Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
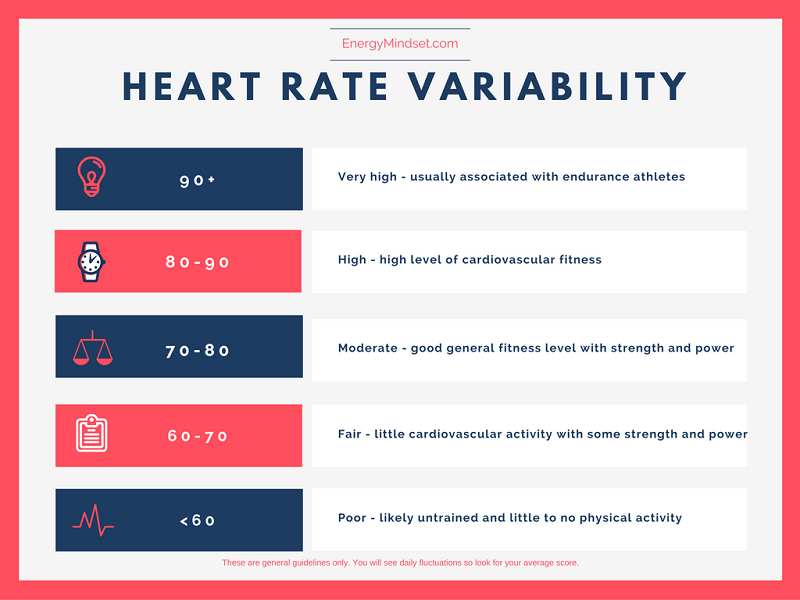
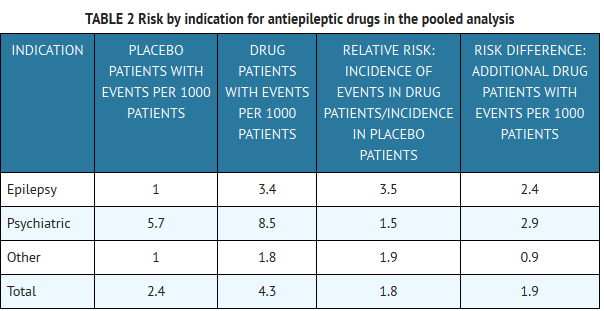
Tachycardia, or a fast heart rate, can be caused by many medications, including antibiotics, antidepressants, and even certain supplements. Abstract Gabapentin (GBP), a GABA analogue, is primarily used as an anticonvulsant for the treatment of partial seizures and neuropathic pain. Whereas a majority of the side effects are associated with the nervous system, emerging evidence suggests there is a high risk of heart diseases in patients taking GBP. In the present study, we first used a preclinical model of rats to investigate Yes, I am experiencing increased heart rate after taking gabapentin. I've been taking this drug for 2 weeks now, and I've done an extensive search of possible side effects, but have not found rapid heart rate listed anywhere. MIne normally is in the 75-85 range, but now I'm in the 90-115 range. That's too high. It is important to note you are at increased risk of becoming addicted to gabapentin the longer you use it, which is why when stopping gabapentin suddenly, you may experience withdrawal symptoms like rapid heart rate. If you experience these symptoms, speak with your doctor immediately. Background: Gabapentin is a commonly used medication used as an anti-convulsant or analgesic. The well-known side-effects of gabapentin are dizziness, drowsiness and fatigue. In rare cases, it can lead to development of new onset congestive heart failure (CHF) or decompensation of pre-existing CHF. We present a case of gabapentin induced CHF with rapid resolution after discontinuing the Though gabapentin has many potential uses, it can cause side effects. Read more about 13 gabapentin side effects here. Learn about the side effects of gabapentin, from common to rare, for consumers and healthcare professionals. Cardiovascular symptoms of gabapentin withdrawal: Some individuals experience an increased heart rate and elevated blood pressure during withdrawal. The severity of these symptoms depends on the dosage and duration of use. Those who took gabapentin recreationally or at very high doses are more likely to experience intense withdrawal symptoms. In this study, we investigated the hemodynamic response to acute and chronic administration of gabapentin, a ligand of auxiliary α 2 δ subunit of VDCCs, in adult SHR with established neurogenic hypertension. The acute gabapentin administration lowered BP and heart rate more in conscious SHR than Wistar-Kyoto rats. Gabapentin can help control seizures as well as nerve pain from shingles. It may sometimes cause side effects, especially if you misuse it. Learn more. Moreover, the use of gabapentin and pregabalin have increased in the USA from 1.2% of adults in 2002 to 3.9% in 2015, with the largest increases in older adults, those with diabetes and those with at least 5 comorbidities. In this focused review, we discuss the cardiovascular safety of gabapentin and pregabalin. Heart Failure GD-Gabapentin: Gabapentin belongs to the class of medications called anti-epileptics. It is used in combination with other seizure control medications to manage and prevent seizures associated with epilepsy. Gabapentin does not cure epilepsy and only works to control seizures as long as the medication is taken. Gabapentin works by affecting the transmission of nerve signals in the brain. In patients with diabetic neuropathy who were prescribed gabapentin and pregabalin, there is an increased risk for heart failure, myocardial infarction, peripheral vascular disease, stroke, deep venous thrombosis, and pulmonary embolism with long-term use. Then, unilateral microinjection of gabapentin into the NTS before and after N (ω)-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME) treatment whether to change blood pressure and heart rate. Fibromyalgia, a chronic pain disorder, impacts approximately 2% of adults in the US. Gabapentin and pregabalin are common treatments to manage fibromyalgia-related pain. Our recent study showed the risk of adverse cardiovascular events increased in Learn more about the symptoms and treatment of this heart rhythm disorder, which causes a rapid heart rate. Gabapentin was discontinued and the patient was started on diltiazem 30 mg per oral four times a day and apixaban 5 mg per oral twice daily. which led to a decrease in the patient’s heart rate to ~60 beats per minute. In patients with diabetic neuropathy who were prescribed gabapentin and pregabalin, there is an increased risk for heart failure, myocardial infarction, peripheral vascular disease, stroke, deep venous thrombosis, and pulmonary embolism with long-term use. Our findings suggest that increased risk fo Do you take Gabapentin and are concerned about Heart rate increased? eHealthMe's data-driven phase IV clinical trials have been referenced on 800+ peer-reviewed medical publications including The Lancet, Mayo Clinic Proceedings, and Nature. Check whether Heart rate increased is associated with a drug or a condition.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |