Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
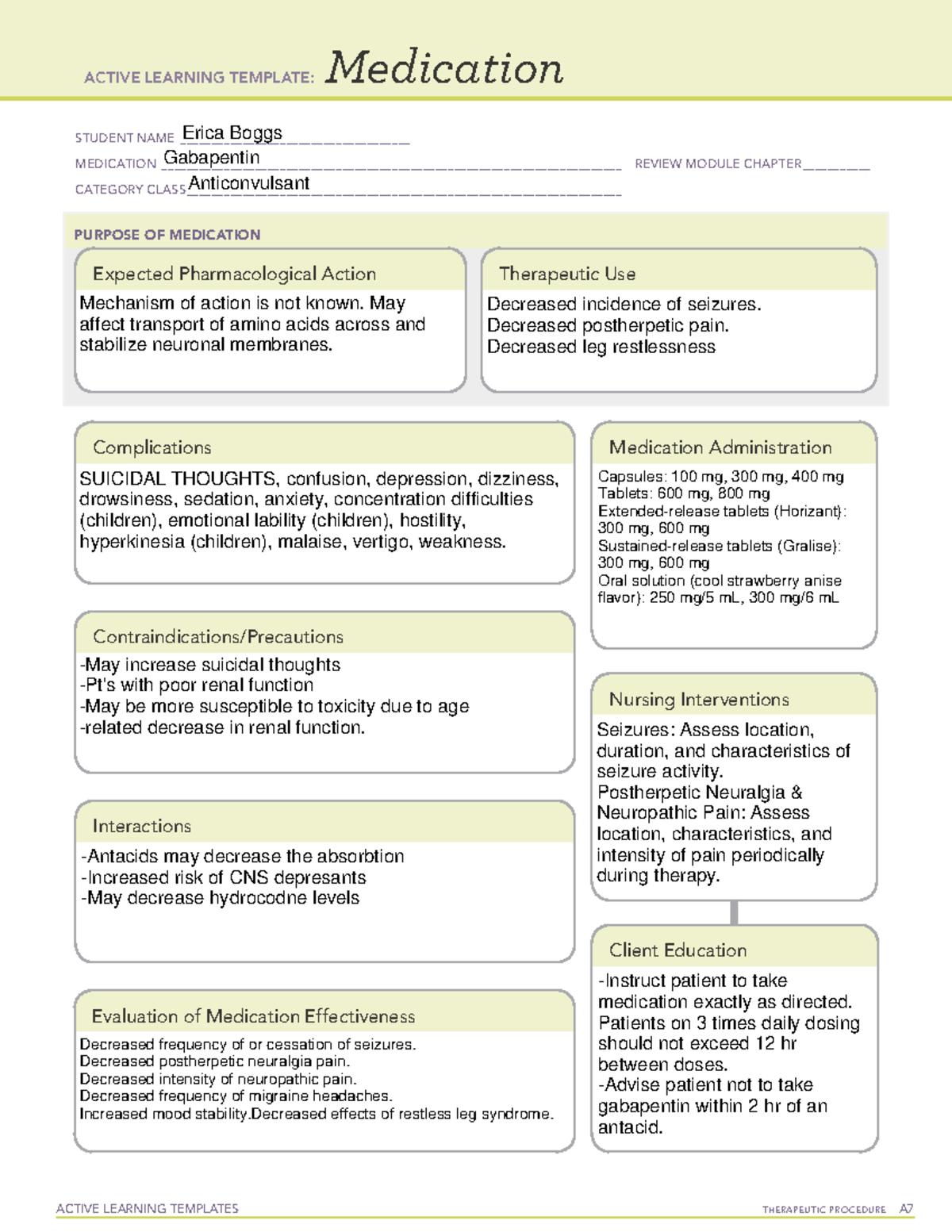
Level up your studying with AI-generated flashcards, summaries, essay prompts, and practice tests from your own notes. Sign up now to access Gabapentin: Uses, Effects, and Patient Education materials and AI-powered study resources. I don’t claim any copyright licensure home notes nursing pharmacology gabapentin considerations and patient teaching gabapentin considerations and patient Introduction In this article, you’ll learn about Gabapentin (Neurontin) nursing implications and patient teachings. Also, its dosage, indication, contraindications, interactions, side effects, nursing assessment, and nursing interventions. What is Gabapentin? Gabapentin is a medication primarily used to treat neuropathic pain and epilepsy. It is also known under the brand names Neurontin and Gralise. As a nurse, understanding the uses, dosages, side effects, and patient education related to gabapentin is crucial for providing optimal care. Gabapentin Nursing Considerations and implications. Learn monitoring, administration, and patient education for safe and effective therapy. Gabapentin Teaching 1979 SN instructed patient about Gabapentin ( Neurontin ). It is a medication used to treat epilepsy, neuropathic pain and hot flashes. It is also used for restless leg syndrome. It is a first line agent for the treatment of neuropathic pain arising from diabetic neuropathy, post-herpetic neuralgia, and central neuropathic pain. Most common side effects of gabapentin in Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center Gabapentin is a medication primarily used to treat partial seizures and neuropathic pain. As a nursing professional, understanding the nuances of gabapentin administration, its side effects, and patient education is crucial for providing high-quality care. Here are five tips for nurses when dealing with gabapentin: Gabapentin is a GABA neurotransmitter analog; however, it does not inhibit GABA uptake or degradation. It appears to interact with GABA cotical neurons, but its relationship to functional activity as an anti convulsant is unknown. Used in conjunction with other anticonvulsants to control certain types of seizures in patients with epilepsy. Effective in treating painful neuropaths. Patient education promotes medication adherence, enhances self-management skills, and empowers patients to actively participate in their pain management, fostering safer and more effective morphine use. Patient Teaching Associated with Gabapentin Advise the patient that gabapentin can be taken with or without food. Instruct to swallow extended-release tablets without breaking, crushing, dissolving, or chewing. Inform to take gabapentin at bedtime to minimize adverse effects. Do not suddenly stop gabapentin due to the increased risk of seizure. Nursing considerations Assessment History: Hypersensitivity to gabapentin; lactation, pregnancy Physical: Weight; T; skin color, lesions; orientation, affect, reflexes; P; R, adventitious sounds; bowel sounds, normal output Interventions Give drug with food to prevent GI upset. Arrange for consultation with support groups for people with epilepsy. If treating neuropathic pain or other pain syndromes (migraine, chronic pain, postherpetic neuralgia), use visual analogue scales and other appropriate pain scales to assess the patient's pain and help document the effects of drug therapy. If treating anxiety or bipolar disorder, monitor any changes in the patient's mood or behavior. Gabapentin may cause suicidal thoughts, ataxia, or lack of muscle control and depression with these things in mind, monitor your patient for changes and behavior and depression while on Gabapentin, make sure you assess seizure activity and pain level in your patient, teach your patient to take this medication exactly as it's directed and to Gabapentin Medication GridNCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health. Open Resources for Nursing (Open RN); Ernstmeyer K, Christman E, editors. Nursing Pharmacology [Internet]. 2nd edition. Eau Claire (WI): Chippewa Valley Technical College; 2023. Antiseizure agents (also known as antiepileptic drugs or anticonvulsants) are drugs used to manage epilepsy, the most prevalent neurological disorder. Antiseizure agents of choice depend on the type of epilepsy, age of the patient, patient tolerance, and specific patient characteristics. Antiseizure Agents: Generic and Brand Names Here is a table of commonly encountered antiseizure agents Monitor pt closely for changes in behavior and depression Assess seizure activity Assess pain level Patient should take medications exactly as prescribed Evaluation The nurse promotes safe and effective relief of pain through assessment, patient education, and monitoring for therapeutic and adverse effects of gabapentin. By understanding gabapentin’s pharmacology, indications, and nursing considerations, healthcare professionals can optimize treatment outcomes and enhance patient quality of life. Continuous vigilance, patient-centered education, and interdisciplinary collaboration are key to successful gabapentin therapy. Gabapentin is a medication commonly prescribed to treat various conditions, including epilepsy, neuropathic pain, and restless legs syndrome. This guide aims to educate patients about important considerations, including dosage instructions, potential side effects, and precautions, to ensure safe and effective use of gabapentin.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |