Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
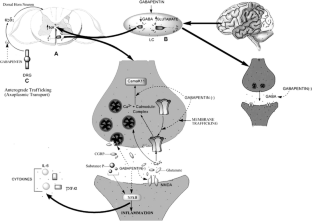
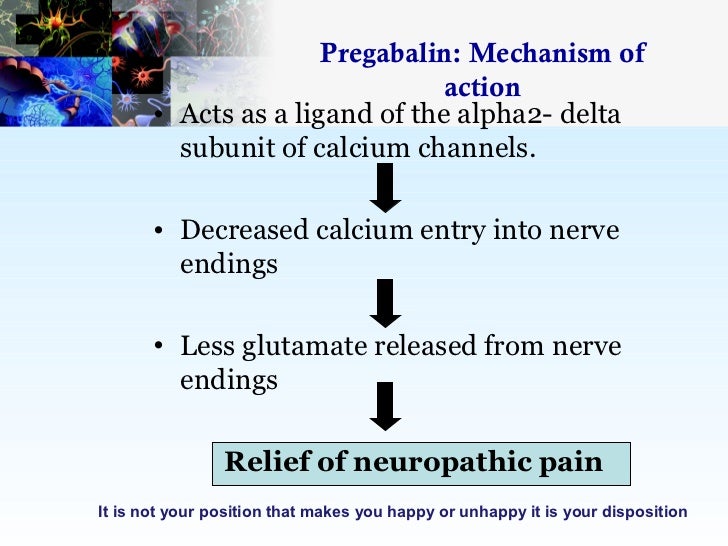
The gabapentinoids, pregabalin and gabapentin, have been the cornerstone of pharmacological management of neuropathic pain. 1 Despite the widespread use in neuropathic pain, the precise mechanism of action is uncertain. Introduction The gabapentinoid drugs gabapentin and pregabalin are antiepileptic drugs that are considered as first-line treatments for the management of neuropathic pain. 1 Pregabalin is also approved for generalised anxiety disorders in the United Kingdom. The mechanisms of action are still unclear despite their widespread use. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication used in the management of peripheral neuropathic pains, postherpetic neuralgia, and partial-onset seizures. Neuropathic pain is a common and potentially treatable cause of considerable lifelong morbidity. Effective pharmacological treatments are scarce, but one group of drugs that has shown promise is Identify the appropriate indications for gabapentin therapy, including neuropathic pain, partial onset seizures, restless legs syndrome, and other relevant neurological and psychiatric conditions. The gabapentinoids, pregabalin and gabapentin, have been the cornerstone of pharmacological management of neuropathic pain.1 Despite the widespread use in neuropathic pain, the precise mechanism of action is uncertain. The effect of gaba-pentinoids in pain are assumed to be because of direct inhibi-tion of voltage gated Ca2þ channels by binding to its a2d-1 subunit resulting in reduction of The present review discusses the effectiveness of gabapentin in different types of neuropathic pain in preclinical as well in clinical settings and also discusses the possible mechanism of action at different levels including at dorsal root ganglion (DRG) and dorsal horn neurons along with at supra-spinal centres. Gabapentin has become popular as a first-line treatment for neuropathic pain because of its efficacy as an antineuropathic agent and relatively benign side-effect profile. However, its mechanism of action is far from clear. This review discusses the available evidence for the postulated mechanisms of action of gabapentin. Gabapentin is commonly used to treat neuropathic pain (pain due to nerve damage). This review updates a review published in 2014, and previous reviews published in 2011, 2005 and 2000. To assess the analgesic efficacy and adverse effects of Neuropathic pain is generally a chronic medical condition, resistant to classical analgesic drugs. Some antidepressants, together with gabapentinoids, are first-line drugs for the treatment of neuropathic pain (Attal et al., 2010). The clinical efficacy of these drugs is well documented, and preclinical research provided insights into the mechanism (s) by which these drugs are acting. This Gabapentin has been clearly demonstrated to be effective for the treatment of neuropathic pain in diabetic neuropathy and postherpetic neuralgia. This evidence, combined with its favourable side-effect profile in various patient groups (including the elderly) and lack of drug interactions, makes it an attractive agent. Gabapentin is an anti-epileptic agent but now it is also recommended as first line agent in neuropathic pain, particularly in diabetic neuropathy and post herpetic neuralgia. α2δ-1, an auxillary subunit of voltage gated calcium channels, has been documented as its main target and its specific bindin The gabapentinoids, pregabalin and gabapentin, have been the cornerstone of pharmacological management of neuropathic pain. 1 Despite the widespread use in neuropathic pain, the precise mechanism of action is uncertain. Technology Gabapentin, an anticonvulsant drug originally developed for the treatment of epilepsy, is used off-label for treating NP in Canada. Its mechanism of action is through binding to calcium channels and modulating calcium influx, resulting in antiepileptic, analgesic, and sedative effects. Gabapentinoids, including gabapentin and pregabalin, are extensively used for treatment of neuropathic pain, restless legs syndrome, and focal seizures. Their efficacy in these disorders is primarily attributed to their effects in inhibiting the functions of the α2δ subunit of presynaptic VGCCs, thereby reducing neurotransmitter release. Gabapentin is an approved treatment as an adjunctive therapy in the management of epilepsy. However, it is most commonly prescribed off-label for other conditions, including anxiety, alcohol use disorder, and chronic pain. Gabapentin (GBP) is a Health Canada approved antiepileptic drug. 5 In the UK, GBP is licensed for the treatment of peripheral and central neuropathic pain in adults and in the US it is marketed for post-herpetic neuralgia (PHN). 3 The mechanism of action for GBP relates to its ability to bind with high-affinity to the alpha-2-delta subunit of Gabapentin [1- (aminomethyl)cyclohexane acetic acid] is␣a␣novel anti-epileptic agent, originally developed as a gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-mimetic compound to treat spasticity, and has been shown to have potent anticonvulsive effects [1, 2]. Initially approved only for use in partial seizures, it soon showed promise in the treatment of chronic pain syndromes, especially neuropathic Here we review the current understanding of the pathophysiological role of the α 2 δ ‐1 subunit, the mechanisms of analgesic action of gabapentinoid drugs and implications for efficacy in the clinic. Despite widespread use, the number needed to treat for gabapentin and pregabalin averages from 3 to 8 across neuropathies.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |