Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
.jpg) |  |
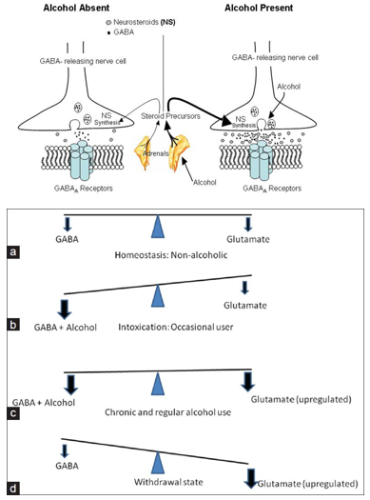
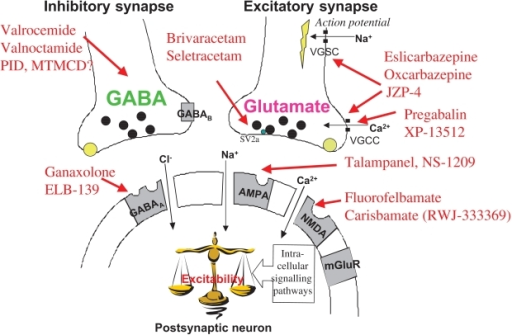
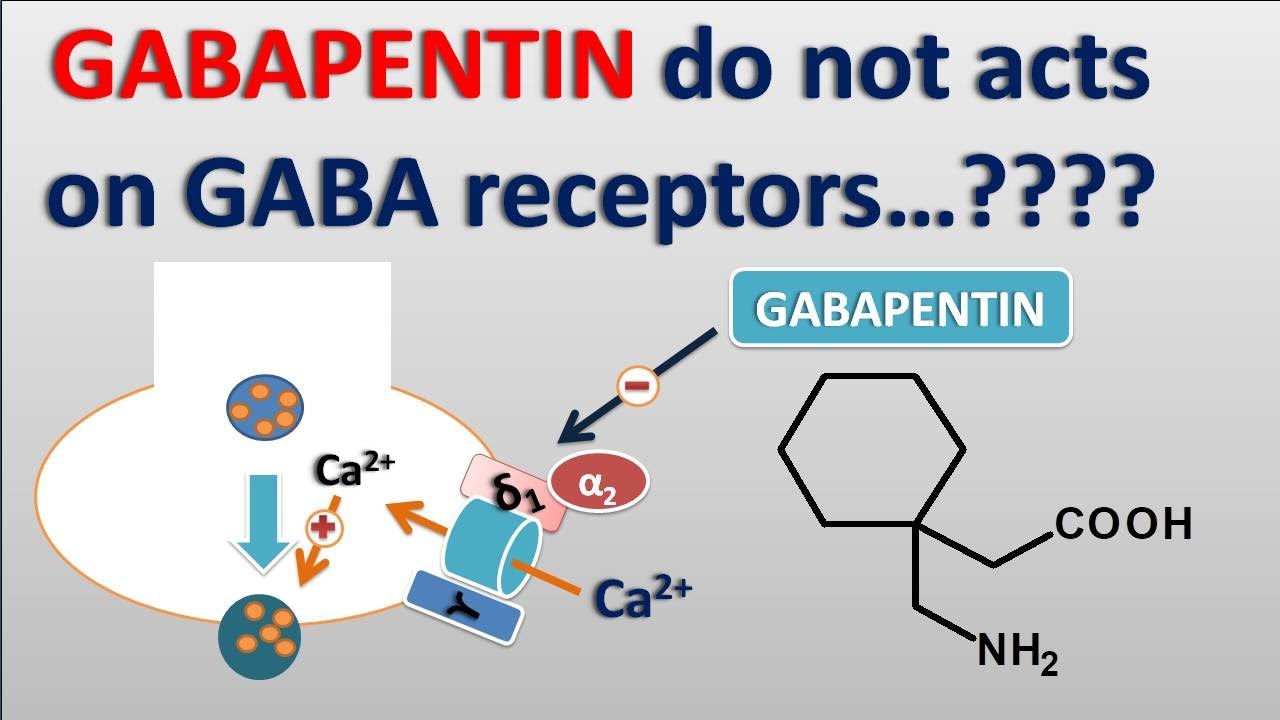
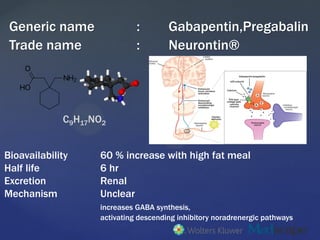
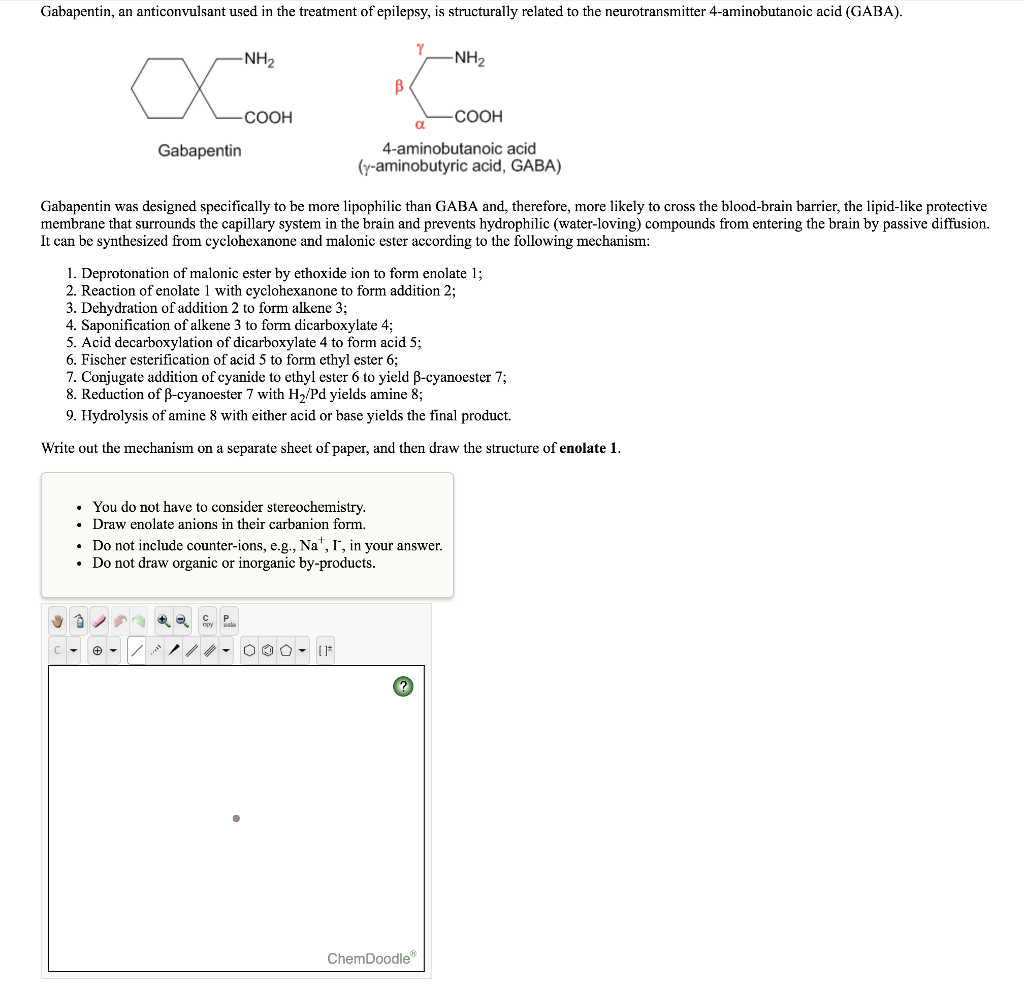
Gabapentin was designed as a GABA analog, and some studies have suggested that it modulates the action of the GABA synthetic enzyme, glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) and the glutamate synthesizing enzyme, branched-chain amino acid transaminase, resulting in increased GABA synthesis. 139 Gabapentin increases non-synaptic GABA responses from Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication used in the management of peripheral neuropathic pains, postherpetic neuralgia, and partial-onset seizures. Gabapentin (GBP) was originally developed as a potential agonist for Gamma-Amino-Butyric-Acid (GABA) receptors, aiming to inhibit the activation of pain-signaling neurons. Contrary to initial expectations, it does not bind to GABA receptors. Gabapentin enhanced expression of δGABA A receptors and increased a tonic inhibitory conductance in neurons. This increased expression likely contributes to GABAergic effects as gabapentin caused ataxia and anxiolysis in wild-type mice but not δ subunit null-mutant mice. In contrast, the antinociceptive properties of gabapentin were observed in both genotypes. Levels of GABA A receptor Introduction Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant drug used as a medication to treat epilepsy and manage neuropathic pain or anxiety disorder. (1) Gabapentin shares a remarkable similarity in structure (see Figure 1 a), function, and clinical uses with the neurotransmitter GABA. For example, it reduces uncontrolled and repetitive neuronal activity, (2) asynchronous neuronal discharge, or nervous Gabapentin (Neurontin®) is a second-generation antiepileptic drug widely used for treatment of neuropathic pain. It is also used to treat anxiety, insomnia, bipolar disorder, and restless leg syndrome. Although first introduced as an adjunct therapy for epilepsy, gabapentin became a blockbuster drug for the management of chronic pain from many nerve conditions [8]. Side effects are usually However, gabapentin was shown to increase expression of δGABAA receptors, inhibitory tone in the cerebellum, and brain GABA concentration in patients, 3,4 while pregabalin enabled a larger neuronal calcium influx for facilitating neurotransmission. 2 These findings substantiate a GABAergic effect of gabapentin and pregabalin. Includes Gabapentin indications, dosage/administration, pharmacology, mechanism/onset/duration of action, half-life, dosage forms, interactions, warnings, adverse Gabapentin is a medication that is commonly prescribed for the treatment of neuropathic pain and as an adjunctive therapy for partial seizures. Understanding its mechanism of action provides valuable insight into how it alleviates symptoms and aids in managing these conditions. First and foremost, gabapentin is structurally similar to the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA Gabapentin is a structural analog of the inhibitory neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Its anticonvulsant, analgesic and anxiolytic properties suggest that it increases GABAergic inhibition; however, the molecular basis for these effects Learn how gabapentin works by binding calcium channel subunits. Full MOA, uses, MCQs, FAQs, and pharmacology inside. Gabapentin [1- (aminomethyl)cyclohexane acetic acid] is␣a␣novel anti-epileptic agent, originally developed as a gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-mimetic compound to treat spasticity, and has been shown to have potent anticonvulsive effects [1, 2]. Initially approved only for use in partial seizures, it soon showed promise in the treatment of chronic pain syndromes, especially neuropathic The chemical structure of gabapentin (Neurontin) is derived by addition of a cyclohexyl group to the backbone of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Gabapentin prevents seizures in a wide variety of models in animals, including generalized tonic-clonic and partial seizures. Gabapentin has no activity at Structure of GABA: gabapentin and pregabalin. 10 Pharmacokinetics The actions of gabapentinoids are mainly at an intracellular site and require active uptake. They undergo facilitated transport across cell membranes through system l -amino acid transporters (LAT) as both drugs are structurally similar to the amino acid leucine. The effects of chronic gabapentin are blocked by an inhibitor of Although the mechanism of gabapentin therapeutic action is unclear, human subjects studies suggest that its administration leads to an overall increase in central GABA levels. Gabapentin, sold under the brand name Neurontin among others, is an anticonvulsant medication primarily used to treat neuropathic pain and also for partial seizures [10][7] of epilepsy. It is a commonly used medication for the treatment of neuropathic pain caused by diabetic neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia, and central pain. [11] It is moderately effective: about 30–40% of those given Gabapentin: Cytochrome P450 Metabolism Pharmacodynamics Mechanism of Action Gabapentin is designed as GABA analog (similar to pregabalin), which means it binds to the α2δ (alpha-2-delta) subunit of presynaptic voltage-sensitive Ca2+ channels (VSCCs), and block the release of excitatory neurotransmitters such as glutamate. 9.1.2.1 Gabapentin Gabapentin is an anti-epileptic drug but its use has expanded to treat multiple other diseases including post-herpetic neuralgia, neuropathic pain, and spasticity. The mechanism of action is not fully understood but may be related to gabapentin’s action on calcium channels leading to diminution of excitatory neurotransmitters. Mechanism of Action Although the exact mechanism of action with the GABA receptors is unknown, researchers know that gabapentin freely passes the blood-brain barrier and acts on neurotransmitters. Gabapentin has a cyclohexyl group to the structure of the neurotransmitter GABA as a chemical structure. Although it has a structure similar to GABA, it does not bind to GABA receptors or influence Gabapentin (GBP) was originally developed as a potential agonist for Gamma-Amino-Butyric-Acid (GABA) receptors, aiming to inhibit the activation of pain-signaling neurons. Contrary to initial expectations, it does not bind to GABA receptors. Instead, it exhibits several distinct pharmacological activities, including: (1) binding to the alpha-2-delta protein subunit of voltage-gated calcium
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
.jpg) |  |