developing dementia and mild cognitive impairment (MCI)--29% and 85 Structure of GABA: gabapentin and pregabalin. 10 Pharmacokinetics The actions of gabapentinoids are mainly at an intracellular site and require active uptake. They undergo facilitated transport across cell membranes through system l -amino acid transporters (LAT) as both drugs are structurally similar to the amino acid leucine. The effects of chronic gabapentin are blocked by an inhibitor of The anti-seizure drug gabapentin is used to treat epilepsy, nerve pain after shingles and restless legs syndrome by affecting chemical messengers in the brain and nerves. Common side effects Receiving six or more prescriptions of the drug gabapentin for low back pain is associated with significantly increased risks of developing dementia and mild cognitive impairment (MCI)—29% and Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication used in the management of peripheral neuropathic pains, postherpetic neuralgia, and partial-onset seizures. Gabapentin is an anti-epileptic drug, also called an anticonvulsant. It is used to treat some types of seizures and nerve pain caused by shingles. A recent study has linked gabapentin, a popular painkiller for lower back pain, to increased risk of dementia and mild cognitive impairment in some adults. Gabapentin has no activity at GABAA or GABAB receptors of GABA uptake carriers of brain. Gabapentin interacts with a high-affinity binding site in brain membranes, which has recently been identified as an auxiliary subunit of voltage-sensitive Ca2+ channels. However, the functional correlate of gabapentin binding is unclear and remains under study. This study supports the warnings from regulatory agencies and highlights the importance of considering this potential risk when prescribing gabapentin and pregabalin to patients with COPD. Primary funding source: Canadian Institutes of Health Research and Canadian Lung Association. Gabapentin, which is used to treat seizures, nerve pain and restless leg syndrome might be linked with increased risk of dementia, a new study says. Those with 12 or more gabapentin prescriptions were 40% more likely to develop dementia and 65% more likely to develop MCI than those prescribed the drug three to 11 times. Researchers noted that because this is an observational study, it cannot draw a direct cause-and-effect association between gabapentin and brain decline. The study found adults taking gabapentin for chronic lower back pain faced a 29 per cent increased risk of dementia and an 85 per cent higher risk of mild cognitive impairment within a decade, compared to back pain sufferers not prescribed the drug. Frequent use of gabapentin for back pain may raise the risk of dementia by 29% and mild cognitive impairment by 85%, new study finds. The PRISMA flow diagram detailing the search results and subsequent stages of screening Study characteristics Out of the selected 50 controlled trials, 29 investigated pregabalin [2, 20 – 47], 16 gabapentin [48 – 63], and 5 studies assessed pregabalin and gabapentin compared to placebo-controlled trials [64 – 68]. A large U.S. medical records study has found that adults prescribed gabapentin six or more times for chronic low back pain face significantly higher risks of dementia (29%) and mild cognitive impairment (85%) within 10 years. Gabapentin (“Neurontin”) has been shown in extensive preclinical and clinical studies to be an effective anticonvulsant drug, which appears to have novel mechanisms of action. Although designed as a GABA analogue it is clearly not GABAmimetic, although Gabapentin prescriptions for chronic back pain were linked to higher dementia and cognitive impairment risk. Risks were especially high for chronic back pain patients ages 35 to 64. The study Introduction Gabapentin is widely used to treat chronic pain, but its association with cognitive decline and dementia remains unclear. This study examined whether gabapentin prescription is associated with dementia in adults with chronic low back pain. Methods We conducted a retrospective cohort study using the TriNetX national database of de-identified patient records from 2004 to 2024
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |