Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
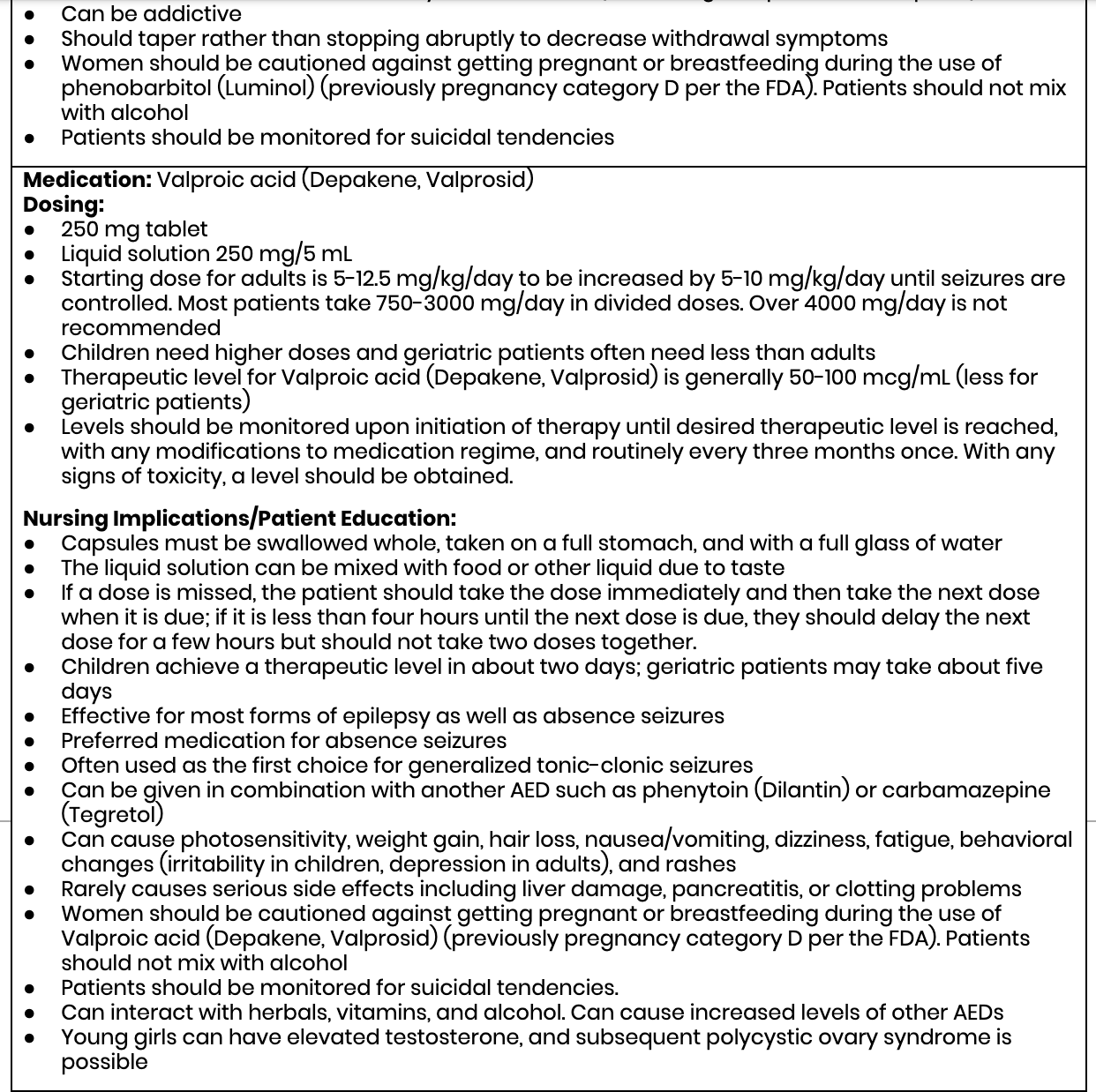
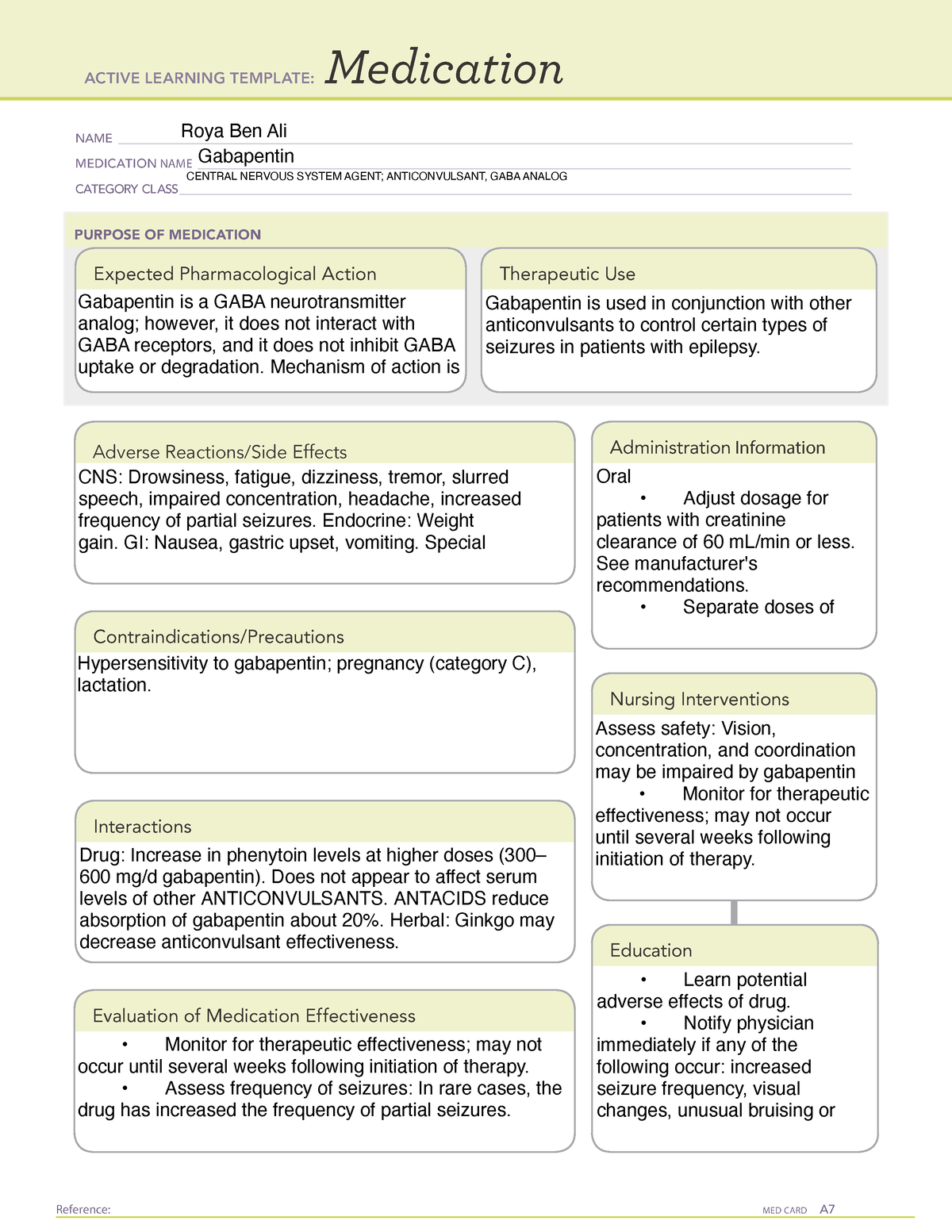
Its use requires careful nursing oversight to ensure safe administration, monitor for side effects, and educate patients on proper use. By understanding gabapentin’s pharmacology, indications, and nursing considerations, healthcare professionals can optimize treatment outcomes and enhance patient quality of life. Gabapentin (Neurontin) MoA: Increases release of GABA into the synapse. Indications: Seizures Side Effects: Fatigue, Xerostomia, Dizziness Drug Interactions: Antacids Nursing Implications: Monitor for possible suicidal ideation. Educate Patient on reporting changes in vision, hallucinations, and fever to their healthcare provider. For example, the two brands of gabapentin, Neurontin and Gralise, have different dosage schedules and indications, despite the same generic name. Neurontin is indicated for treatment of partial onset seizures, but Gralise is not. This newsletter will focus on Neurontin as an example of the GABA analogues, and its role in pain management We use Gabapentin for the prevention of seizures for peripheral neuropathy, for neuropathic pain and for the prevention of migraines. So some of the side effects that we see with Gabapentin are things like drowsiness, facial edema, hypertension, and confusion. So let's take a look at a few nursing considerations. Gabapentin is a GABA neurotransmitter analog; however, it does not inhibit GABA uptake or degradation. It appears to interact with GABA cotical neurons, but its relationship to functional activity as an anti convulsant is unknown. Used in conjunction with other anticonvulsants to control certain types of seizures in patients with epilepsy. Effective in treating painful neuropaths. Drug Name Generic Name : gabapentin Brand Name: Apo-Gabapentin (CAN), Gen-Gabapentin (CAN), Neurontin Classification: Antiepileptic Pregnancy Category C Dosage & Route Available forms : Capsules—100, 300, 400 mg; tablets—100, 300, 400, 600, 800 mg; oral solution—250 mg/5 mL ADULTS Epilepsy: Starting dose is 300 mg PO tid, then titrated up as needed. Maintenance: 900–1,800 mg/day PO in Nursing Considerations for Gabapentin Related Nursing Diagnoses Acute pain Risk for injury Risk for infection (related to decreased white blood count) Risk for suicide, impaired oral mucous membrane, constipation as potential side effects of gabapentin Nursing Assessment Assess for allergies to gabapentin Monitor for changes in neurological status, changes in mood, or thoughts of suicide Gabapentin Medication GridNCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health. Open Resources for Nursing (Open RN); Ernstmeyer K, Christman E, editors. Nursing Pharmacology [Internet]. 2nd edition. Eau Claire (WI): Chippewa Valley Technical College; 2023. Gabapentin Teaching 1979 SN instructed patient about Gabapentin ( Neurontin ). It is a medication used to treat epilepsy, neuropathic pain and hot flashes. It is also used for restless leg syndrome. It is a first line agent for the treatment of neuropathic pain arising from diabetic neuropathy, post-herpetic neuralgia, and central neuropathic pain. Most common side effects of gabapentin in · You may experience these side effects: Dizziness, blurred vision (avoid driving or performing other tasks requiring alertness or visual acuity); GI upset (take drug with food or milk, eat frequent small meals); headache, nervousness, insomnia; fatigue (periodic rest periods may help). Neurontin Pre-Administration Assessment: Post Administration Evaluation: Nursing Considerations: So some of the side effects that we see with Gabapentin are things like drowsiness, facial edema, hypertension, and confusion. So let's take a look at a few nursing considerations. Even seemingly harmless things like chamomile, valerian, and kava-kava can potentiate the CNS depressive effects of gabapentin. Neurontin and Horizant can be taken without regard to meals. Horizant, which is often taken for restless leg syndrome, is generally taken at 5 pm. Gralise should be taken with the evening meal for maximum bioavailability. gabapentin (ga-ba- pen -tin) Neurontin Classification Therapeutic: analgesic adjuncts, therapeutic, anticonvulsants, mood stabilizers Introduction In this article, you’ll learn about Gabapentin (Neurontin) nursing implications and patient teachings. Also, its dosage, indication, contraindications, interactions, side effects, nursing assessment, and nursing interventions. What is Gabapentin? Gabapentin is a medication primarily used to treat neuropathic pain and epilepsy. It is also known under the brand names Neurontin and Gralise. As a nurse, understanding the uses, dosages, side effects, and patient education related to gabapentin is crucial for providing optimal care. Learn about antiseizure drugs (antiepileptics, anticonvulsants) including hydratoins, barbiturates, benzodiazepines, succinimides and more. So some of the side effects that we see with Gabapentin are things like drowsiness, facial edema, hypertension, and confusion. So let's take a look at a few nursing considerations. Gabapentin is a medication commonly prescribed to treat various conditions, including epilepsy, neuropathic pain, and restless legs syndrome. This guide aims to educate patients about important considerations, including dosage instructions, potential side effects, and precautions, to ensure safe and effective use of gabapentin. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication commonly prescribed for epilepsy, neuropathic pain, and various off-label uses. Understanding proper nursing considerations is crucial for safe and effective patient care.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |