Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
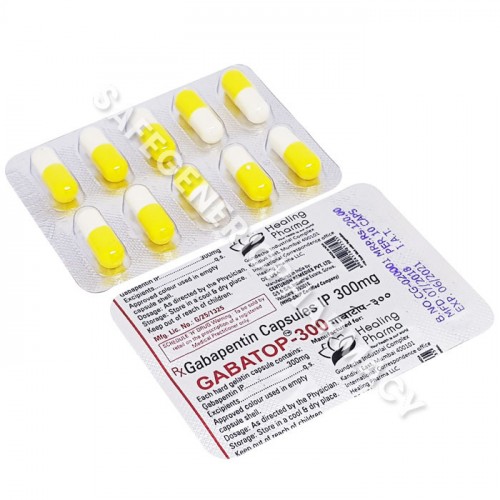 |  |
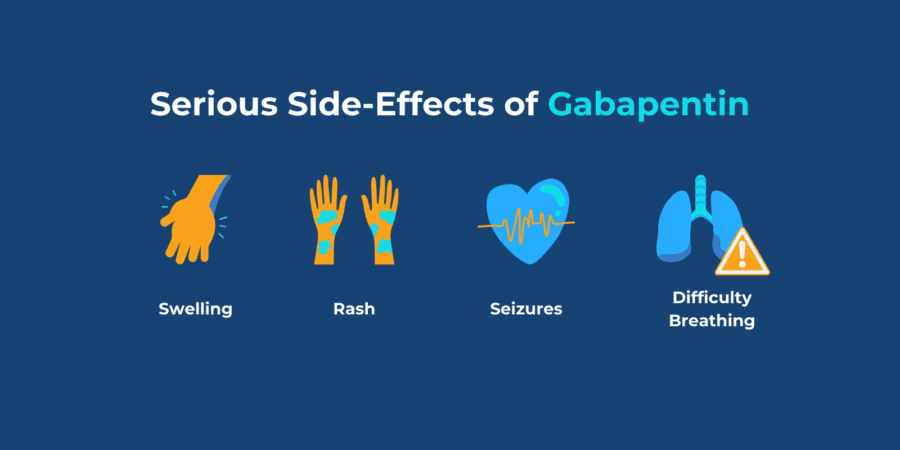
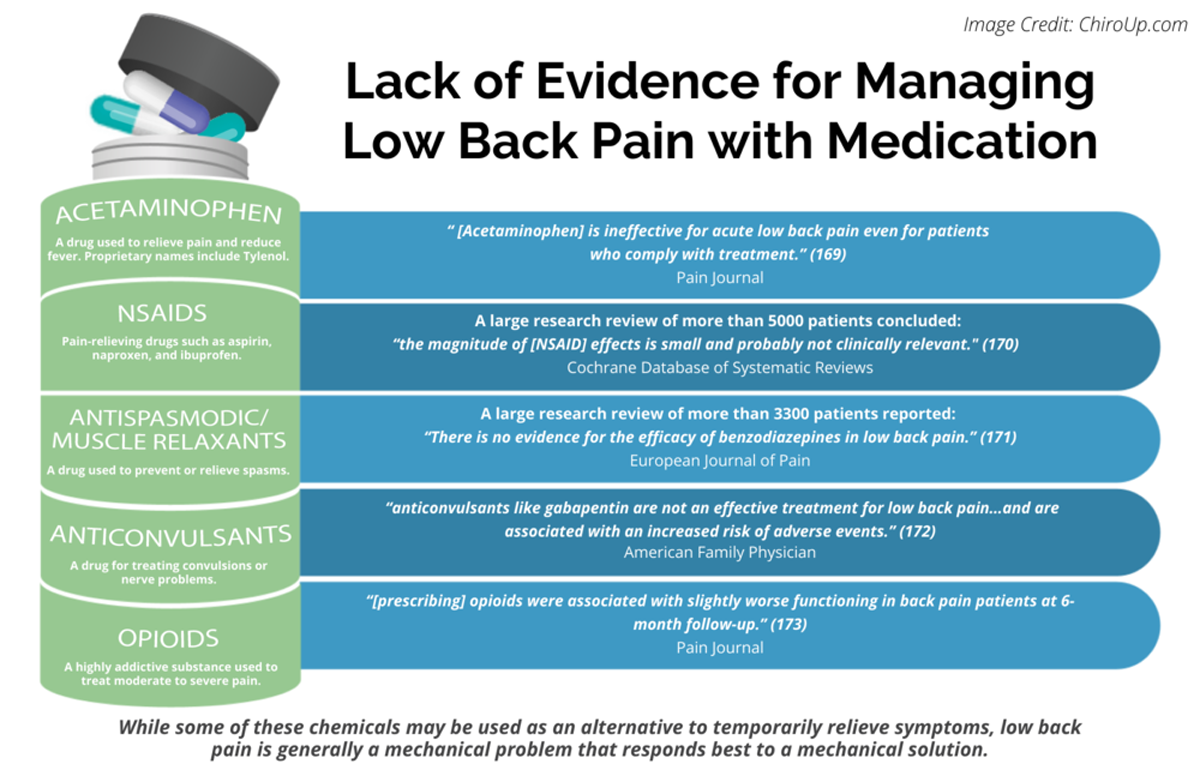
Low back pain is pain in the lumbosacral area of the back. It can be described as non-specific, mechanical, musculoskeletal, or simple (if it is not associated with serious or potentially serious causes). Episodes of back pain do not usually last long, with rapid improvements in pain and disability seen within a few weeks to months. Sciatica (radicular pain or radiculopathy) is neuropathic leg Gabapentin is also effective for the treatment of neuropathic pain. Neuropathic pain may respond to opioid analgesics. There is evidence of efficacy for tramadol hydrochloride, morphine, and oxycodone hydrochloride; however, treatment with morphine or oxycodone hydrochloride should be initiated only under specialist supervision. Dose and use Gabapentin should be given at least 2h after antacids containing aluminium or magnesium. For both neuropathic pain and epilepsy, a rapid upward titration is suggested in the SPC (Table 1). However, in order to reduce undesirable effects, a slower titration of the initial dose of gabapentin over several weeks is advisable in elderly patients, those with renal impairment (see below Why have I been prescribed this? Gabapentin is used to help reduce pain. It is especially good for nerve pain, such as burning, shooting, stabbing, pins and needles, crawling, electric shock like pain Gabapentin belongs to a group of medicines called anticonvulsants and can also be used to treat epilepsy Pregabalin is another pain medication that works in a similar way to Gabapentin, they SIGN 136 recommends amitriptyline or gabapentin as first line medicine in neuropathic pain, dependent on clinical preference and patient factors (including the risks below). Keywords: Gabapentin, pregabalin, pain management, adverse effects, pharmacology Introduction The gabapentinoid drugs gabapentin and pregabalin are antiepileptic drugs that are considered as first-line treatments for the management of neuropathic pain. 1 Pregabalin is also approved for generalised anxiety disorders in the United Kingdom. View amitriptyline hydrochloride information, including dose, uses, side-effects, pregnancy, breast feeding and contra-indications. Gabapentin and pregabalin should usually be prescribed for their licensed indications (epilepsy and neuropathic pain), and generalised anxiety disorder (only pregabalin). Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication used in the management of peripheral neuropathic pains, postherpetic neuralgia, and partial-onset seizures. Gabapentin is an anti-epileptic drug, also called an anticonvulsant. It is used to treat some types of seizures and nerve pain caused by shingles. Results from studies where gabapentin has been used to treat nerve pain (in diabetic neuropathy and post-herpetic neuralgia) indicate that the drug is normally well tolerated. You can discuss your pain medication with your doctor, pharmacist or pain specialist. They can give you - • Advice on which pain medicines may help. • Help you find the best way to take your medicines. • Advise you on increasing your dose safely if your pain is worse and on taking less medication safely when your pain is more settled. 714FM.3 MANAGEMENT OF NEUROPATHIC PAIN IN ADULTS This guideline covers the treatment of neuropathic pain in adults in primary and secondary care. Paediatric patients with neuropathic pain should be referred to secondary care for Specialist advice. Gabapentin and Pregabalin prescribing for neuropathic pain. Prescribing in patients aged 65 years or over. Gabapentin and Pregabalin prescribing for neuropathic pain. Prescribing in patients aged 65 years or over. View pregabalin information, including dose, uses, side-effects, renal impairment, pregnancy, breast feeding, monitoring requirements and important safety information. Detailed Gabapentin dosage information for adults and children. Includes dosages for Restless Legs Syndrome, Epilepsy and Postherpetic Neuralgia; plus renal, liver and dialysis adjustments. Gabapentin is a medicine which may help improve your nerve pain, such as shooting, stabbing, or burning pain. Gabapentin works by changing the way that nerves send messages to your brain. If the messages are reduced, then the pain will be reduced. Gabapentin is also used to treat epilepsy and anxiety, but you are taking it for pain. Gabapentin is licensed for the treatment of peripheral neuropathic pain such as painful diabetic neuropathy and postherpetic neuralgia in adults [ABPI, 2020a]. However, the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) recommends gabapentin as a first-line treatment option for adults with all neuropathic pain (except trigeminal neuralgia) [NICE, 2019a]. View gabapentin information, including dose, uses, side-effects, renal impairment, pregnancy, breast feeding, monitoring requirements and important safety information. View gabapentin information, including dose, uses, side-effects, renal impairment, pregnancy, breast feeding, monitoring requirements and important safety information.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |