Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
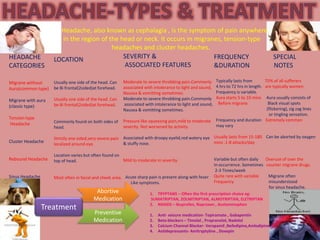
Migraine is a primary headache disorder characterized by recurrent disabling attacks. Pharmacologic treatment of acute migraine episodes should be individualized based on route of administration Gabapentin does not decrease the frequency of migraine headaches and is not recommended for prophylactic therapy. The migraine headache rate during the second 4 weeks of the SP2 for patients maintaining a stable dose of 2400 mg/day gabapentin is presented in Table 3 for the placebo- and gabapentin-treatment groups. B. MIGRAINE ABORTIVE TREATMENT (Used to stop a migraine.) Post-dose observation time (no fly warning) is based on half-life of medication. ACCEPTABLE when used occasionally. Unacceptable for daily use. If multiple abortive medications are required on a recurring basis to stop symptoms, this is considered complicated migraine and the AME should Abortive treatments are more effective if they are given early in the course of the headache; a large single dose tends to work better than repetitive small doses. For some patients, oral agents are less effective because of poor absorption secondary to migraine-induced gastric stasis and vomiting. Tension-type, migraine, and cluster headaches are the most common primary headaches. Primary headaches are differentiated by clinical criteria from the International Classification of Headache Discover the potential of gabapentin for preventing migraine attacks and headaches. While not a first-line treatment, it can be effective in combination with other options. Gabapentin (GBP), originally an antiepileptic drug, is more commonly used in the treatment of pain, including headache disorders. Off-label GBP is used in headache disorders with some success, some failure, and much debate. Migraine treatments are probably the most discussed issue among patients with Migraine because of their huge impact on our lives. Discussions of Migraine treatments can be quite confusing. Migraine treatments fall into three categories – preventive, abortive, and rescue. Recurrent migraines can be functionally disabling and can impair quality of life. The disabling nature of migraine headaches leads to frequent visits to outpatient clinics and emergency department facilities, causing significant health and financial burdens. Headaches fall in the top five causes of emergency department visits and the top twenty reasons for outpatient visits.[1] The overall My migraine specialist prescribes me nurtec as a preventative. I take it every other day, and I take it on additional days when I know I will have additional triggers as per her instructions. While there are several trials that support the efficacy of various drugs for migraine prophylaxis against placebo, there is limited evidence addressing the comparative safety and efficacy of these drugs. We conducted a systematic review and network meta-analysis to facilitate comparison between drugs for migraine prophylaxis. A. Acute (abortive) treatment Abortive medications for migraine can be classified into; first line and second line drugs, or specific and nonspecific drugs. Nonspecific drugs are analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs, while specific treatments include drugs like ergots or triptans, which target 5HT1 receptors specifically. Gabapentin is a drug that’s approved to help prevent seizures in people with epilepsy and treat nerve pain from shingles. It’s also sometimes used off-label for migraine prevention. Migraine headaches are a debilitating condition that affects approximately 1% of the US population. Goals of migraine prophylaxis include reduction in headache severity and frequency, improved Gabapentin is an effective prophylactic agent for patients with migraine. In addition, gabapentin appears generally well tolerated with mild to moderate somnolence and dizziness. Gabapentin, originally developed as an antiepileptic drug, has garnered interest for its potential efficacy in migraine management. While traditionally used for neuropathic pain and epilepsy, recent research suggests its utility as an abortive treatment for migraines. Unlike conventional migraine medications such as triptans, gabapentin works through a different mechanism, primarily by Learn the effective migraine treatments, including preventative medications and abortive drugs, to manage symptoms, reduce attacks, and improve daily life. The abortive (symptomatic) therapy of migraine ranges from the use of simple analgesics such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or acetaminophen to triptans, antiemetics, calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) antagonists, lasmiditan, and dihydroergotamine. Migraine headaches can be treated with two drug approaches: abortive and preventive. Learn more from WebMD about how each type works to curb or shorten migraines.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |