Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 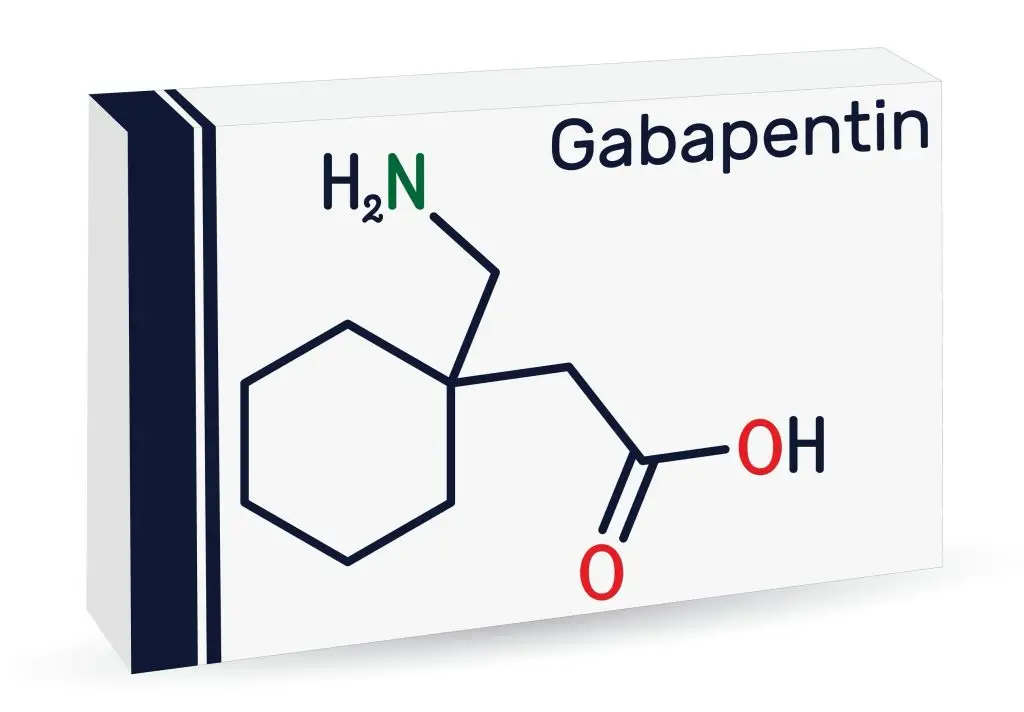 |
Read on to learn more about which sciatic medications may help to alleviate nerve pain, including medications like Lyrica and gabapentin. Sciatica is a symptom rather than a specific diagnosis 4 and is used broadly to refer to pain that radiates along the path of the sciatic nerve. 5 The commonest cause of sciatica is impingement of lumbosacral nerve roots, as they emerge from the spinal canal, by a herniated intervertebral disc (fig 1). For a person with sciatica, see the CKS topic on Sciatica (lumbar radiculopathy). Offer a choice of amitriptyline, duloxetine, gabapentin, or pregabalin. Titrate the dosage according to response and tolerability. Gabapentin is a drug used to treat nerve pain. This type of pain is often not relieved by normal painkillers. It can be used in combination with other painkillers to improve your pain relief. How does gabapentin work? Gabapentin works by changing the way in which nerves send messages to your brain. Gabapentin is a medicine which may help improve your nerve pain, such as shooting, stabbing, or burning pain. Gabapentin works by changing the way that nerves send messages to your brain. If the messages are reduced, then the pain will be reduced. Gabapentin is also used to treat epilepsy and anxiety, but you are taking it for pain. NICE clinical guidelines advise the NHS on caring for people with specific conditions or diseases and the treatments they should receive. The information applies to people using the NHS in England and Wales. Gabapentin is used to treat epilepsy. It's also taken for nerve pain, which can be caused by different conditions, including diabetes and shingles. Nerve pain can also happen after an injury. In epilepsy, it's thought that gabapentin stops seizures by reducing the abnormal electrical activity in the brain. Prescribing Gabapentinoids for chronic pain Gabapentin and Pregabalin are not suitable for treating long-term low back pain4 unless the pain is of neuropathic character. Some lower back pain is made up of a combination of musculoskeletal and neuropathic symptoms so gabapentin or pregabalin can be used as initial treatment options in these cases. To achieve substantial benefit in post-herpetic The typical starting dose of gabapentin for sciatic nerve pain for most patients is 300mg once a day. Your physician may increase the dosage up to three times a day. Sciatica literally means your sciatic nerve is inflamed. As a result if you are able to take anti-inflammatory medications such as Naproxen or Diclofenac these may be helpful. However, these can cause heartburn or stomach problems; if you experience these, please consult your GP. Exercise programmes, manual therapy (spinal manipulation, mobilisation, or soft-tissue techniques such as massage), and psychological therapies should be considered for managing low back pain with or without sciatica. Spinal decompression may be considered in patients with sciatica when pain and function has not improved with non-surgical treatment (including drug treatment). 714FM.3 MANAGEMENT OF NEUROPATHIC PAIN IN ADULTS This guideline covers the treatment of neuropathic pain in adults in primary and secondary care. Paediatric patients with neuropathic pain should be referred to secondary care for Specialist advice. Gabapentin — rare risk of severe respiratory depression even without concomitant opioid medicines (ref: MHRA Oct17). Patients at higher risk are those with compromised respiratory function, respiratory or neurological disease, renal impairment, concomitant use of central nervous system (CNS) depressants, and elderly people. Gabapentin is used to treat some types of persistent pain. It is especially good for nerve pain, such as burning, shooting or stabbing pain. Gabapentin belongs to a group of medicines called anticonvulsants which are also used to treat epilepsy. Gabapentin works by changing the way that nerves send messages to your brain. Low back pain is pain in the lumbosacral area of the back, between the bottom of the ribs and the top of the legs. Up to 60% of the adult population can expect to have low back pain at some time in their life. Examples of specific causes of low back pain include sciatica, intra-abdominal pathology, or ankylosing spondylitis. Non-specific low back pain refers to when the pain cannot be NHS medicines information on dosage for gabapentin, how to take it and what to do if you miss a dose or take too much. Is Gabapentin Good For Sciatica Pain? Gabapentin has earlier shown potential in providing relief for chronic sciatica; however, recent studies indicate its ineffectiveness in reducing pain and disability associated with low back pain and sciatica. Gabapentin and pregabalin should usually be prescribed for their licensed indications (epilepsy and neuropathic pain), and generalised anxiety disorder (only pregabalin). Read about how gabapentin treats epilepsy and nerve pain and how to take it. NHS medicines information on gabapentin – what it's used for, side effects, dosage, and who can take it. The evidence showed that gabapentinoids did not improve sciatica symptoms, and oral corticosteroids did not improve pain or function, but may have an impact on quality of life. Both increased the risk of adverse events in the long-term.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |