Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
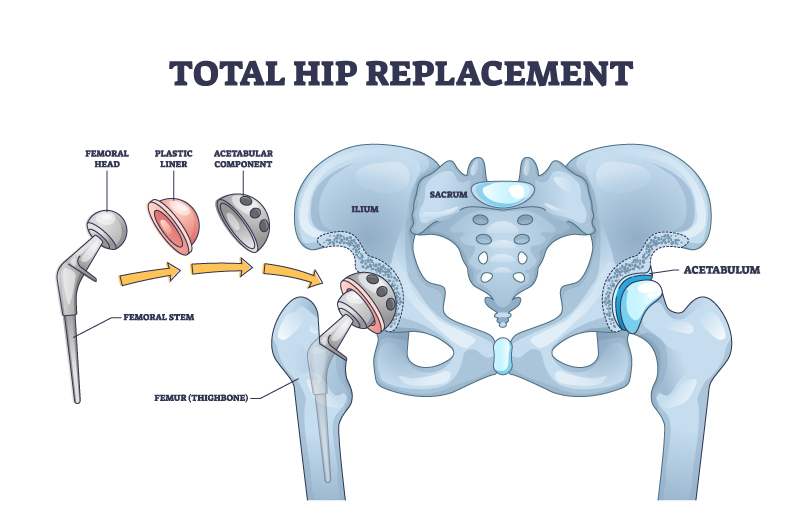
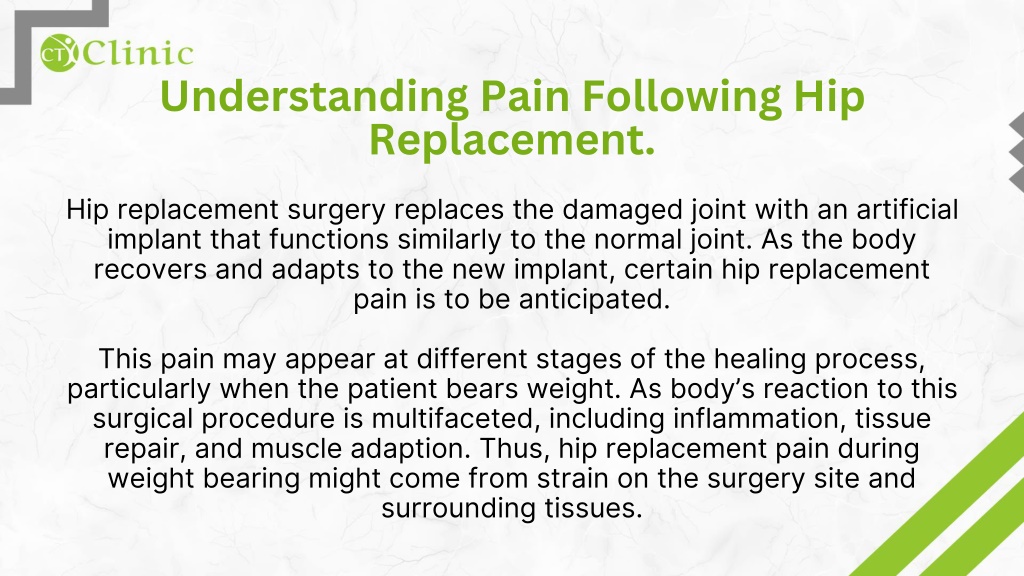
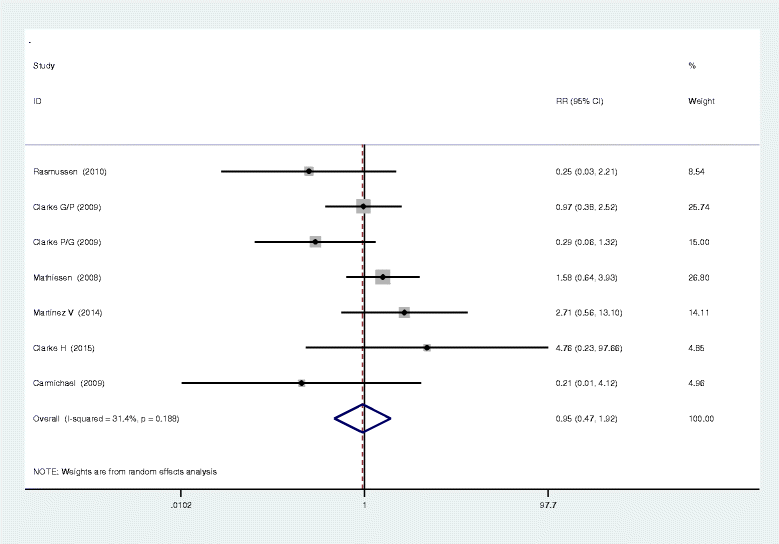
Neurontin (gabapentin), generally prescribed for the treatment of nerve pain, is sometimes used to relieve severe pain caused by knee osteoarthritis (OA). Osteoarthritis, also known, as wear-and-tear arthritis, can often become so severe that joint replacement surgery is needed. Using gabapentin The following keywords including pain management, postoperative pain, total knee arthroplasties, total knee replacement, and gabapentin were used for searching. 1. Inclusion criteria. Studies were considered eligible for inclusion if they met the following criteria: Study design: Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) with placebo report in English. Neuroactive Medications Another type of medicine used as part of a multimodal pain regimen after hip replacement are medicines that target nerve pain – namely gabapentin (Neurontin) or pregabalin (Lyrica). Using these medications decreases the amount of opioids required after hip replacement. Abstract Total Hip replacement (THR) is a well-discussed topic, and it offers excellent results in patients suffering from end-stage osteoarthritis (OA). However, despite the fact that patients can fully bear weight immediately after the surgery, THR is often associated with a great amount of postoperative pain affecting recovery and rehabilitation. Therefore, the efficient management of pain Background: Postoperative pain after total knee arthroplasty (TKA) and total hip arthroplasty (THA) influence patients' rehabilitation and life quality. Although gabapentin has been widely used for analgesia, its efficacy is still controversial in TKA and THA. This meta-analysis was performed to assess the efficacy and safety of gabapentin following TKA and THA. Method: Electronic databases What is Gabapentin and how does it work for hip pain? Gabapentin is a medication that is commonly prescribed for the treatment of nerve pain. It is known to be effective in relieving pain caused by conditions such as shingles, diabetic neuropathy, and post-herpetic neuralgia. However, it can also be used to alleviate hip pain caused by various conditions, including hip osteoarthritis, hip Therefore, the management of pain after total joint arthroplasty has substantial benefits for the patient to achieve early functional recovery. In recent decades, multimodal analgesia techniques including gabapentin have generally been used for pain control in order to reduce the side effects of morphine such as sedation, nausea, and vomiting [7]. Abstract Gabapentin is routinely used in preoperative multimodal anesthesia to reduce pain following total joint arthroplasty (TJA) surgery. Evolving evidence has shown it is ineffective in reducing postoperative pain and should be used cautiously in this patient population due to its adverse effects. Gabapentin may be prescribed either before or after surgery to help with postsurgical pain. However, it should be used with caution due to the high risk of abuse. Background Postoperative pain after total knee arthroplasty (TKA) and total hip arthroplasty (THA) influence patients’ rehabilitation and life quality. Although gabapentin has been widely used for analgesia, its efficacy is still controversial in TKA and THA. This meta-analysis was performed to assess the efficacy and safety of gabapentin following TKA and THA. Method Electronic databases Learn about the use of gabapentin as a potential treatment option after hip replacement surgery and its effectiveness in managing pain and improving recovery. Hip pain can be debilitating, making everyday activities like walking or sitting incredibly painful. If you're suffering from hip pain and looking for relief, you may have heard about gabapentin. Gabapentin is a medication commonly used to treat nerve pain, but can it also help with hip pain? In this article, we will explore the potential benefits of gabapentin for hip pain and whether it is a Abstract Background: Pain management after total hip arthroplasty (THA) varies and has been widely studied in recent years. Gabapentin as a third-generation antiepileptic drug that selectively affects the nociceptive process has been used for pain relief after THA. This meta-analysis was conducted to examine the efficacy of gabapentin in THA. Gabapentin is routinely used in preoperative multimodal anesthesia to reduce pain following total joint arthroplasty (TJA) surgery. Evolving evidence has shown it is ineffective in reducing postoperative pain and should be used cautiously in this patient population due to its adverse effects. The pu Gabapentinoids in Total Joint Arthroplasty: The Clinical Practice Guidelines of the American Association of Hip and Knee Surgeons, American Society of Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine, American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, Hip Society, and Knee Gabapentin, a drug traditionally used for the relief of neuropathic pain, was compared in variable doses to placebo in relieving postoperative pain. Gabapentin resulted in less total patient-controlled analgesia (PCA) morphine use over 48 hours postoperatively (P <0.05), better active knee flexion on postoperative days (PODs) 2 and 3 (P <0.05 for both), and less pruritus (P <0.05) than placebo The following medical subject heading terms, keywords, and their combinations were used: “pain management, postoperative pain, total hip arthroplasties, total hip replacement, and gabapentin”. The search was limited to randomised controlled trials (RCTs) in humans and published in English up to December 2015. We did not identify statistically significant or clinically meaningful differences in our primary and secondary outcomes related to perioperative use of gabapentin enacarbil in patients having primary hip or knee arthroplasties. Background Pain management after total hip arthroplasty (THA) varies and has been widely studied in recent years. Gabapentin as a third-generation antiepileptic drug that selectively affects the nociceptive process has been used for pain relief after THA. This meta-analysis was conducted to examine the efficacy of gabapentin in THA. Methods An electronic-based search was conducted using the The shift towards multimodal pain regimens, including gabapentin, has taken place without attention to ensuring that they, like opioids, are appropriately discontinued soon after surgery. The prevalence of prolonged use of post-operative gabapentin among older adults is unknown, as are the factors associated with prolonged use.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |