Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
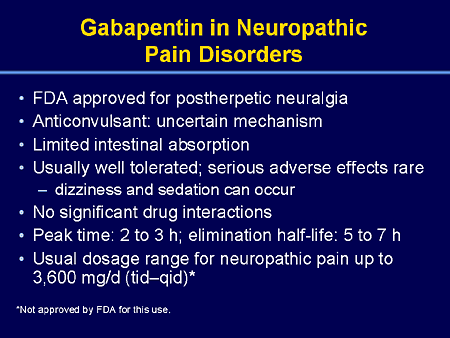
A full blood count, renal profile, and liver ultrasound scan were also normal. Gabapentin induced cholestasis was thought likely and the drug was stopped. After this, clinical symptoms and liver function tests improved gradually (figure). Can gabapentin cause liver enzymes to be elevated? Gabapentin is a unique anticonvulsant used as an adjunctive therapy in managing epilepsy and neuropathic pain syndromes. Gabapentin is primarily excreted unchanged by the kidneys. Therefore, renal function significantly influences drug levels in the body. In patients with impaired kidney function, gabapentin can accumulate to toxic levels if dosages aren’t adjusted accordingly. This accumulation may lead to increased side effects such as drowsiness or confusion. Learn about the potential effects of Gabapentin on your liver and kidneys. Find out if it is safe to use and how to protect your organs while taking this medication. The liver plays a vital role in metabolizing medications, including gabapentin. While most individuals tolerate gabapentin without significant issues, there are rare instances where liver function may be compromised. This article delves deep into the relationship between gabapentin and liver health, exploring mechanisms of action, potential side effects, case studies, and recommendations for Question I have a patient with trigeminal neuralgia who was taking 1600 mg of gabapentin and had serious elevations of liver function tests (aspartate transaminase 258 U/L, alanine transaminase Gabapentin (GPN) is a new antiepileptic agent currently in used as add-on therapy in adult patients suffering from partial seizures. The extent of liver damage at different dosage and long term There are various reports that the elevation of liver enzymes after chronic antiepileptic medication would reflect hepatocellular damage. Our previous and several other studies shows that long term treatment with old or new anti epileptic drugs affect liver function from transient state to a fatal liver damage (1,8-10). Gapentin is not metabolized by the liver, and its effects on the liver and kidneys are similar to previous studies. In rare cases, gabapentin can cause DRESS (drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms). Incidence Gabapentin affects nerves and chemicals in your body that are involved in some types of pain and in seizures. Drug manufacturer Pfizer classifies abnormal liver function tests as an infrequent side effect for gabapentin 5. There is insufficient data to estimate incidence for these or establish whether gabapentin is the sole cause of elevated liver function tests, notes Pfizer Gabapentin is eliminated through the kidneys and, therefore, doesn’t typically cause liver injury. Learn safe dosage recommendations for people with liver disease. Changes in liver function may be attributed to free radical damage induced by gabapentin, as documented in this study, where the drug enhanced antioxidant defense systems and elevated liver NO Gabapentin is a unique anticonvulsant that is used as adjunctive therapy in management of epilepsy and for neuropathic pain syndromes. Therapy with gabapentin is not associated with serum aminotransferase elevations, but several cases of clinically apparent liver injury from gabapentin have been reported. Introduction: Gabapentin is an anti-convulsant that is also used off-label to treat neuropathic pain. It is not metabolized by the liver, and there have been few reports of hepatotoxity associated with it. We present a rare case of gabapentin-induced hepatotoxicity occurring in a young male. Case Description/Methods: A 41-year-old male with an extensive past medical history including type 1 Unveiling Gabapentin's Potential Impact on Liver Health Gabapentin is a widely prescribed medication, primarily known for its efficacy in managing seizures and neuropathic pain. Understanding its potential effects, especially concerning liver health, is paramount. This exploration delves into the intricacies of gabapentin's interaction with the MeSH terms Anticonvulsants / therapeutic use Cyclohexanecarboxylic Acids* / adverse effects Drug-Related Side Effects and Adverse Reactions* Gabapentin / adverse effects Hepatitis* Humans gamma-Aminobutyric Acid / adverse effects Nine patients with liver injury due to phenytoin received other AEDs and they include levetiracetam (n=5), levetiracetam plus gabapentin (n=1), levetiracetam and lamotrigine (n=1), and topiramate (n=1), zonisamide (n=1). Two patients with valproate liver injury had other AED use and they include lamotrigine (n=1) and zonisamide (n=1). Gabapentin, a gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) analogue, has infrequently been reported to cause liver injury; however, the causality in the previous reports is contested. Herein, we report a gabapentin-induced hepatocellular injury in a patient without another identifiable cause for acute liver injury. Key takeaways: Gabapentin (Neurontin, Horizant, Gralise) usually isn’t bad for your liver or kidneys. In most cases, it has no harmful effect on these organs. In rare instances, gabapentin can cause DRESS (drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms) syndrome. This is a severe allergic reaction that can cause damage to major organs, including the liver and kidneys. If you have Discussion: Gabapentin induced liver injury is rare with few reported cases, many of which did not exclude other etiologies. In this case, the key elements of diagnosing DILI were met including gabapentin initiation closely preceding liver injury, other etiologies excluded, and discontinuation of gabapentin leading to improvement.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |