Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 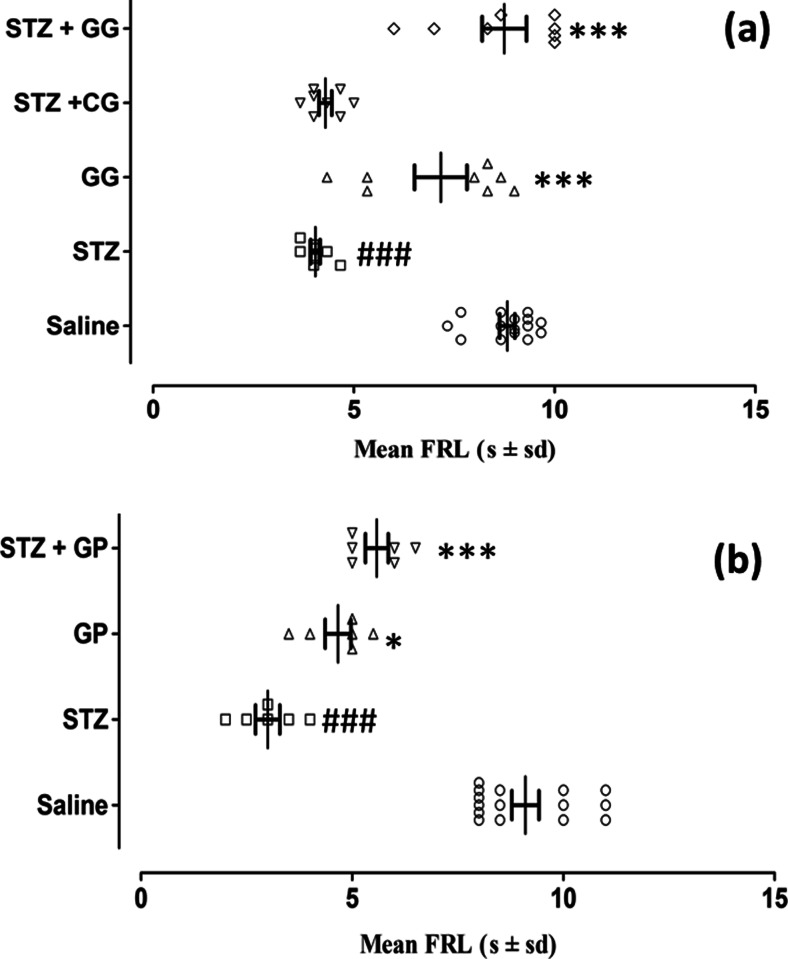 |
Gabapentin (Neurontin), though FDA approved for the treatment of the neuropathic pain of post-herpetic neuralgia, has not been studied in localized provoked vulvodynia, but is used for treatment and considered helpful. Vaginal pain, known as vulvodynia, is common in CFS and Fibromyalgia. Though it often improves over time by addressing with the overall "SHINE Protocol," medication is helpful for symptomatic relief. We begin by adding Neurontin and Elavil for sleep in those with Vulvodynia, but these sometimes cause unacceptable side effects. This new study showed that putting the Neurontin (Gabapentin) in a Vulvodynia is a leading cause of dyspareunia in premenopausal women, causing considerable morbidity and sexual dysfunction. A multimodal approach is used to treat vulvodynia. Alongside psychosocial interventions and physiotherapy, pharmacological treatment such as oral gabapentin are used in the treatment of vulvodynia. The essential guide to gabapentin for vulvodynia - discover all the essential information about one of the most popular medical vulvodynia treatment options, including usage, dosage, best practices, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and warnings. Vulvodynia is a debilitating condition characterized by chronic vulvar pain, with a detrimental impact on the patient's overall quality of life. Its etiology is multifactorial, but still in the process of being clearly outlined. Anticonvulsants. Gabapentin (Neurontin; Pfizer, New York, NY) and carbamazepine (Tegretol; Novartis Cor-poration Pharmaceuticals) have been used to treat vulvodynia [8, 9]. Gabapentin is begun at a dose of 300 mg orally for 3 days, then gradually is increased to a maximum of 3,600 mg total daily dosage. See Table 2 for specific dosing instructions. Gabapentin, used to manage neuropathic pain disorders, is the most studied and used anticonvulsant for vulvodynia 4. Dosage can be increased over time from 300 mg total daily to a maximum dose of 3,600 mg daily (1,200 mg by mouth three times a day), and may need adjustment to avoid adverse effects. Abstract Vulvodynia is a leading cause of dyspareunia in premenopausal women, causing considerable morbidity and sexual dysfunction. A multimodal approach is used to treat vulvodynia. Alongside psychosocial interventions and physiotherapy, pharmacological treatment such as oral gabapentin are used in the treatment of vulvodynia. Topical formulations of gabapentin have shown promise in animal Vulvodynia is a leading cause of dyspareunia in premenopausal women, causing considerable morbidity and sexual dysfunction. A multimodal approach is used to treat vulvodynia. Alongside psychosocial interventions and physiotherapy, pharmacological treatment such as oral gabapentin are used in the tre Antiepileptics treat vulvodynia by calming the central nervous system and are used to treat neuropathic pain conditions. 89 , 90 In a multicenter double‐blind crossover RCT, oral gabapentin did not reduce dyspareunia. 90 There is no evidence to support the use of oral gabapentin for vulvodynia. Background: Vulvodynia is defined in this international consensus as persistent vulvar pain that occurs for >3 months without an identifiable cause and with several potential associated factors. At present there is no univocal consensus in the Reviews and ratings for Gabapentin when used in the treatment of vulvodynia. 10 reviews submitted with a 6.6 average score. For treating vulvodynia, gabapentin works by inhibiting pain signals that are sent from damaged neurons. The retrospective study that was published in Obstetrics and Gynecology showed that gabapentin cream was well tolerated and effective for women experiencing vulvodynia. Although gabapentin is recommended and commonly prescribed for vulvodynia, its value in such cases is usually associated with complaints that have neuropathic components, such as dynamic allodynia. Your visit / Patient information leaflets Gabapentin for the treatment of vulvodynia This page gives you information about the medication gabapentin which you have been prescribed to reduce the pain of vulvodynia. Vulvodynia is pain in the vulva (area around the outside of the vagina) that lasts at least 3 months and does not have a specific cause. To evaluate whether extended-release gabapentin is more effective than placebo among women with vulvodynia. In a multicenter double-blind, placebo-controlled randomized crossover trial, gabapentin (1200 – 3000 mg/day) was compared to placebo. The Twenty-five trials explored the use of oral and topical medications in the treatment of vulvodynia. Data Synthesis: Vulvodynia is a poorly understood disease with an unknown etiology. Oral tricyclic antidepressants and gabapentin continue to be the most commonly used treatments for vulvodynia pain. III.Methods: A retrospective study was designed to ascertain clinical responses to topical gabapentin. Patient demographic and medical characteristics, including present and prior treatment for vulvodynia, were routinely collected. The final outcome was defined by a comparison between pretreatment and posttreatment mean pain scores based on a discrete visual analog scale of 0 to 10 Abstract Objective: To evaluate whether extended-release gabapentin is more effective than placebo among women with vulvodynia. Methods: In a multicenter double-blind, placebo-controlled randomized crossover trial, gabapentin (1,200-3,000 mg/d) was compared with a placebo. The diagnosis of vulvodynia is made after taking a careful history, ruling out infectious or dermatologic abnormalities, and eliciting pain in response to light pressure on the labia, introitus
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |