Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 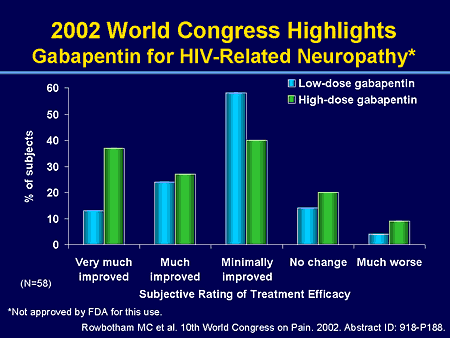 |
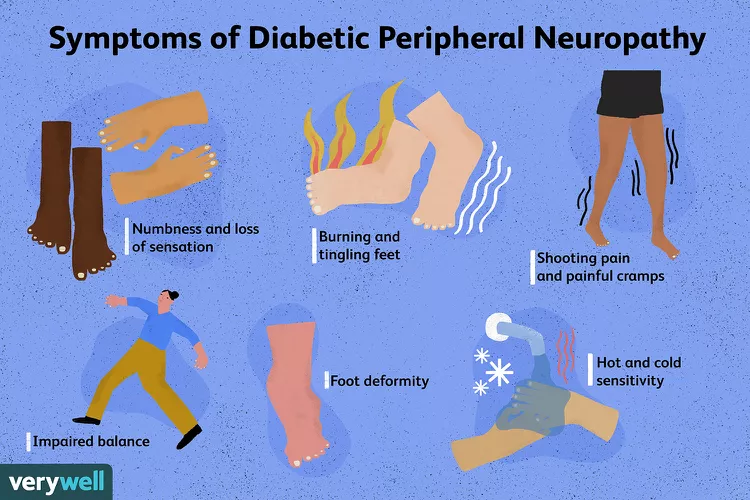
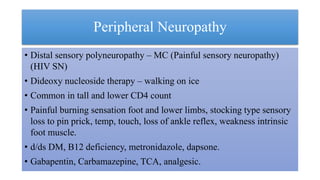
Neuropathic pain can be severe and debilitating and results when there is damage to or dysfunction of the central or peripheral nervous system.1 Sensory neuropathy is a complication of HIV infection, affecting up to 40% of HIV-infected individuals.2 In 2014, the Public Health Agency of Canada estimated that approximately 75,000 Canadians were living with HIV (including AIDS), with 2,000 to The objective of this study was to assess the efficacy and safety of Gabapentin as the sole analgesic in patients with HIV-related painful neuropathy. Nineteen patients with HIV-related painful neuropathy were administered Gabapentin. Efficacy was evaluated with two 100-mm Visual Analogue Scales (VA INTRODUCTION Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection is associated with various peripheral nervous system manifestations, the most common of which is distal symmetric polyneuropathy (DSPN) [1]. Peripheral polyneuropathy should be distinguished from other forms of neuropathy, such as mononeuropathies (focal involvement of a single nerve) and polyradiculopathies (involvement of a nerve root KEY FINDINGS One systematic review, one randomized controlled trial, and one non-randomized study were identified regarding the clinical effectiveness of gabapentin for the treatment of HIV-associated neuropathic pain. A small placebo-controlled trial showed that gabapentin was more effective than placebo in reducing pain and sleep interference in patients with HIV-associated neuropathy [38]. There is limited evidence for the use of gabapentin for the treatment of HIV-associated neuropathy. One relevant RCT, included in a systematic review, and one non-randomized study were identified. The studies suggest that gabapentin may improve pain and related sleep disturbances caused by HIV-associated sensory neuropathy; however, due to the limitations of the evidence, the effectiveness of Jazebi et al. option of prescribing medications (e.g. gabapentin) used for general neuropathic pain. These treatments are nonspeciic and not efective at treating HIV-SN when compared to placebos. Treatments targeting the pathogenic pathways would greatly benefit for the growing population of long-term HIV living with HIV-SN. In addition patients with HIV-SN are more likely to be prescribed The studies suggest that gabapentin may improve pain and related sleep disturbances caused by HIV-associated sensory neuropathy; however, due to the limitations of the evidence, the effectiveness of gabapentin for patients with HIV-associated neuropathy is inconclusive. Gabapentin reduced pain significantly and improved sleep in a small study with 24 patients. 80 Lamotrigine provided some pain relief in a study of 227 patients with HIV DSP, especially in those patients who were treated with neurotoxic medications. 81, 82 A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of pregabalin failed to demonstrate The studies suggest that gabapentin may improve pain and sleep disturbances caused by HIV-associated sensory neuropathy, however the small sample size of each study and limitations in the analyses conducted prevent strong conclusions. Gabapentin appeared to be well-tolerated, with somnolence being the most frequently reported side effect. Summary Peripheral neuropathy continues to affect the lives of persons living with HIV. First-line treatment with pregabalin or gabapentin for HIV neuropathic pain has limited data on adequate response. Exercise and self-management strategies may provide benefit in pain reduction. The purpose of this report is to examine the evidence for the use of gabapentin for the treatment of adults with HIV-associated neuropathic pain. There is limited evidence for the effect of gabapentin on other NP conditions including: chronic lower back pain, fibromyalgia, mixed NP, trigeminal neuralgia, nerve injury pain, and HIV-associated neuropathy. Further high-quality studies would reduce uncertainty regarding the effectiveness of gabapentin for those indications. Peripheral neuropathy continues to affect the lives of persons living with HIV. First-line treatment with pregabalin or gabapentin for HIV neuropathic pain has limited data on adequate response. Exercise and self-management strategies may provide benefit in pain reduction. Peripheral neuropathy has emerged as the most common neurologic complication of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. It will continue to play an important role in HIV infection given the fact that HIV-infected individuals are living longer, are at risk of long-term metabolic complications, and face an increasing exposure to potentially neurotoxic antiretroviral drugs. We review the Gabapentin may improve pain and sleep disturbances caused by HIV-associated sensory neuropathy. In a randomized, double-blind placebo-controlled study, Hahn et al. (2004) reported that gabapentin was more effective than the placebo at reducing pain and sleep interference in patients with HIV-SN, though the study was performed on a small number Patient Population The systematic review 8 included any double-blind RCT including adult patients receiving gabapentin for neuropathic pain. It identified one RCT 5 on HIV-associated neuropathy which included 26 adults with distal-symmetric polyneuropathy due to HIV itself (n=16) or potentially caused by neurotoxic antiretroviral drugs (n=10). Gabapentin (Neurontin) and S- (+)-3-isobutylgaba represent a novel class of selective antihyperalgesic agents Peripheral neuropathy in a cohort of human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients: incidence and relationship to other nervous system dysfunction A randomized trial of amitriptyline and mexiletine for painful neuropathy in HIV infection Gabapentin reduced pain significantly and improved sleep in a small study with 24 patients. 80 Lamotrigine provided some pain relief in a study of 227 patients with HIV DSP, especially in those patients who were treated with neurotoxic medications. 81, 82 A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of pregabalin failed to demonstrate OAKLAND, CALIF. — Two anticonvulsants are competing in popularity for treating peripheral neuropathy in patients with HIV infection: gabapentin and lamotrigine, said Lisa Capaldini, M.D., at a conference sponsored by the American Foundation for AIDS Research.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |