Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
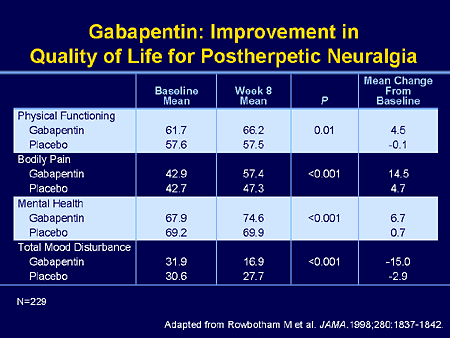
Abstract Objective: This article reviews evidence-based psychiatric uses of gabapentin, along with associated risks. Method of Research: An extensive literature review was conducted, primarily of articles searchable in PubMed, relating to psychiatric uses, safety, and adverse effects of gabapentin. Results: Evidence supports gabapentin as a treatment for alcohol withdrawal and alcohol use Gabapentin is a nerve pain medication and anticonvulsant that has proven to be effective for people who have hard-to-treat depression or other mood disorders. Gabapentin is commonly used off-label in the treatment of psychiatric disorders with success, failure, and controversy. A systematic review of the literature was performed to elucidate the evidence for clinical benefit of gabapentin in psychiatric Taking Neurontin for Anxiety Bipolar disorder is a complicated mental health problem that requires medical treatment. Those who have been prescribed Neurontin should discuss any concerns with the prescribing doctor as depending on your symptoms, the benefit may outweigh any perceived risks. The use of gabapentinoids off-label for other psychiatric conditions should also be re-considered. In general, psychotropic medications require longer term efficacy and safety studies before allowing widespread use. Definition Gabapentin is a prescription medication originally developed to treat seizures and nerve pain but is now widely used off-label for managing anxiety, alcohol withdrawal, and certain mood disorders. Marketed under the brand name Neurontin, gabapentin works by stabilizing electrical activity in the brain and altering the way the nervous system responds to pain or stress. In mental While gabapentin offers many potential benefits for various mental health conditions, it is essential to use it under professional guidance. The medication can cause drowsiness, affecting driving or operating heavy machinery. Gabapentin has potential side effects such as dizziness, fatigue, and weight gain. This article reviews evidence-based psychiatric uses of gabapentin, along with associated risks. An extensive literature review was conducted, primarily of articles searchable in PubMed, relating to psychiatric uses, safety, and adverse effects of Method of research: An extensive literature review was conducted, primarily of articles searchable in PubMed, relating to psychiatric uses, safety, and adverse effects of gabapentin. Gabapentin, also known as Gralise and Neurontin, is an anticonvulsant medication typically used in the treatment of epilepsy, along with various other physical and mental health treatments. Always use this medication exactly as prescribed and consult with your doctor prior to starting any other medications (prescribed or over the counter) while taking gabapentin, as adverse effects can occur. Gabapentin is widely prescribed off label in medical practice, including psychiatry. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) warned of risks associated with gabapentin combined with central nervous system depressant (CNS-D) drugs, which are commonly prescribed in psychiatric treatment. This study examined off-label outpatient gabapentin use for psychiatric indications and concomitant CNS-D Abstract Objective: Gabapentin is commonly used off-label in the treatment of psychiatric disorders with success, failure, and controversy. A systematic review of the literature was performed to elucidate the evidence for clinical benefit of gabapentin in psychiatric disorders. Objective: Gabapentin (GBP) is an anticonvulsant medication that is also used to treat restless legs syndrome (RLS) and posttherapeutic neuralgia. GBP is commonly prescribed off-label for psychiatric disorders despite the lack of strong evidence. Explore gabapentin's role in mental health treatment, including its uses, benefits, and potential risks. Learn about dosage, effectiveness, and side effects. Is gabapentin a good option for treating anxiety disorders? This is what research says and why caution is important. Although not officially approved for anxiety, gabapentin’s calming effects on the nervous system have made it a subject of interest in mental health. Pregabalin, a derivative of gabapentin, was approved for use in 2004, primarily for treating neuropathic pain and as an adjunct therapy for partial seizures. Gabapentin is commonly used off-label in the treatment of psychiatric disorders with success, failure, and controversy. A systematic review of the literature was performed to elucidate the evidence for clinical benefit of gabapentin in psychiatric disorders. 7. You may be able to have gabapentin delivered to your door. Here at Brightside Health, we do medication differently, using precision psychiatry to find the right treatment for your unique needs. It all starts with you filling out our free online assessment, after which we will assess your situation and match you with a psychiatric provider. This use of gabapentin for the treatment of anxiety is referred to as an off-label use, meaning there is limited data on its effectiveness to treat anxiety. Other off-label uses include treating alcohol withdrawal for alcohol use disorder and hot flashes associated with menopause. Abstract Background: Bipolar disorder is a common and debilitating psychiatric illness. Several antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) have been approved for the treatment of bipolar disorder. Gabapentin gained a large market share of AED use in the late 1990s in spite of a lack of randomized clinical trial (RCT) evidence and no labeled indication from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for its use in
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |