Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | +causing+AED-induced+seizure+worsening.+CBZ+can+both+aggravate+and+induce+new+seizure+types+including+absence%2C+atonic%2C+or+myoclonic+seizures+in+patients+with+generalized+epilepsies.+Vigabatrin+and+gabapentin+have+been+found+to+induce+absence+and+myoclonic+seizures.+Benzodiazepines+have+been+reported+to+precipitate+tonic+seizures+in+patients+with+Lennox%E2%80%93Gastaut+syndrome.+Lamotrigine+has+been+reported+to+worsen+myoclonic%2C+clonic%2C+and+tonic-clonic+seizures+in+the+patients+with+Dravet+syndrome.1%E2%80%933+Therefore%2C+AED-induced+seizure+worsening+must+be+considered+in+all+patients+whose+seizures+are+worse+with+the+introduction+of+the+new+AED..jpg) |
 |  |
 |  |
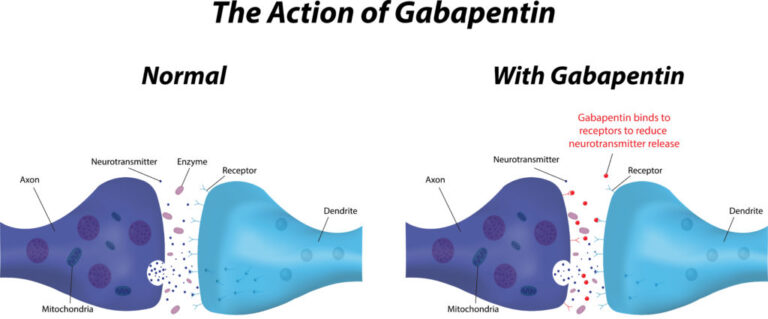 |  |
Gabapentin can help control seizures as well as nerve pain from shingles. It may sometimes cause side effects, especially if you misuse it. Learn more. For the patients who did not respond within the first 2 h (ten patients), gabapentin was switched to clomethiazole or clonazepam. While 73 % of patients responded to gabapentin 800 mg initially, there were increasing AWS in one subject and two subjects had a seizure in the following 36 h. Neurosteroids and Seizure Activity In The Pediatric Population (Human And Animal Data) Epilepsy in children is a crucial problem, because its prevalence is greater than epilepsy in the adult population. This is associated with the increased susceptibility of immature cerebral tissue to spontaneous neuronal discharges. Due to the high risk of irreversible pathological changes, it is recommended The results showed that gabapentin effectively reduced seizures when used as an additional treatment. Compared to a placebo, gabapentin was almost twice as likely to reduce seizures by 50% or more. The most common side effects associated with gabapentin were ataxia (poor co‐ordination and unsteady gait), dizziness, fatigue and drowsiness. Gabapentin for partial seizures: According to the guidelines from the American Epilepsy Society, clinicians might consider gabapentin as a potential option for patients aged 60 and older with new-onset focal epilepsy, as it could be similarly effective and better tolerated compared to carbamazepine. [9] Gabapentin was most effective against maximal elec- troshock-induced seizures in postnatal (5) and adult (4) animals, and prolonged the latency to tonic-clonic con- vulsions and death after injection of N-methyl-D- aspartate (6). I looked up seizures and Gabapentin and the journal or pharmacy & pharmacology, they reported 5 seizures during the trails of the drug. So while its known as an anti-seizure medication, it can cause seizures with some people. Abstract Purpose: To report on the occurrence of myoclonus in patients receiving gabapentin (GBP) for the treatment of epilepsy. Methods: Clinic charts of 104 consecutive patients started on GBP were reviewed. All patients were treated by the same physician, and most were specifically asked about the presence of myoclonus. The NICE (2022) 17 guideline recommends against the use of gabapentin in people with myoclonic seizures or people with epilepsy with myoclonic-atonic seizures because it may exacerbate seizures. Hyponatremia is a known adverse effect in patients on various drugs, including patients using anticonvulsant drugs, otherwise known as antiseizure medications (ASMs) [2]. ASMs are a group of medications commonly used to treat epilepsy and other seizure disorders [3]. ASMs work through various mechanisms [4]. Consideration in ASM choice must include looking at the spectrum of efficacy To date there is no available therapy to prevent epileptogenesis or other co-morbidities following SE. In most experiments dealing with consequences of SE in partial (focal) or generalized epilepsy models, SE is induced by systemic drug administration or local injection of convulsants into limbic brain structures (temporal lobe epilepsy models). Gabapentin should be considered for the treatment of clozapine-induced seizures and/or as a prophylaxis for patients taking clozapine who are at increased risk for seizures, especially patients whose best previous clinical response was to clozapine. Abstract Background: Epilepsy is one of the most common chronic neurological disorders, affecting more than 50 million people globally. In this review we summarised the evidence from randomised controlled trials of gabapentin used as monotherapy for the treatment of focal epilepsy, both newly diagnosed and drug-resistant, with or without secondary generalisation. For the next five months she came frequently to the ER with injuries, pain and seizures, seeking gabapentin. After obtaining 25 capsules (300mg) she had a three-day hospitalization for obtundation and bizarre movements with normal CT and EEG. Gabapentin (GA ba PEN tin) has been approved by the FDA as adjunctive therapy in the treatment of focal onset seizures, with and without secondary generalization, in pediatric patients 3 years and older with epilepsy. Gabapentin should be considered for the treatment of clozapine-induced seizures and/or as a prophylaxis for patients taking clozapine who are at increased risk for seizures, especially patients whose best previous clinical response was to clozapine. 1. Devinsky O, Pacia SV: Seizures during clozapine therapy. Gabapentin has shown efficacy in treating several types of seizures, including partial seizures and secondary generalized seizures. Its action as a GABA analog allows increased inhibition in the central nervous system, which is beneficial for patients with focal seizures originating in specific brain regions. Gabapentin (gab-ah-PEN-tin) is the generic name (non-brand name) of the seizure medicine Neurontin (nur-ON-tin) used in the United States, Canada, the UK, and some other countries. Another commonly used name for gabapentin is GBP. Neurontin is sold in the United States by Pfizer Inc. Gabapentin (GBP) and pregabalin (PGB) are FDA approved for adjunctive treatment of partial seizures and for treatment of post-herpetic neuralgia. Both drugs are primarily eliminated by renal excretion. However, PGB or GBP induced myoclonus has only been reported infrequently in case reports/series. Background: Myoclonus may be linked to a variety of causes, including epilepsy, postanoxic brain injury, metabolic encephalopathies and focal central nervous system lesions. Various drugs also have been reported to induce myoclonus. Gabapentin-induced myoclonus has been reported previously, especially in cases with impaired renal function or epilepsy.
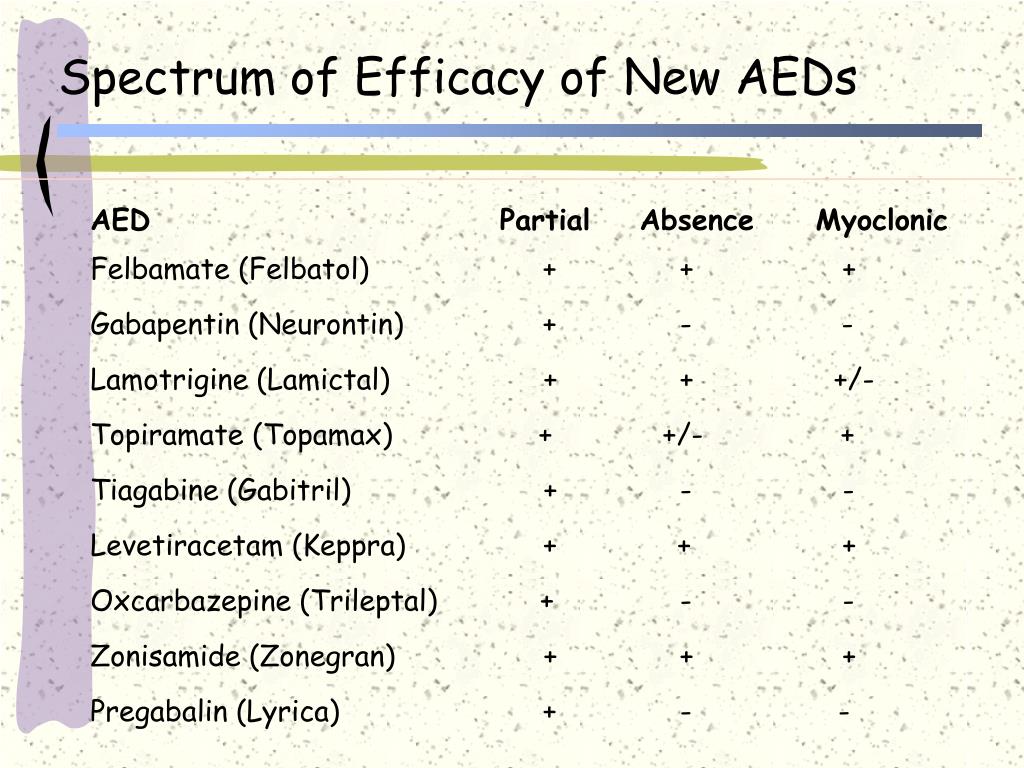
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | +causing+AED-induced+seizure+worsening.+CBZ+can+both+aggravate+and+induce+new+seizure+types+including+absence%2C+atonic%2C+or+myoclonic+seizures+in+patients+with+generalized+epilepsies.+Vigabatrin+and+gabapentin+have+been+found+to+induce+absence+and+myoclonic+seizures.+Benzodiazepines+have+been+reported+to+precipitate+tonic+seizures+in+patients+with+Lennox%E2%80%93Gastaut+syndrome.+Lamotrigine+has+been+reported+to+worsen+myoclonic%2C+clonic%2C+and+tonic-clonic+seizures+in+the+patients+with+Dravet+syndrome.1%E2%80%933+Therefore%2C+AED-induced+seizure+worsening+must+be+considered+in+all+patients+whose+seizures+are+worse+with+the+introduction+of+the+new+AED..jpg) |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |