Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
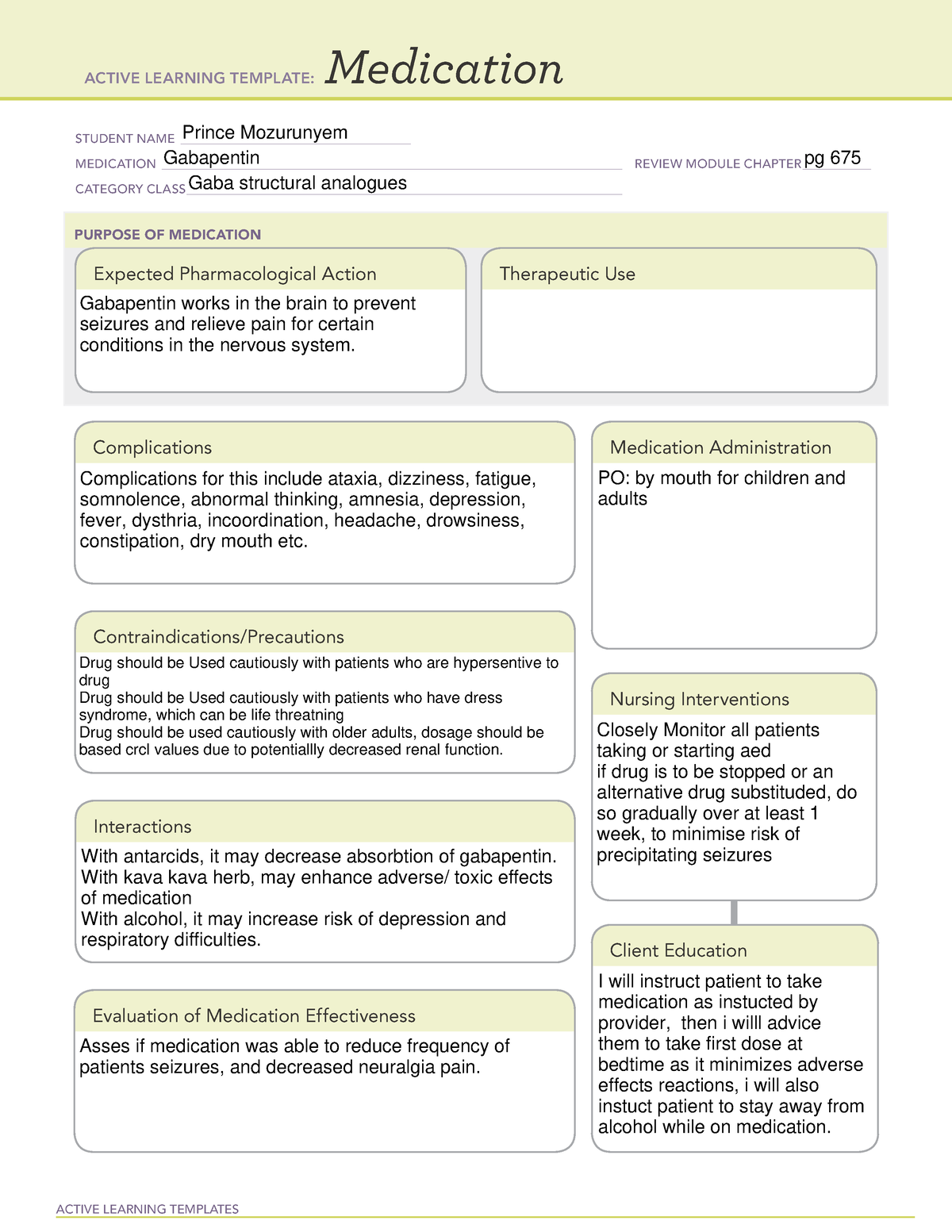
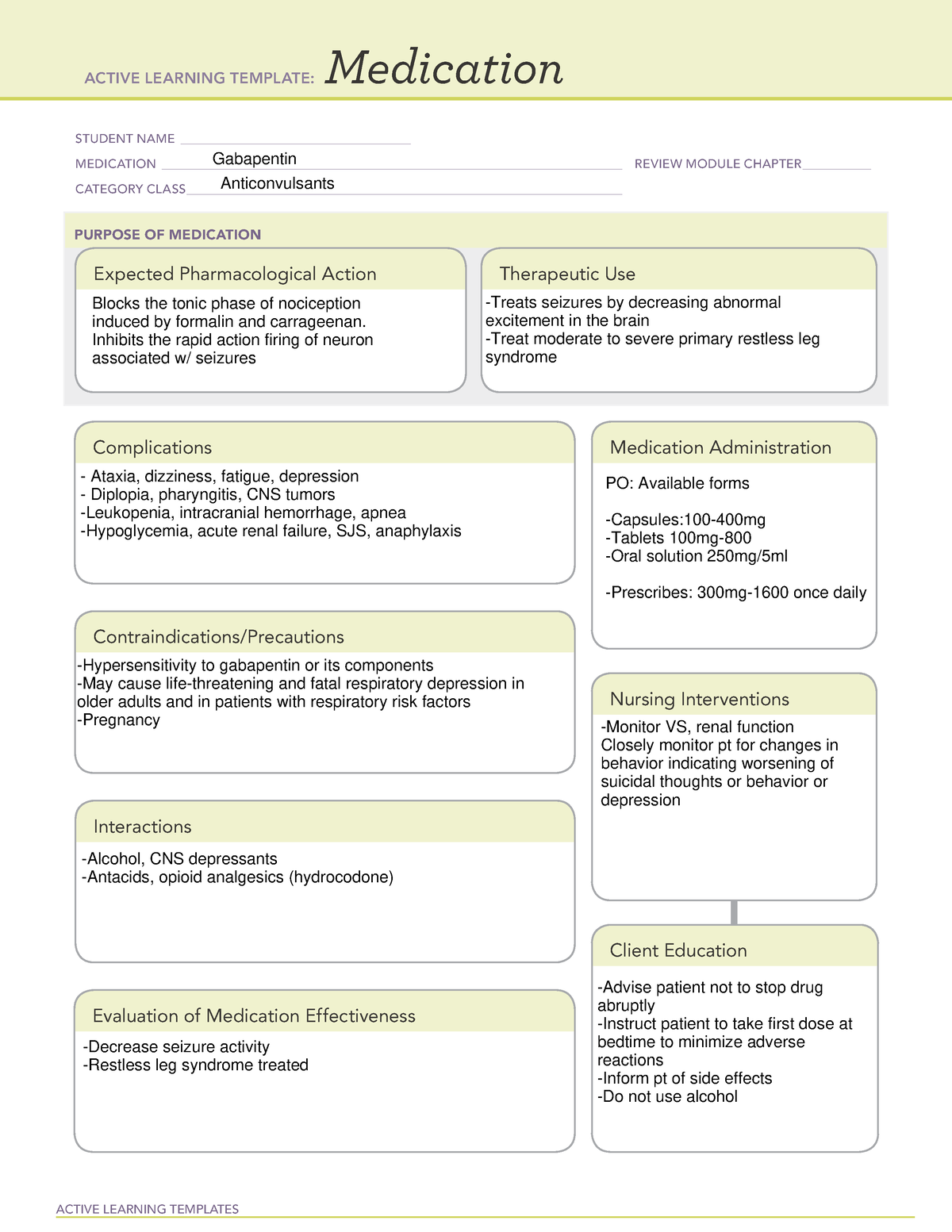
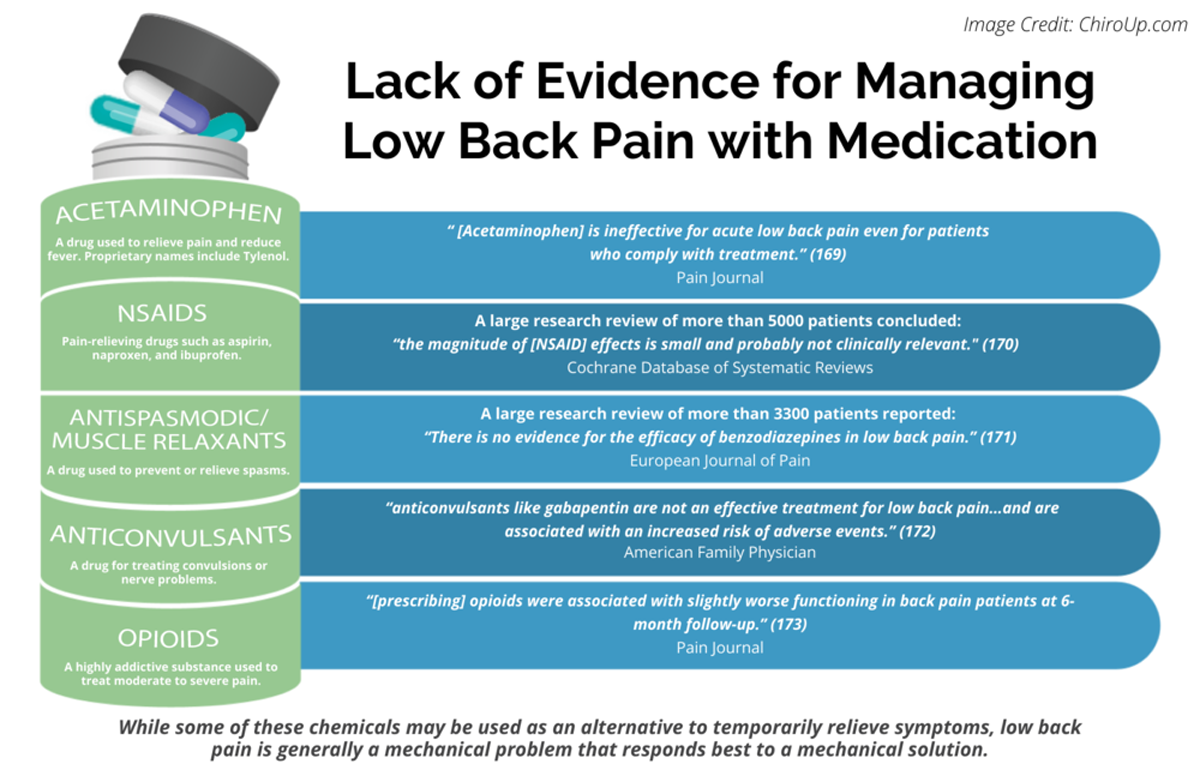
Antiseizure agents (also known as antiepileptic drugs or as anticonvulsants) are drugs used to manage epilepsy, the most prevalent neurological disorder. Antiseizure agents of choice depends on the type of epilepsy, age of the patient, patient tolerance, and specific patient characteristics. Table of Common Drugs and Generic Names Here is a table of commonly encountered antiseizure agents Indications for Use Gabapentin is used for partial seizures and neuropathic pain. Nursing Considerations Across the Lifespan This drug can cause harm to the fetus of pregnant women. Gabapentin use in pediatric patients with epilepsy 3 to 12 years of age is associated with the occurrence of central nervous system related adverse events. Gabapentin is a medication commonly prescribed to treat various conditions, including epilepsy, neuropathic pain, and restless legs syndrome. This guide aims to educate patients about important considerations, including dosage instructions, potential side effects, and precautions, to ensure safe and effective use of gabapentin. Learn about gabapentin, an anticonvulsant used for seizures and neuropathic pain, and its nursing implications. Find out how to assess, administer, monitor, and teach patients on gabapentin. Neurontin Pre-Administration Assessment: Post Administration Evaluation: Nursing Considerations: Gabapentin and Nursing: Key Considerations for Safe and Effective Patient Care Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant and analgesic medication commonly encountered in various clinical settings. Nurses play a vital role in ensuring its safe and effective use. It's crucial for nurses to have a comprehensive understanding of gabapentin's pharmacology, administration guidelines, potential adverse effects Generic Name Gabapentin Trade Name Neurontin Indication Seizures, peripheral neuropathy, neuropathic pain, prevention of migraines Action Exact method of action unknown, may play a role in stabilizing neural membranes Therapeutic Class Analgesic adjuncts, anticonvulsants, mood stabilizers Pharmacologic Class None Nursing Considerations • May cause suicidal thoughts, confusion, depression In this guide are five nursing diagnosis for seizures nursing care plans including their nursing interventions and nursing assessment. Nursing considerations Assessment History: Hypersensitivity to gabapentin; lactation, pregnancy Physical: Weight; T; skin color, lesions; orientation, affect, reflexes; P; R, adventitious sounds; bowel sounds, normal output Interventions Give drug with food to prevent GI upset. Arrange for consultation with support groups for people with epilepsy. Mechanism of action not understood; antiepileptic activity may be related to its ability to inhibit polysynaptic responses and block posttetanic potentiation. Introduction In this article, you’ll learn about Gabapentin (Neurontin) nursing implications and patient teachings. Also, its dosage, indication, contraindications, interactions, side effects, nursing assessment, and nursing interventions. What is Gabapentin? Gabapentin is a medication primarily used to treat neuropathic pain and epilepsy. It is also known under the brand names Neurontin and Gralise. As a nurse, understanding the uses, dosages, side effects, and patient education related to gabapentin is crucial for providing optimal care. Generic Name Gabapentin Trade Name Neurontin Indication Seizures, peripheral neuropathy, neuropathic pain, prevention of migraines Action Exact method of action unknown, may play a role in stabilizing neural membranes Therapeutic Class Analgesic adjuncts, anticonvulsants, mood stabilizers Pharmacologic Class None Nursing Considerations • May cause suicidal thoughts, confusion, depression Learn about gabapentin, a GABA analogue used for postherpetic neuralgia and seizures, and its nursing process considerations. Find out how to calculate dosage, monitor adverse effects, and avoid interactions with opioids. Gabapentin nursing interventions focus on seizure control, pain management, and adverse effect mitigation, utilizing pharmacological and non-pharmacological strategies to optimize patient outcomes and minimize side effects, ensuring safe and effective medication administration. Gabapentin Medication GridNCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health. Open Resources for Nursing (Open RN); Ernstmeyer K, Christman E, editors. Nursing Pharmacology [Internet]. 2nd edition. Eau Claire (WI): Chippewa Valley Technical College; 2023. This article provides an in-depth exploration of gabapentin from a nursing perspective, covering its classification, dosage, therapeutic actions, indications, adverse effects, contraindications, and critical nursing considerations, including assessment, interventions, and patient teaching. Implementation with Rationale These are vital nursing interventions done in patients who are antiseizure agents: Monitor for adverse effects and provide appropriate supportive care as needed to help patient cope with these effects. Monitor CBC results to detect bone marrow suppression early and provide prompt intervention. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication commonly prescribed for epilepsy, neuropathic pain, and various off-label uses. Understanding proper nursing considerations is crucial for safe and effective patient care. Interventions Guard against falls and trauma (hip fractures, head injury, and so forth), especially if gait and balance are affected by drowsiness, dizziness, or ataxia. Implement fall prevention strategies, especially if balance is impaired (See Appendix E).
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |