Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
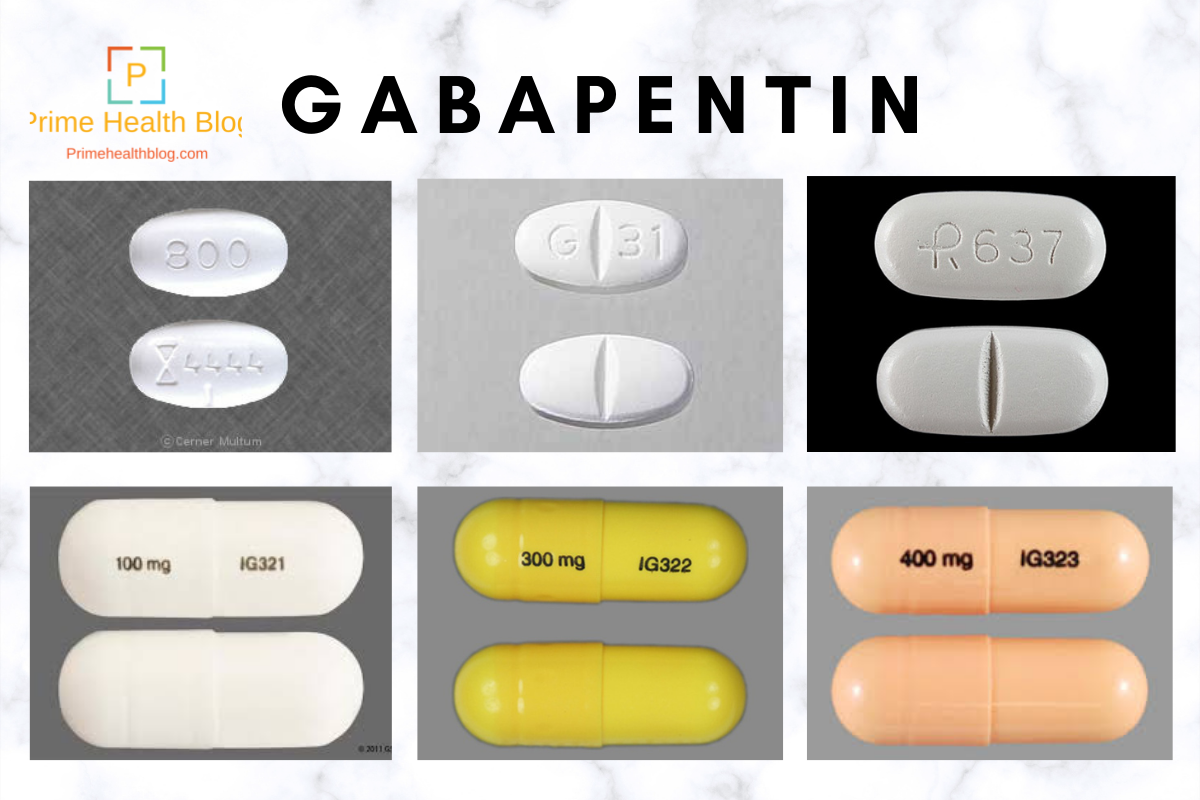
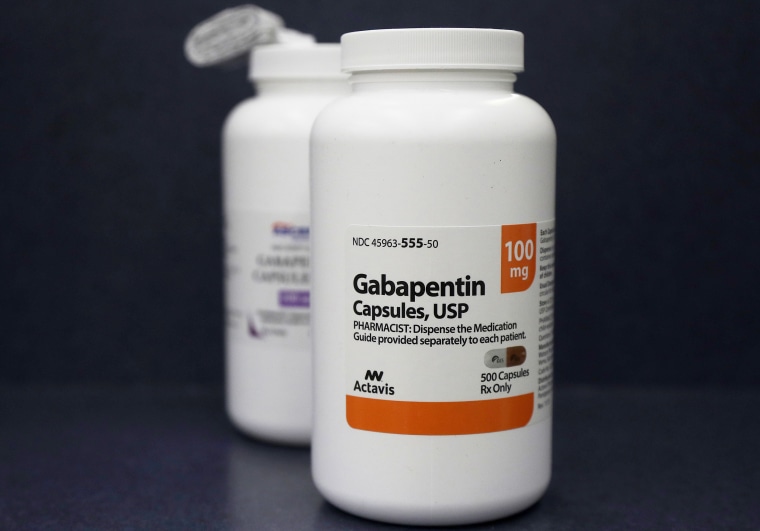
Gabapentin is commonly used to treat and prevent seizures in people with epilepsy or to treat nerve pain (postherpetic neuralgia) that can occur after a viral infection called shingles. Doctors prescribe gabapentin to treat epilepsy, restless legs syndrome, and some types of nerve pain. Learn more the drug's uses, risks, and safety here. If you've been prescribed gabapentin for nerve pain, you may begin to feel pain relief within two to four weeks of starting it, depending on your dosage. You should take gabapentin for as long as your healthcare provider tells you to. Gabapentin is approved to treat seizures and postherpetic neuralgia, a type of nerve pain following shingles. Neuropathic pain caused by diabetic peripheral neuropathy and spinal cord injury Restless leg syndrome (gabapentin enacarbil) Gabapentin is frequently used off-label for: Neuropathy caused by other etiologies such as chronic regional pain syndrome (CRPS), cancer, multiple sclerosis, phantom limb pain, HIV Vasomotor symptoms (i.e. hot flashes Receiving six or more prescriptions of the drug gabapentin for low back pain is associated with significantly increased risks of developing dementia and mild cognitive impairment (MCI)—29% and SHIPPING & RETURNS Track Order Shipping Info Store Pickup Same Day Delivery Returns Product Recall Information Rebates Price Match Promise SHOPPING TOOLS Idea boards Shop College Shop Movers Shop Catalogs Shop Personalized Invitations Shop by Brand Shop Clearance & Savings Buying Guides Guides & Advice Coupons Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication prescribed for a variety of conditions. Learn about its uses, side effects, and what you should know if you've been prescribed this medication. Find out how gabapentin and Lyrica are used for pain control and when they can be used together. Therapeutics Letter 75 examines new evidence from unpublished trials on the use of gabapentin for pain. Conclusions and recommendations Misleading promotion pushed gabapentin to blockbuster status; scientific evidence suggests gabapentin has a minor role in pain control. Gabapentin reduces neuropathic pain by < 1 point on a 0-10 point scale and benefits about 15% of carefully selected patients Gabapentinoid drugs—specifically gabapentin (Neurontin) and pregabalin (Lyrica)—are increasingly being prescribed for pain because physicians and patients seek alternatives to opioids in the Gabapentin Patient Tips Medically reviewed by Carmen Pope, BPharm. Last updated on June 18, 2024. How it works Upsides Downsides Bottom Line Tips Response/effectiveness Interactions FAQ 1. How it works Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant with pain-relieving effects that may be used to treat partial-onset seizures or relieve nerve pain. Research has shown gabapentin binds strongly to a specific Learn about the side effects of gabapentin, from common to rare, for consumers and healthcare professionals. Gabapentin is an anti-epileptic drug, also called an anticonvulsant. It is used to treat some types of seizures and nerve pain caused by shingles. Gabapentin is also used to manage a condition called postherpetic neuralgia, which is pain that occurs after shingles. Gabapentin works in the brain to prevent seizures and relieve pain for certain conditions in the nervous system. It is not used for routine pain caused by minor injuries or arthritis. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant. Detailed Gabapentin dosage information for adults and children. Includes dosages for Restless Legs Syndrome, Epilepsy and Postherpetic Neuralgia; plus renal, liver and dialysis adjustments. Gabapentin capsules, tablets, and oral solution are used along with other medications to help control certain types of seizures in people who have epilepsy. Gabapentin capsules, tablets, and oral solution are also used to relieve the pain of postherpetic neuralgia (PHN; the burning, stabbing pain or aches that may last for months or years after an attack of shingles). Gabapentin extended Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication used in the management of peripheral neuropathic pains, postherpetic neuralgia, and partial-onset seizures. Consumer information about the medication GABAPENTIN - ORAL (Neurontin), includes side effects, drug interactions, recommended dosages, and storage information. Read more about the prescription drug GABAPENTIN - ORAL. Gabapentin is approved to prevent and control partial seizures, relieve postherpetic neuralgia after shingles and moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome. Learn what side effects to watch for, drugs to avoid while taking gabapentin, how to take gabapentin and other important questions and answers. Gabapentin is available in both branded and generic forms. Gabapentin is commonly used to treat some types of nerve pain but is classified as an anticonvulsant medicine, not as an opioid or painkiller. Gabapentin was first approved in 1993 and is used to treat: postherpetic neuralgia, a nerve pain caused by the shingles virus (herpes zoster), restless legs syndrome (RLS), a painful movement disorder in the legs partial seizures in adults and children
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |