Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
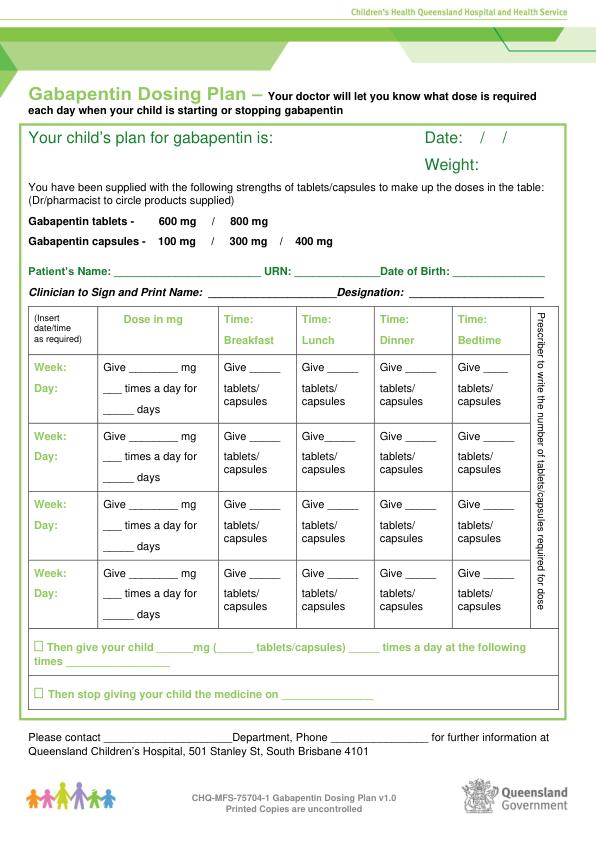 |  |
If you think there has been an overdose, call your poison control center or get medical care right away. Be ready to tell or show what was taken, how much, and when it happened. Consumer Information Use and Disclaimer This generalized information is a limited summary of diagnosis, treatment, and/or medication information. UpToDate UpToDate Gabapentin (Neurontin) is most often abused in conjunction with other drugs and can cause adverse side effects. Learn about Gabapentin overdose risks. View gabapentin information, including dose, uses, side-effects, renal impairment, pregnancy, breast feeding, monitoring requirements and important safety information. Gabapentin is a medication often prescribed for anxiety, nerve pain, and seizures. However, it can be addictive and lead to overdose. Learn more here. Clinicians have limited experience with assessment and treatment of overdose from newer anticonvulsant medications. The aim of this investigation was to evaluate clinical effects of newer anticonvulsant overdose, determine if a relationship exists Gabapentin Overdose in a Pediatric Patient: A Potentially Underdiagnosed but Serious Cause of Persistent Hypoglycemia Linh Nguyen, DO; James Carrington, DO; Jane Benson, MD; Lisa Awe, MD Nemours Children’s Health and University of Florida A potentially lethal overdose can begin at about 49 grams. A standard gabapentin dose is about 50 mg per day for children and about 300mg to 600mg for those 12 and older. However, the exact amount of grams that result in overdose can change depending on if the gabapentin is mixed with other substances, such as drugs or alcohol. Discover the risks of gabapentin overdose. Learn the signs, actions to take, and prevention strategies for a safer experience. Toxicity from gabapentin and pregabalin overdose is commonly encountered. Treatment is supportive, and the use of extracorporeal treatments (ECTRs) is controversial. The EXTRIP workgroup conducted systematic reviews of the literature and summarized findings following published methods. Thirty-three articles (30 patient reports and 3 pharmacokinetic studies) met the inclusion criteria. High Gabapentin overdoses can be dangerous, especially when it’s used alongside other substances. Learn how to avoid a gabapentin overdose and what to do about one. Results: There were 20 cases with gabapentin as the sole substance in doses ranging from 50 mg to 35 g. Ten of the 20 cases involved children and adolescents. Clinical effects developed early and resolved within 10 hours in most patients. Seven cases were managed in the home with only observation. Four of these patients remained asymptomatic. The amino acid antiepileptic medication (AED) gabapentin (GBP) is authorized for adjunctive use in the treatment of partial seizures in adults and children over the age of 12, whether or not they progress to secondary generalization Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and glutamate ratios may be increased through biochemical effects, ion-channel Neurontin (gabapentin) is a medication that is used for several different conditions such as nerve pain, epilepsy, and many others. While overdoses with gabapentin are rare, it is important to know the symptoms of an overdose and the risk factors that increase the likelihood of an overdose. To avoid an overdose, take gabapentin as directed. Abstract Introduction: Gabapentin and pregabalin (gabapentinoids) are increasingly prescribed to children and adolescents off label for various conditions despite limited data and concerns for adverse outcomes including misuse and overdose. The extent of gabapentinoid use in children and adolescents is unknown. Gabapentin is a relatively safe drug, but it should not be ingested in large amounts. Learn the possibility of gabapentin overdose and its serious withdrawal side effects. Overdose with newer anticonvulsant agents include: Gabapentin, Lamotrigine, Levetiracetam, Oxcarbazepine, Pregabalin, Tiagabine, Topiramate and Vigabatrin. These medications can cause lethargy or agitation in overdose, increase risk of death combined with opioids, and manifest a withdrawal syndrome. This topic will discuss the evaluation and management of gabapentinoid poisoning and withdrawal. A summary table to facilitate emergency management is provided (table 1). The therapeutic dose of gabapentin falls between 800 mg and 1,800 mg per day, but 3,600 mg daily may be used in certain cases. [11] Taking higher doses than prescribed, taking gabapentin more frequently than prescribed, or mixing gabapentin with other drugs can increase the risk of overdose – particularly central nervous system depressants like benzodiazepines, opioids, and alcohol. From 2000 to 2014, drug overdose deaths increased 137% in the United States, and 61% of these deaths included some form of opiate. The vast majority of opiate-related drug fatalities include multiple drugs, although there is scant data
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |