Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
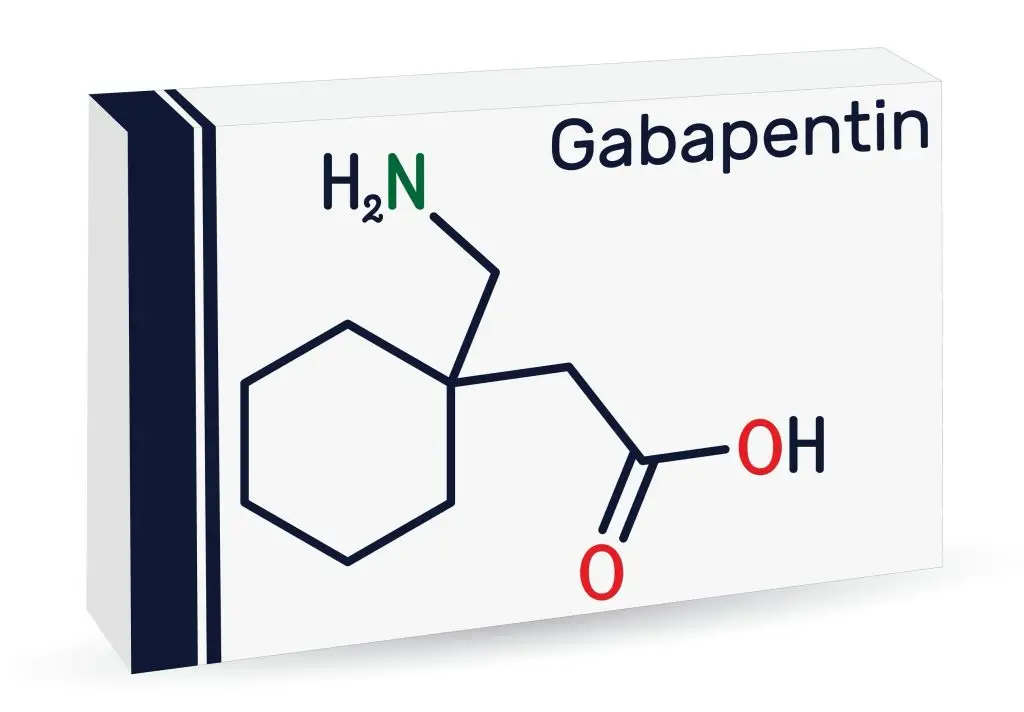
Gabapentin is an anti-epileptic drug, also called an anticonvulsant. It is used to treat some types of seizures and nerve pain caused by shingles. Gabapentin administration requires meticulous nursing care. Nurses ensure proper medication administration, closely monitor side effects such as drowsiness and dizziness, and assess for drug interactions. Patient education is crucial to promote adherence and minimize adverse effects. Nurses vigilantly monitor patients for respiratory depression, especially when gabapentin is used with other Medical information for Gabapentin on Pediatric Oncall including Mechanism, Indication, Contraindications, Dosing, Adverse Effect, Interaction, Renal Dose, Hepatic Dose. This is not an all-inclusive list of possible drug interactions, adverse effects, precautions, nursing considerations, or patient instructions. Please consult further with a pharmacist for complete information. The recommended maintenance dose of NEURONTIN in patients 5 to 11 years of age is 25 mg/kg/day to 35 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses. NEURONTIN may be administered as the oral solution, capsule, or tablet, or using combinations of these formulations. Dosages up to 50 mg/kg/day have been well tolerated in a long-term clinical study. Gabapentin and Nursing: Key Considerations for Safe and Effective Patient Care Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant and analgesic medication commonly encountered in various clinical settings. Nurses play a vital role in ensuring its safe and effective use. It's crucial for nurses to have a comprehensive understanding of gabapentin's pharmacology, administration guidelines, potential adverse effects Screen patients for risk factors and contraindications before initiating gabapentin therapy, such as renal impairment, history of substance misuse, or concurrent medication interactions. Apply patient-centered approaches to gabapentin prescribing, tailoring dosage adjustments and treatment plans based on individual needs and preferences. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication commonly prescribed for epilepsy, neuropathic pain, and various off-label uses. Understanding proper nursing considerations is crucial for safe and effective patient care. Gabapentin capsules are given orally with or without food. Gabapentin capsules should be swallowed whole with plenty of water. If gabapentin dose is reduced, discontinued, or substituted with an alternative medication, this should be done gradually over a minimum of 1 week (a longer period may be needed at the discretion of the prescriber). May cause suicidal thoughts, confusion, depression, drowsiness, ataxia, facial edema, hypertension I don’t claim any copyright licensure home notes nursing pharmacology gabapentin considerations and patient teaching gabapentin considerations and patient For example, the two brands of gabapentin, Neurontin and Gralise, have different dosage schedules and indications, despite the same generic name. Neurontin is indicated for treatment of partial onset seizures, but Gralise is not. This newsletter will focus on Neurontin as an example of the GABA analogues, and its role in pain management Contraindications Hypersensitivity. Lactation. Nursing considerations Assessment History: Hypersensitivity to gabapentin; lactation, pregnancy Physical: Weight; T; skin color, lesions; orientation, affect, reflexes; P; R, adventitious sounds; bowel sounds, normal output Interventions Give drug with food to prevent GI upset. Gabapentin is a GABA neurotransmitter analog; however, it does not inhibit GABA uptake or degradation. It appears to interact with GABA cotical neurons, but its relationship to functional activity as an anti convulsant is unknown. Used in conjunction with other anticonvulsants to control certain types of seizures in patients with epilepsy. Effective in treating painful neuropaths. This article provides an in-depth exploration of gabapentin from a nursing perspective, covering its classification, dosage, therapeutic actions, indications, adverse effects, contraindications, and critical nursing considerations, including assessment, interventions, and patient teaching. Gabapentin is a medication commonly prescribed to treat various conditions, including epilepsy, neuropathic pain, and restless legs syndrome. This guide aims to educate patients about important considerations, including dosage instructions, potential side effects, and precautions, to ensure safe and effective use of gabapentin. Introduction In this article, you’ll learn about Gabapentin (Neurontin) nursing implications and patient teachings. Also, its dosage, indication, contraindications, interactions, side effects, nursing assessment, and nursing interventions. Learn about antiseizure drugs (antiepileptics, anticonvulsants) including hydratoins, barbiturates, benzodiazepines, succinimides and more. Read this chapter of Davis's Drug Guide for Rehabilitation Professionals online now, exclusively on F.A. Davis PT Collection. F.A. Davis PT Collection is a subscription-based resource from McGraw Hill that features trusted content from the best minds in PT. Point of Care - Clinical decision support for Gabapentin. Treatment and management. Indications, Mechanism of Action, Administration, Adverse Effects, Contraindications, Monitoring, Toxicity, Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |