Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 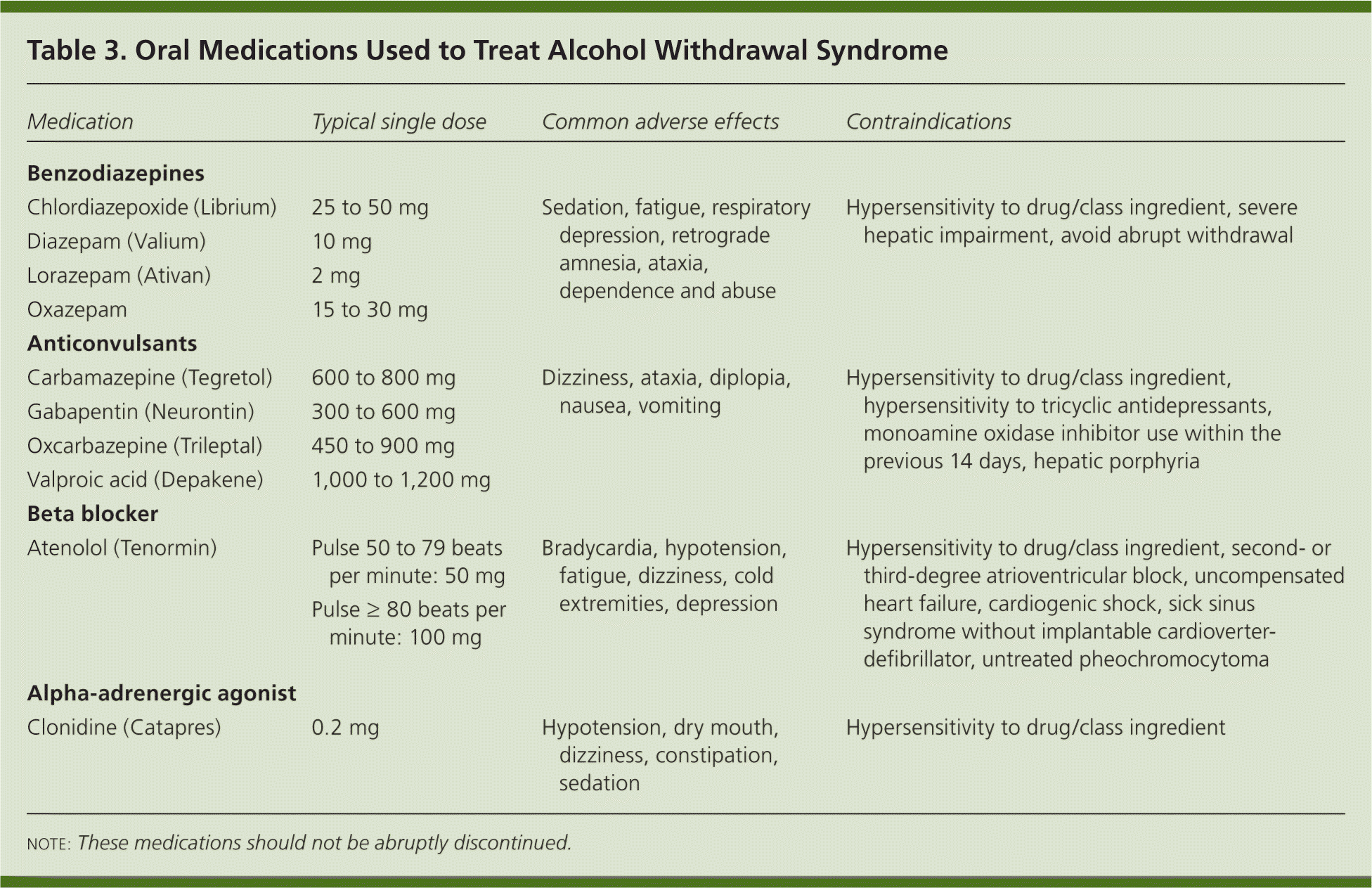 |
A total of 150 alcohol-dependent individuals were randomly assigned to a 16-week course of naltrexone alone (50 mg/day [N=50]), naltrexone (50 mg/day) with gabapentin (up to 1,200 mg/day [N=50]) added for the first 6 weeks, or double placebo (N=50). Gabapentin is used off-label in alcohol withdrawal care. This guide covers clinical evidence, side effects, and treatment guidelines. Early initiation of high-dose gabapentin was associated with a significant reduction in benzodiazepine exposure, faster stabilization of alcohol withdrawal-related symptoms, and shorter hospital length of stay. Future studies evaluating gabapentin's effect on long-term safety and hospital readmissio A study published this week concluded that gabapentin can relieve alcohol withdrawal symptoms but is most effective for people with a history of more severe symptoms after a few days of abstinence. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant that helps to control and reduce severe epileptic seizures. According to a 2020 study, people who took gabapentin for alcohol withdrawal tolerated it well. This article examines a role for gabapentin in reducing alcohol consumption in a specific subpopulation of alcohol use disorder patients: those with high alcohol intake and high levels of withdrawal symptoms. Results and Discussion: The available evidence on gabapentin for alcohol use disorder suggests that this treatment successfully alleviates problems related to alcohol abuse, including withdrawal symptoms, dependence, and cravings. However, more research is needed to determine the effectiveness of gabapentin for preventing relapse. Context Gabapentin can be a second-line, off-label treatment for moderate to severe AUD. 3 Recommended as first-line are acamprosate (NNT = 12) and naltrexone (NNT = 20). 3, 4 Gabapentin misuse in the general population is about 1%, and up to 15% to 22% in patients with a history of opioid abuse. Risk with alcohol abuse history is less clear. 5 Interventions: Gabapentin up to 1200 mg/d, orally, vs placebo along with 9 medical management visits (20 minutes each). Main outcomes and measures: The percentage of individuals with no heavy drinking days and those with total abstinence were compared between treatment groups and further evaluated based on prestudy alcohol withdrawal symptoms. Gabapentin reduces alcohol consumption and craving, which may help patients to maintain abstinence. These results, together with the virtual absence of side effects and a favorable safety profile, support gabapentin as a potential drug for the treatment of alcohol withdrawal and dependence. Find out what you need to know about gabapentin for alcohol withdrawal and discover the pros, cons, risks, and benefits, and how it may affect health. While benzodiazepines are considered the standard of care for alcohol withdrawal, gabapentin is a valuable alternative that can also help with cravings and abstinence long term. Read on to find out more. Our patient’s progress, with unrelenting response and efficacy to gabapentin alone, merits further consideration for the use of gabapentin in the substantial reduction of alcohol-drinking behaviors, as either a mono-therapy or in combination with other FDA-approved agents, in the treatment and management of AUD. Expert opinion Alcohol use disorder represents a challenge and large, unmet medical need. Evidence from single-site studies lend support to the safety and efficacy of gabapentin as a novel treatment for alcohol use disorder, with unique benefits for alcohol-related insomnia and negative affect, relative to available treatments. QuestionIs gabapentin efficacious in the treatment of alcohol use disorder in adults with a history of alcohol withdrawal symptoms? FindingsIn this randomized clinical trial, gabapentin compared with placebo significantly increased the number of people with total abstinence and reduced drinking. Restarting gabapentin may be considered if withdrawal symptoms become overwhelming, but this should be done under strict medical supervision. Establishing the Initial Dose Reduction Medical professionals may employ various strategies to determine the initial dose reduction for Gabapentin. Studies of the efficacy of gabapentin for treating alcohol use disorder (AUD) have yielded mixed findings. The aims of our study were to estimate gabapentin’s effects on six alcohol-related outcomes, test potential moderators, examine publication Gabapentin has been used for years in hospitals to treat patients with acute alcohol withdrawal, which is characterized by symptoms such as sweating, tremors, anxiety, and irritability. Numerous clinical studies have tested this agent as a therapy for long-term alcohol reduction, but the results have been mixed; gabapentin is not FDA approved for AUD. Wondering about mixing gabapentin with your evening glass of wine? You're not alone! Many patients ask about this common concern when they're prescribed this medication. While the official answer isn't a strict "no," there are important things to consider before combining these two substances. Gabapentin and alcohol are both central The anticonvulsant drug gabapentin is used off-label to treat alcohol-related withdrawal, cravings, anxiety, and insomnia. Although it is well tolerated and has demonstrated efficacy for mild alcohol withdrawal and early abstinence, there is concern about its potential for abuse. Gabapentin should be prescribed only as a second-line alternative to standard therapies, and only after screening
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |