Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
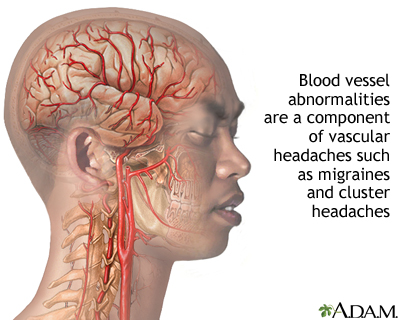
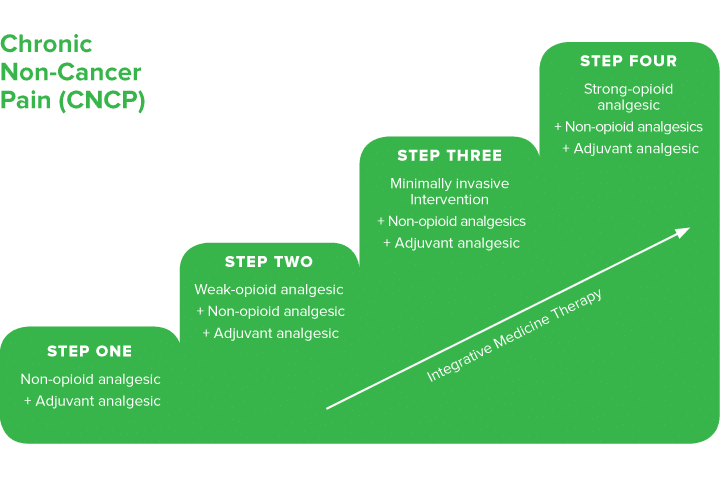
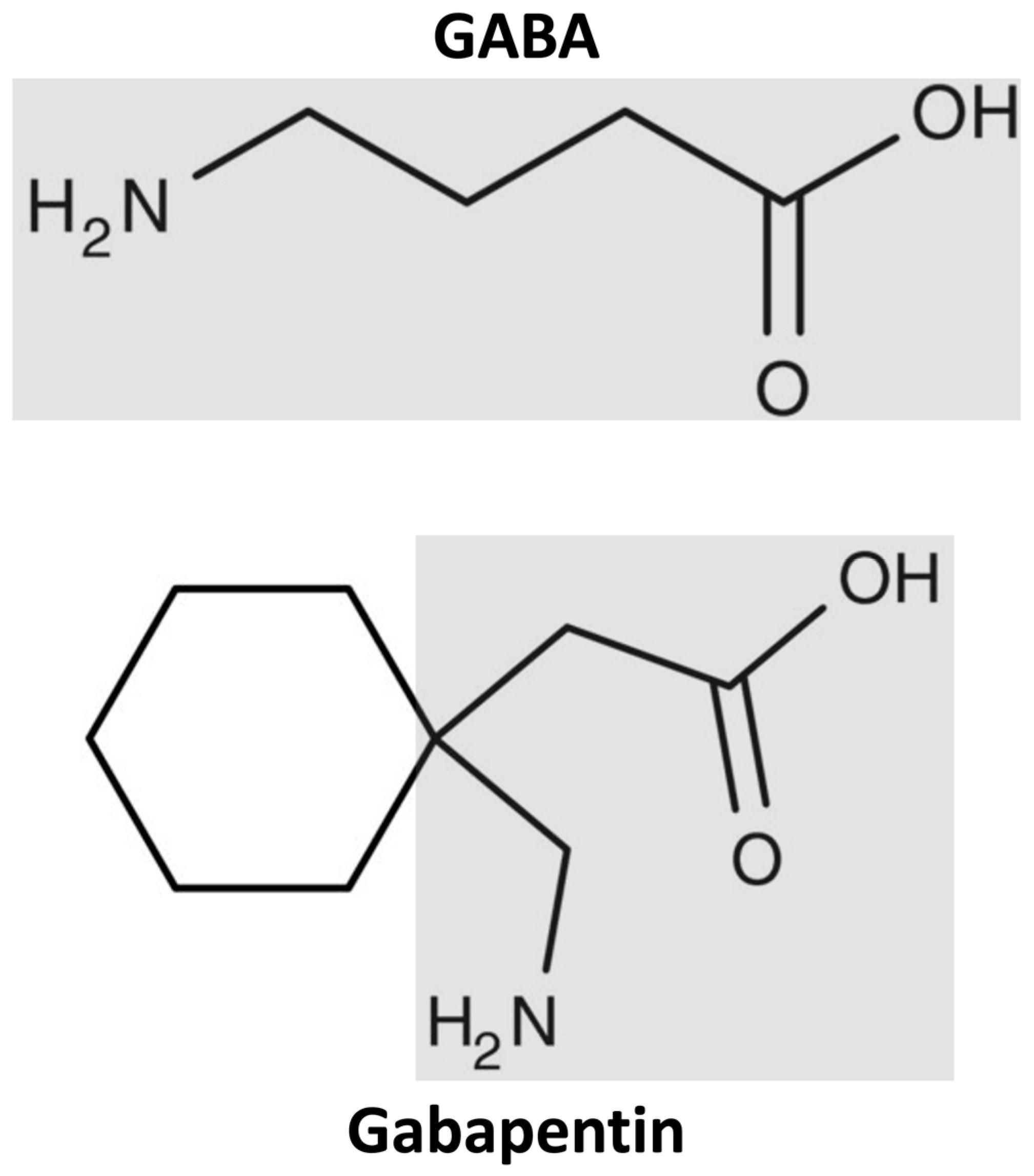
Gabapentin for Adults With Neuropathic Pain: A Review Key Messages Overall, evidence suggests that there is a greater reduction in neuropathic pain (NP) with gabapentin compared with placebo in adults who have a variety of conditions, including diabetic peripheral neuropathy and postherpetic neuralgia. Background: Gabapentin and pregabalin are commonly prescribed medications to treat pain in patients with dia-betic neuropathy. Gabapentin and pregabalin can cause fluid retention, which is hypothesized to be associated with cardiovascular diseases. However, whether long-term use of gabapentin and pregabalin is associated with adverse cardiovascular diseases remains unknown. This study aims to Flow chart showing the management of persons with peripheral arterial disease. Conclusion There is good evidence to support therapy to reduce vascular risk factors in patients with peripheral vascular disease. The mainstay of medical therapy for all patients should include lipid lowering, blood pressure control, and an antiplatelet agent. In patients with rest pain, analgesic drugs are Gabapentin is often used as a neuropathic analgesic for diabetes-related lower extremity paresthesia 12 as well as for phantom limb pain and complex regional pain syndrome in patients with severe PAD. 13 Additionally, they are widely prescribed off-label in the management of many other conditions due to their efficacy in pain management. Pain management is an important adjunct in treating peripheral artery disease (PAD), and may help prevent or limit extent of limb loss by facilitating mobilisation and exercise therapy. Pain relief is also important for symptom palliation when surgical revascularisation is not possible or surgery has not relieved pain adequately. These studies researched the use of intravenous lidocaine, intravenous ketamine, oral gabapentin and the combination of transdermal buprenorphine and epidural morphine/ropivacaine infusion. All studies showed an improvement in severity of ischaemic pain in CLI but with varying side effect profiles and quality. Pain associated with severe vascular disease can be the result of a combination of nociceptive, inflammatory, and neuropathic mechanisms. Cross-talk between sensory neurones and the sympathetic nervous system (sympathetic–afferent coupling) may contribute to the pain of vascular disease. There is no clear evidence that the choice of intraoperative or postoperative analgesic technique in Background Gabapentin and pregabalin are commonly prescribed medications to treat pain in patients with diabetic neuropathy. Gabapentin and pregabalin can cause fluid retention, which is hypothesized to be associated with cardiovascular diseases. However, whether long-term use of gabapentin and pregabalin is associated with adverse cardiovascular diseases remains unknown. This study aims to Pain in chronic venous insufficiency is a common complication. Although lifestyle modification remains the foundation of treatment for pain associated with chronic venous sufficiency, compression devices, various pharmacologic agents, and minimally invasive vascular procedures have emerged as safe and effective treatments for pain in these Subsequently, it was approved by the FDA for treating fibromyalgia (2007) and spinal cord injury-related pain (2012) (Goodman and Brett, 2019). Gabapentin enacarbil with extended-release pharmacokinetics is a pro-drug of gabapentin that was approved by the FDA in 2011 for the treatment of restless legs syndrome in adults (Kim and Deeks, 2016). Conclusion: In patients with diabetic neuropathy who were prescribed gabapentin and pregabalin, there is an increased risk for heart failure, myocardial infarction, peripheral vascular disease, stroke, deep venous thrombosis, and pulmonary embolism with long-term use. Our findings suggest that increased risk for adverse cardiovascular events, along with other side effects, the efficacy of pain Gabapentin is a medication primarily used for nerve pain and seizures, but its effectiveness in treating peripheral vascular disease (PVD/PAD) is unclear. While some individuals may report trying gabapentin for PVD/PAD, the data suggests it is not a highly effective treatment option. Gabapentin and pregabalin are commonly prescribed medications to treat pain in patients with diabetic neuropathy. Gabapentin and pregabalin can cause fluid retention, which is hypothesized to be associated with cardiovascular diseases. Gabapentin is often prescribed to stroke patients to alleviate post-stroke pain and improve recovery. Learn about its benefits, dosage guidelines, and potential side effects. Gabapentin may help if there is a burning or neuropathic component to the pain (7). Renal dosing is often needed given the high incidence of concomitant kidney disease (see Fast Fact #49). Differences in Pain Management of Peripheral Vascular Disease and Peripheral Artery Disease When diagnosing peripheral artery disease, a common condition in people with diabetes, leg pain may arise from intermittent claudication and ischemia. The study has demonstrated that gabapentin is a useful adjuvant in the management of CLI and leads to significant reductions in pain scores and improves night pain for most patients. Licensed to: UpToDate Marketing Professional Support Tag : [1103 - 40.77.190.172 - 735D1958AA - PR14 - UPT - NP - 20250603-02:06:13UTC] - LG Gabapentin and pregabalin are common treatments to manage fibromyalgia-related pain. Our recent study showed the risk of adverse cardiovascular events increased in diabetic neuropathy patients who were prescribed gabapentin or pregabalin. An observational pilot study was performed on 20 consecutive patients with CLI who were taking all experiencing rest pain despite high dose opiate analgesia. None of the patients were candidates for reconstructive surgery or angioplasty due to the anatomical distribution of their vascular disease or presence of co-morbidities. Gabapentin was commenced at 300 mg daily and titrated to 300 mg tds
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |