Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
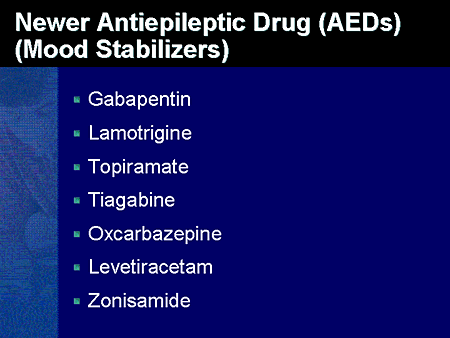 |
Gabapentin - Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant drug commonly used as adjunctive therapy to treat partial seizures. Therapeutic drug monitoring is useful to optimize dose and to avoid toxicity. Methods: Seventeen healthy adults were randomly assigned to receive topiramate, gabapentin, and lamotrigine and underwent GABA measurements using a 4.1-T magnet from a 13.5-mL volume over the occipital region. GABA concentrations and serum levels were measured at 3 and 6 hours following administration of an acute single dose of one of the drugs. Gabapentin is an antiepileptic drug that is effective in treating seizures, neuropathies, and a variety of neurological and psychological maladies. Although designed as a gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) analogue, gabapentin does not bind to GABA receptors, nor does it affect the neuronal uptake or degradation of GABA. Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and glutamate are implicated in numerous neuropsychiatric and substance abuse conditions, but their spectral overlap with other resonances makes them a challenge to quantify in humans. Gabapentin, marketed for the treatment of seizures and neuropathic pain, has been sh Gabapentin is a prescription medication known as a gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) analogue. GABA reduces the excitability of nerve cells (neurons) in the brain, which play a role in seizures and the transmission of pain signals. Gabapentin (Neurontin®) is an oral antiepileptic agent that is structurally related to the neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) but it does not interact with GABA receptors in the brain. Its mechanism of action is unknown but it has properties in common with other anticonvulsant medications. Gabapentin is only 3% bound to circulating protein in the blood and is not appreciably Several drugs have been developed which have notable effects in increasing GABA levels, one of which is Gabapentin (1- (aminomethyl)cyclohexaneacetic acid [Neurontin®]) (GBP). GBP is a widely prescribed drug, typically used to treat conditions such as epilepsy and neuralgia, and was originally synthesised as an analogue of GABA. Although the mechanism of gabapentin therapeutic action is unclear, human subjects studies suggest that its administration leads to an overall increase in central GABA levels. Pearson’s correlation analysis was performed to examine the relationship between change in GABA concentration with gabapentin administration and baseline GABA levels. Treatment of mice with gabapentin did not increase GABA, taurine, or alanine levels, or neurosteroids in the brain. They further demonstrated the physiological significance of these alterations in a behavioral assay for motor incoordination and anxiety behavior. Again, it would be pretty rare to have blood levels drawn. Gabapentin is usually started low and titrated up to an effective dose. Below is the most common dosage for neuropathy: Initiate therapy at 300 mg PO as a single dose on day 1, then 600 mg/day (300 mg PO twice daily) on day 2, and 900 mg/day (300 mg PO three times per day) on day 3. In general, it seems that gabapentin has risks of being misused based on the increased level of prescriptions, related fatalities, recreational misuse and higher doses of self-administration. The main reasons for gabapentin misuse are as follows: getting high, alleviating opioid withdrawal symptoms and potentiating methadone effects. GABA was elevated in patients taking gabapentin compared with 14 complex partial epilepsy patients, matched for antiepileptic drug treatment. Brain GABA levels appeared to be higher in patients taking high-dose gabapentin (3,300-3,600 mg/day) than in those taking standard doses (1,200-2,400 mg/day). Gabapentin, marketed for the treatment of seizures and neuropathic pain, has been shown to increase in vivo GABA concentration in the brain of both rodents and humans. Gabapentin is a structural analog of the inhibitory neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Its anticonvulsant, analgesic and anxiolytic properties suggest that it increases GABAergic inhibition; however, the molecular basis for these effects Gabapentin enhanced expression of δGABA A receptors and increased a tonic inhibitory conductance in neurons. This increased expression likely contributes to GABAergic effects as gabapentin caused ataxia and anxiolysis in wild-type mice but not δ subunit null-mutant mice. In contrast, the antinociceptive properties of gabapentin were observed in both genotypes. Levels of GABA A receptor Gabapentin, therefore, introduces GABA-like changes into the brain, diminishing abnormal activity, and giving the patient more mood regulation and protection from seizures. For these reasons, gabapentin has been approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of epileptic seizures and neuropathic pain. Gabapentin is an antiepileptic drug effective as add-on therapy in treating complex partial seizures and partial seizures with secondary generalization. Gabapentin does not bind to serum proteins and does not exhibit pharmacokinetic interactions with other antiepileptic drugs. Gabapentin is a structural analog of the inhibitory neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Its anticonvulsant, analgesic and anxiolytic properties suggest that it increases GABAergic inhibition; however, the molecular basis for these effects is unknown as gabapentin does not directly modify GABA type A (GABAA) receptor function, nor does it modify synaptic inhibition. Here, we Gabapentin in the treatment of anxiety and depression: Gabapentin is sometimes prescribed off-label for patients with bipolar disorder to reduce anxiety levels or for anxiety disorders.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |