Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
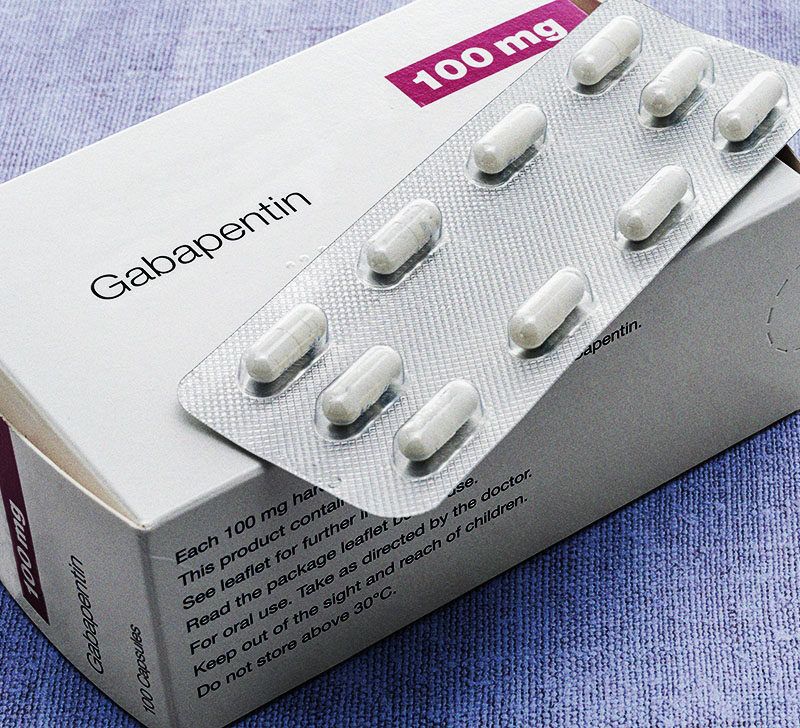
The liver is responsible for the selective uptake, concentration, metabolism, and excretion of most drugs. Both prescription and over-the-counter medications can cause hepatotoxicity through a variety of mechanisms. Measures such as drug dose adjustment can help prevent adverse drug reactions (eg, acute kidney injury) in patients with cirrhosis. Gabapentin is a unique anticonvulsant that is used as adjunctive therapy in management of epilepsy and for neuropathic pain syndromes. Therapy with gabapentin is not associated with serum aminotransferase elevations, but several cases of clinically apparent liver injury from gabapentin have been reported. This class, which includes gabapentin and pregabalin, is not metabolized by the liver. Therefore, risks in patients with advanced liver disease are not greatly increased. However, there are case reports of pregabalin‐induced hepatoxicity. 4 Gabapentin and pregabalin are renally excreted, so dosages need to be adjusted for renal failure. Detailed Gabapentin dosage information for adults and children. Includes dosages for Restless Legs Syndrome, Epilepsy and Postherpetic Neuralgia; plus renal, liver and dialysis adjustments. View gabapentin information, including dose, uses, side-effects, renal impairment, pregnancy, breast feeding, monitoring requirements and important safety information. Gabapentin should be used with extreme caution in patients with pre-existing liver disease, and dosage adjustments may be necessary. Regular monitoring of liver function is essential. Find medical information for gabapentin on epocrates online, including its dosing, contraindications, drug interactions, and pill pictures. DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION SECTION Gabapentin capsules are given orally with or without food. Gabapentin capsules should be swallowed whole with plenty of water. If gabapentin dose is reduced, discontinued, or substituted with an alternative medication, this should be done gradually over a minimum of 1 week (a longer period may be needed at the discretion of the prescriber). 2.1 Postherpetic DESCRIPTION Neurontin® (gabapentin) Capsules, Neurontin (gabapentin) Tablets, and Neurontin (gabapentin) Oral Solution are supplied as imprinted hard shell capsules containing 100 mg, 300 mg, and 400 mg of gabapentin, elliptical film-coated tablets containing 600 mg and 800 mg of gabapentin or an oral solution containing 250 mg/5 mL of gabapentin. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy. Hepatic Impairment Because gabapentin is not metabolized, studies have not been conducted in patients with hepatic impairment. Renal Impairment Dosage adjustment of GRALISE is necessary in patients with impaired renal function. GRALISE should not be administered in patients with creatinine clearance <30 mL/min or in patients undergoing Gabapentin is eliminated through the kidneys and, therefore, doesn’t typically cause liver injury. Learn safe dosage recommendations for people with liver disease. Gabapentin-Induced Liver ToxicityAm J Ther. 2022 Nov-Dec;29 (6):e751-e752. doi: 10.1097/MJT.0000000000001208. Epub 2020 Jun 5. DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION 4.1 Dosing Considerations Because GABAPENTIN is eliminated solely by renal excretion, dosage adjustments are recommended for patients with renal impairment (including elderly patients with declining renal function) and patients undergoing hemodialysis. Medical information for Gabapentin on Pediatric Oncall including Mechanism, Indication, Contraindications, Dosing, Adverse Effect, Interaction, Renal Dose, Hepatic Dose. Gabapentin package insert / prescribing information for healthcare professionals. Includes: indications, dosage, adverse reactions and pharmacology. Max dosage 3600mg if patient already on gabapentin Taper dose > 7 days to discontinue [1] Pediatric Dosing Partial seizures Adjunct for partial seizures with out secondary generalization in patients> 12yo with epilepsy; also adjunctive therapy for partial seizures in patients 3-12 years <3 years: Safety and efficacy not established Opioids should be used cautiously and initiated with immediate-release products at low doses with extended intervals and close monitoring. All pain medications should be titrated carefully to achieve safe and adequate pain relief in patients with hepatic impairment. Cirrhosis is defined as permanent liver fibrosis secondary to damage or injury. Medscape - Seizure dosing for Neurontin, Gralise (gabapentin), frequency-based adverse effects, comprehensive interactions, contraindications, pregnancy & lactation schedules, and cost information. Gabapentin doesn’t hurt the liver or kidneys in most cases. However, taking a safe gabapentin dose is important to prevent potential side effects.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |