Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
/GettyImages-1304614867-26555bf20166412c8089724d5d3dcf93.jpg) |  |
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/chronic-kidney-disease-overview-1132509_final-3537757c10114a8fa532359abe616d47.png) |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
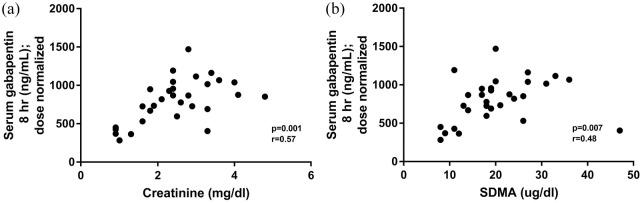
Gabapentin is frequently used as an analgesic in patients with chronic kidney disease. Although gabapentin is well known for its favorable pharmacokinetics, it is exclusively eliminated renally, and patients with chronic kidney disease are at risk for toxicity. Existing literature on such risk is lacking. Abstract Background: Gabapentinoids (GPs) are frequently prescribed in individuals with chronic kidney disease (CKD); however, their exclusive renal elimination warrants dose adjustments to decrease risk of toxicity. This study evaluated GP prescribing patterns and whether excessive dosing was associated with increased incidence of gabapentinoid-related adverse events (GRAEs). Abstract Background: Gabapentin is frequently used as an analgesic in patients with chronic kidney disease. Although gabapentin is well known for its favorable pharmacokinetics, it is exclusively eliminated renally, and patients with chronic kidney disease are at risk for toxicity. Existing literature on such risk is lacking. With a growing chronic kidney disease epidemic,22,23an increasing number of patients with chronic kidney disease will be exposed to gabapentin. This study demonstrates that gabapentin dosage for patients with chronic kidney disease has been insufficiently adjusted and that the risk of gabap-entin toxicity has been underrecognized. Gabapentin is frequently used as an analgesic in patients with chronic kidney disease. Although gabapentin is well known for its favorable pharmacokinetics, it is exclusively eliminated renally, and patients with chronic kidney disease are at risk for toxicity. Gabapentin is widely used in the management of pain. It is entirely excreted through the renal system so this needs to be considered in any patient becoming acutely ill and developing renal failure. Gabapentin is frequently used as an analgesic in patients with chronic kidney disease. Although gabapentin is well known for its favorable pharmacokinetics, it is exclusively eliminated renally, and patients with chronic kidney disease are at risk for toxicity. Existing literature on such risk is lacking. Gabapentin and pregabalin are used for neuropathic pain in CKD patients but require renal adjustments. INTRODUCTION Pain is one of the most common and distressing symptoms among patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) [1]. The prevalence of pain has been associated with substantially lower health-related quality of life and greater psychosocial distress, insomnia, and depressive symptoms [2-9]. Gabapentinoids, including gabapentin and pregabalin, are frequently prescribed as opioid alternatives. Given that gabapentinoids are eliminated from the body by the kidney, we sought to determine the risk of serious adverse events in patients with chronic kidney disease who started a gabapentinoid at a higher versus a lower dose. Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive dangerously high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, which can lead to all sorts of problems. An alternative we recommend instead of Gabapentin is Alpha Lipoic Acid. People most commonly use alpha-lipoic acid for nerve pain in cases of diabetes. Notwithstanding, most reports of toxicities were associated with concentrations higher than 15 mg/L for gabapentin and concentrations higher than 13 mg/L for pregabalin, whereas individuals with normal renal function on maximum recommended dosing yielded concentrations of ~5–8 mg/L for gabapentin and 2.8–8.2 mg/L for pregabalin. 22–25 The Gabapentin’s apparent total clearance is 100 mL/ min in adults with normal renal function, which is essentially equivalent to CrCl and does not suggest the involvement of tubular reabsorption.1 Some evidence suggest that active tubular secretion mediated by organic cation transporter-1 (OCT-1) may play a role in gabapentin’s renal clearance. Gabapentin and pregabalin are often used in patients with CKD primarily to treat neuropathic pain and restless leg syndrome and given the high prevalence of diabetes in this population, the proportion who receive these drugs is very high. In patients with normal renal function, the maximum dose of gabapentin is 3600mg daily in divided doses. However, gabapentin is renally cleared and so the Some people, such as those with kidney disease, have an increased risk of harm when using these drugs. Keywords: gabapentin, nonmedical use, off-label prescribing, pregabalin Box 1. Off-label uses of gabapentinoids. acute postoperative pain alcohol use disorder alcohol withdrawal anxiety disorders attention deficit hyperactivity disorder Gabapentin can be used by kidney disease patients, but dosage adjustments are critical. Learn how to safely use gabapentin with kidney issues and discover alternative medications. Gabapentinoids are opioid substitutes whose elimination by the kidneys is reduced as kidney function declines. To inform their safe prescribing in older adults with chronic kidney disease (CKD), we examined the 30-day risk of serious adverse events according to the prescribed starting dose. This is a severe allergic reaction that can cause damage to major organs, including the liver and kidneys. If you have existing kidney problems, you may need a lower dose of gabapentin. This is because the kidneys help the body get rid of gabapentin. If you have impaired kidney function, gabapentin may build up in the body and cause side effects. Gabapentin is frequently used as an analgesic in patients with chronic kidney disease. Although gabapentin is well known for its favorable pharmacokinetics, it is exclusively eliminated renally, and patients with chronic kidney disease are at risk for toxicity. Existing literature on such risk is lacking. Gabapentin dosing ranges from 100 to 3600 mg daily and pregabalin dosing is 25 to 600 mg daily. 1, 2 Gabapentin and pregabalin exhibit greater than 90% kidney elimination and adjustments to dose and frequency are recommended for patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD). 1, 2 For patients with a creatinine clearance (CrCl) below 60 mL/min, a
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
/GettyImages-1304614867-26555bf20166412c8089724d5d3dcf93.jpg) |  |
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/chronic-kidney-disease-overview-1132509_final-3537757c10114a8fa532359abe616d47.png) |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |