Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
+Analgesic+similar+to+gabapentin.jpg) |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
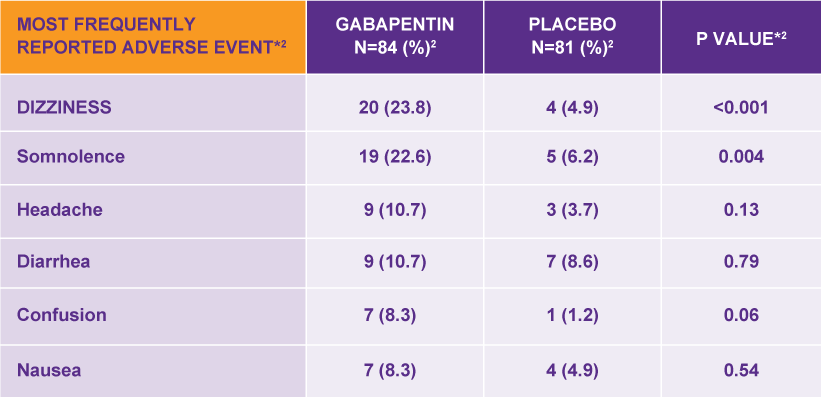 |  |
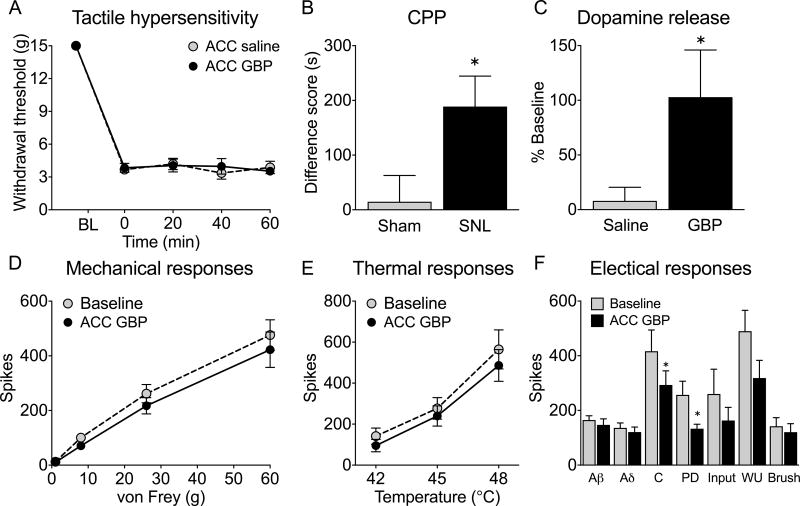
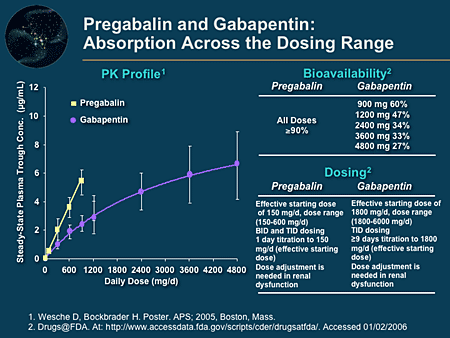
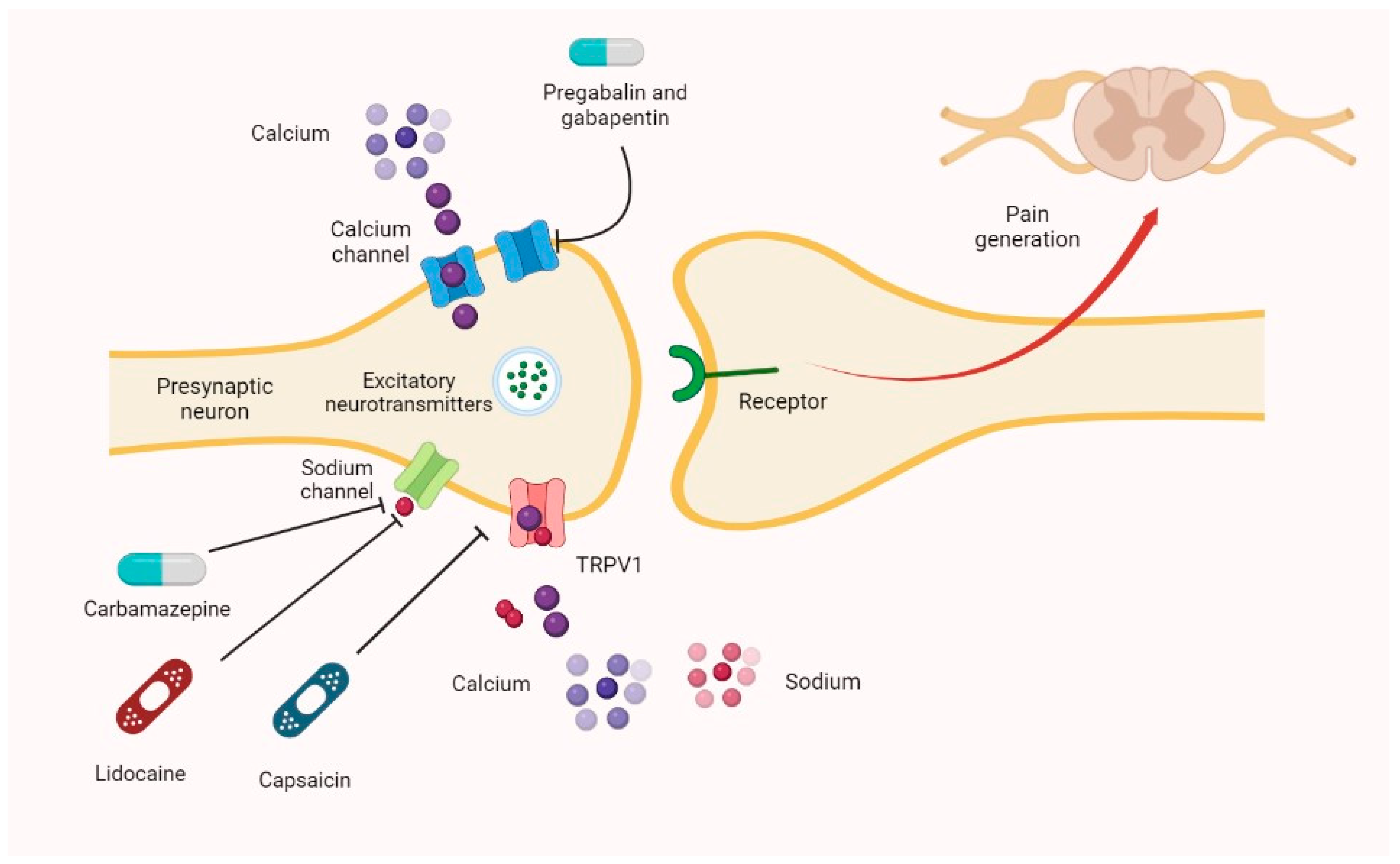
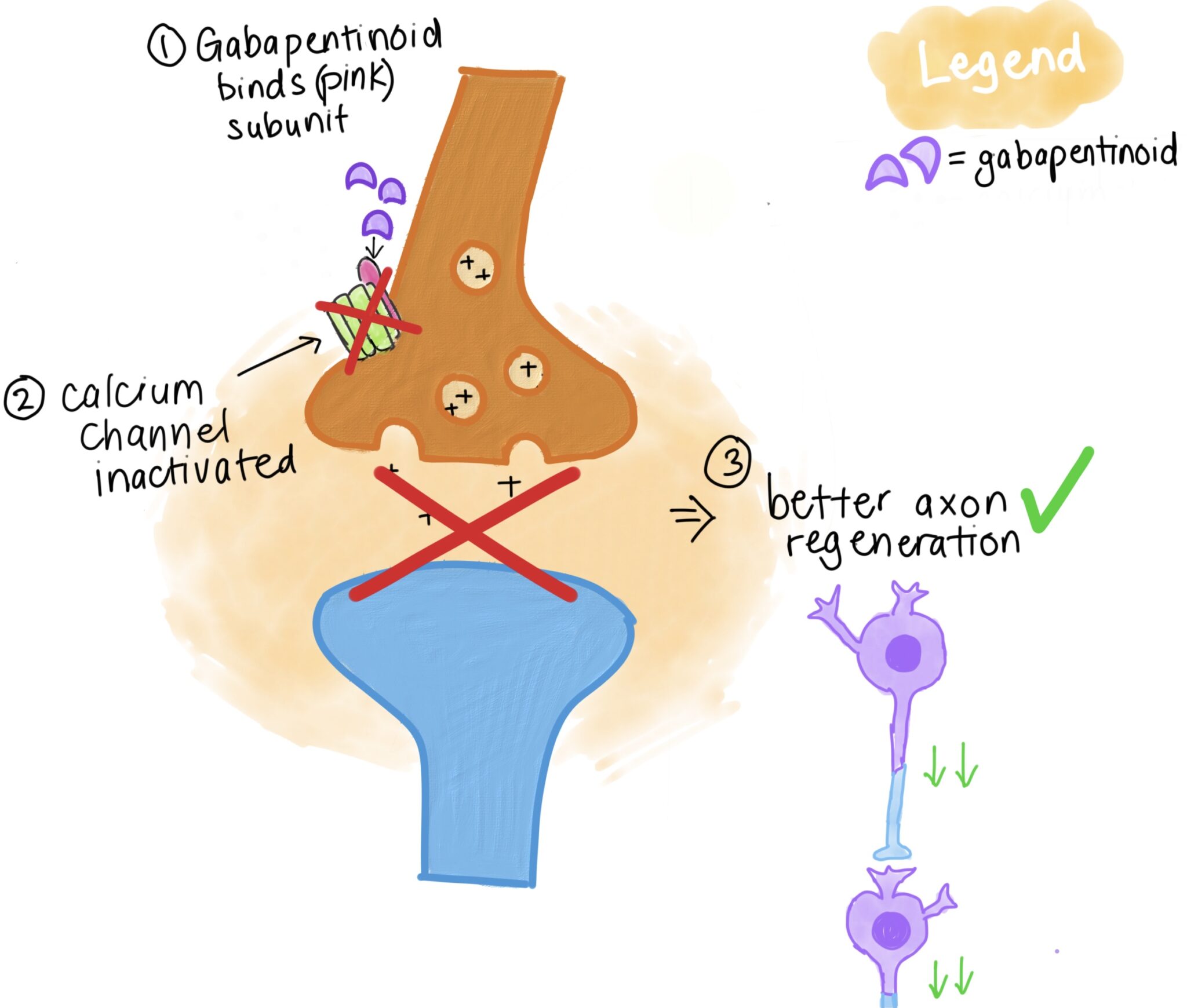
When used to treat a type of seizure disorder, called a partial onset seizure, gabapentin decreases the abnormal activity in the brain that causes the seizures. When used to treat nerve pain, or neuralgia, following a herpes zoster (shingles) infection, gabapentin may reduce the response to painful stimuli. Gabapentin for Neuropathic Pain Background for FF #49: Gabapentin (Neurontin) is an antiepileptic that has FDA indication to treat postherpetic neuralgia and partial onset seizures. This Fast Fact will review gabapentin’s role in neuropathic pain. See Fast Fact #289 for a comparison of gabapentin with pregabalin, a similar neuropathic analgesic. Gabapentin (GBP) is a Health Canada approved antiepileptic drug. 5 In the UK, GBP is licensed for the treatment of peripheral and central neuropathic pain in adults and in the US it is marketed for post-herpetic neuralgia (PHN). 3 The mechanism of action for GBP relates to its ability to bind with high-affinity to the alpha-2-delta subunit of There is limited evidence for the effect of gabapentin on other NP conditions including: chronic lower back pain, fibromyalgia, mixed NP, trigeminal neuralgia, nerve injury pain, and HIV-associated neuropathy. Further high-quality studies would reduce uncertainty regarding the effectiveness of gabapentin for those indications. Oral gabapentin (1200-3600 mg/d for 4-12 weeks) for patients with moderate or severe neuropathic pain from postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) or painful diabetic neuropathy (PDN) is associated with pain reduction of at least 50% in 14% to 17% more patients than placebo. Abstract This paper reviews the pharmacology and clinical effectiveness of gabapentin in the treatment of neuropathic pain. Gabapentin has antihyperalgesic and antiallodynic properties but does not have significant actions as an anti-nociceptive agent. Its mechanisms of action appear to be a complex synergy between increased GABA synthesis, non-NMDA receptor antagonism and binding to the Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant with pain-relieving effects that may be used to treat partial-onset seizures or relieve nerve pain. Research has shown gabapentin binds strongly to a specific site (called the alpha2-delta site) on voltage-gated calcium channels and this is thought to be the way gabapentin works to relieve nerve pain and lower Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication used in the management of peripheral neuropathic pains, postherpetic neuralgia, and partial-onset seizures. Includes Gabapentin indications, dosage/administration, pharmacology, mechanism/onset/duration of action, half-life, dosage forms, interactions, warnings, adverse Gabapentin [1- (aminomethyl)cyclohexane acetic acid] is␣a␣novel anti-epileptic agent, originally developed as a gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-mimetic compound to treat spasticity, and has been shown to have potent anticonvulsive effects [1, 2]. Initially approved only for use in partial seizures, it soon showed promise in the treatment of chronic pain syndromes, especially neuropathic Introduction The gabapentinoid drugs gabapentin and pregabalin are antiepileptic drugs that are considered as first-line treatments for the management of neuropathic pain. 1 Pregabalin is also approved for generalised anxiety disorders in the United Kingdom. The mechanisms of action are still unclear despite their widespread use. Identify the appropriate indications for gabapentin therapy, including neuropathic pain, partial onset seizures, restless legs syndrome, and other relevant neurological and psychiatric conditions. Gabapentin typically takes 1 to 2 hours to start working, but full effects may take several days to reach. Gabapentin, often prescribed for neuropathic pain, seizures, and restless leg syndrome, has become a common choice for many seeking relief. Understanding how long it takes for gabapentin to take effect is crucial for those using it for the first time or adjusting their dosage. The onset Gabapentin [1- (aminomethyl)cyclohexane acetic acid] is␣a␣novel anti-epileptic agent, originally developed as a gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-mimetic compound to treat spasticity, and has been shown to have potent anticonvulsive effects [1, 2]. Initially approved only for use in partial seizures, it soon showed promise in the treatment of chronic pain syndromes, especially neuropathic It can take one to two weeks to feel the full effects of Gabapentin for nerve pain. Some people use this medication long-term. Learn how long you should take Gabapentin for nerve pain. Background: Gabapentin is commonly used to treat neuropathic pain (pain due to nerve damage). This review updates a review published in 2014, and previous reviews published in 2011, 2005 and 2000. Objectives: To assess the analgesic efficacy and adverse effects of gabapentin in chronic neuropathic pain in adults. Search methods: For this update we searched CENTRAL), MEDLINE, and Embase for Gabapentin is commonly used to treat neuropathic pain (pain due to nerve damage). This review updates a review published in 2014, and previous reviews published in 2011, 2005 and 2000. To assess the analgesic efficacy and adverse effects of
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
+Analgesic+similar+to+gabapentin.jpg) |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |