Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
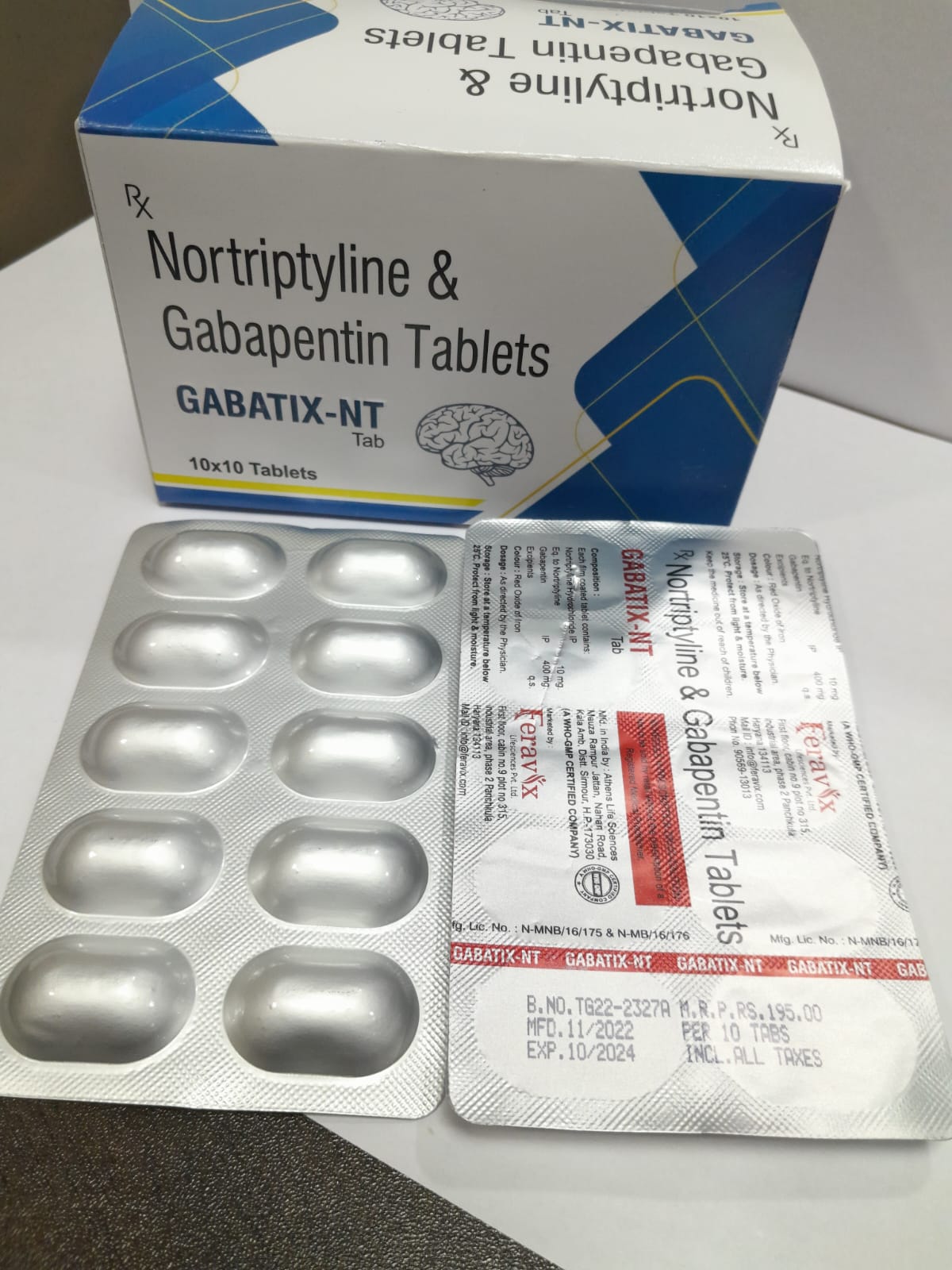
Uses of Gabapentin Gabapentin is primarily used to treat epilepsy in people older than 12 and partial seizures in children ages 3 to 12. It is also FDA-approved to treat a condition called postherpetic neuralgia —the nerve-related pain complication of a herpes zoster attack (shingles) that can occur in adults. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication prescribed for a variety of conditions. Learn about its uses, side effects, and what you should know if you've been prescribed this medication. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication used in the management of peripheral neuropathic pains, postherpetic neuralgia, and partial-onset seizures. Gabapentin (GBP), originally an antiepileptic drug, is more commonly used in the treatment of pain, including headache disorders. Off-label GBP is used in headache disorders with some success, some failure, and much debate. Due to this ambiguity, a clinical evidence literature review was performed investigating GBP's efficacy in headache disorders. Gabapentin is an effective prophylactic agent for patients with migraine. In addition, gabapentin appears generally well tolerated with mild to moderate somnolence and dizziness. Gabapentin is approved to prevent and control partial seizures, relieve postherpetic neuralgia after shingles and moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome. Learn what side effects to watch for, drugs to avoid while taking gabapentin, how to take gabapentin and other important questions and answers. Gabapentin is available in both branded and generic forms. Gabapentin is used "off-label" for migraine prevention and treatment, including migraines with or without aura, vestibular migraines. It reduces the frequency of headaches, pain intensity, and the use of symptomatic medications 1, 2. If you have a headache most days, you might have one of the most disabling headache conditions, chronic daily headaches. Aggressive treatment and long-term management might help. Introduction: Severe, often sudden-onset headache is the principal presenting symptoms of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage (aSAH). We hypothesized that gabapentin would be safe and tolerable for aSAH-induced headaches and would reduce concurrent We offer a panoramic view of nociception, from a central perspective, and discuss various pharmacological options available to treat headache and neck pain. We also debate the role of a new antiepileptic drug, gabapentin, in the management of headache and neck pain. It is now considered to be an emergent treatment for pain syndrome. Pain Relief: Gabapentin’s pain-relieving properties could provide much-needed relief during a migraine attack, helping individuals cope with the pain. Preventive Potential: Gabapentin’s ability to modulate nerve activity makes it a candidate for migraine prevention, offering a proactive approach to managing this condition. Sudden severe headache is a cardinal symptom and the most common complaint amongst patients presenting with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. The multifactorial etiology of these headaches makes pharmacotherapy problematic. Current aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage guidelines have limited or no recommendations for headache treatment. Gabapentin is a drug that’s approved to help prevent seizures in people with epilepsy and treat nerve pain from shingles. It’s also sometimes used off-label for migraine prevention. Gabapentin was originally used as a muscle relaxant and an anti-spasmodic. However, it was later discovered that gabapentin has the potential of an anticonvulsive medication and can be used as an adjunct to more potent anticonvulsants. The medication also proves beneficial in managing certain types of neural pain and psychiatric disorders. We plan to use gabapentin (GBP), an FDA approved non-narcotic pain medication for neuropathic pain, which is also an alpha-2-delta (A2DR) receptor analogue to reduce the pain and decrease the need for narcotics. GBP has been shown to decrease neuropathic and non-neuropathic pain in variety of perioperative and postoperative conditions. A2DR affinity also has some neuroprotective effect in Abstract Objective: Gabapentin (GBP), originally an antiepileptic drug, is more commonly used in the treatment of pain, including headache disorders. Off-label GBP is used in headache disorders with some success, some failure, and much debate. Discover whether gabapentin is a reliable treatment for migraines, including benefits, potential risks, and alternatives to consider. Gabapentin has a wide range of off-label applications, including as a treatment option for neuropathic pain, migraine prevention, and headaches, including tension and cluster types. A new review indicates that gabapentin may be an effective adjunct therapy for primary headache syndromes, but that there is not enough evidence to support its use as a primary treatment.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |