Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
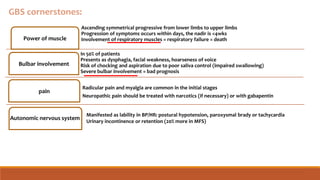 |  |
Orthostatic hypotension is a frequent cause of falls and syncope, impairing quality of life. It is an independent risk factor of mortality and a common cause of hospitalizations, which exponentially increases in the geriatric population. We present a management plan based on a systematic literature review and understanding of the underlying pathophysiology and relevant clinical pharmacology The perioperative use of gabapentin is dis-cussed, previous reports of intraoperative hypotension re-lated to its use reviewed, and its potential role in periop-erative BP changes presented. This page includes the following topics and synonyms: Medication Causes of Orthostatic Hypotension, Orthostatic Hypotension due to Medication, Drug-Induced Orthostatic Hypotension, Drug-Induced Hypotension, Drug-Induced Syncope, Medication-Induced Syncope. Orthostatic hypotension (OH) is an abnormal blood pressure response to standing, which is associated with an increased risk of adverse outcomes such as syncope, falls, cognitive impairment, and mortality. Medical therapy is one the most common Orthostatic hypotension is defined as a decrease in blood pressure of 20 mm Hg or more systolic or 10 mm Hg or more diastolic within three minutes of standing from the supine position or on Introduction Orthostatic hypotension (OH), defined as a reduction in systolic blood pressure (BP) of 20 mm Hg or diastolic BP of 10 mm Hg within 3 minutes of assuming an erect posture [1], is estimated to affect 30% to 70% of older adults [2] and is commonly associated with use of med-ications [3]. Neurogenic orthostatic hypotension (OH) is a disabling disorder caused by impairment of the normal autonomic compensatory mechanisms that maintain upright blood pressure. Nonpharmacologic treatment is always the first step in the management of this Orthostatic hypotension is a chronic, debilitating illness that is difficult to treat. The therapeutic goal is to improve postural symptoms, standing time, and function rather than to achieve upright normotension, which can lead to supine The symptom complex in orthostatic hypotension consisting of lightheadedness, dizziness, or faintness occurring with prolonged standing is called chronic orthostatic intolerance. These symptoms may also be associated with an exaggerated tachycardia but no fall in blood pressure, a disorder called the postural tachycardia syndrome (POTS). Drug-induced orthostatic hypotension is an important clinical problem. When symptomatic, it is poorly tolerated by the patient, and can be a cause for discontinuing treatment. It may have more serious consequences if it leads to syncope, falls and injury, or to sustained loss of perfusion of vital o Orthostatic hypotension (OH) is an abnormal blood pressure response to standing, which is associated with an increased risk of adverse outcomes such as syncope, falls, cognitive impairment, and mortality. Medical therapy is one the most common causes of OH, since numerous cardiovascular and psychoactive medications may interfere with the blood pressure response to standing, leading to drug Orthostatic hypotension tends to be worse early in the morning because of nighttime pressure diuresis with volume depletion (discussed later in this article), and the diagnosis of orthostatic hypotension is hence more readily made in the morning 27. The diagnosis of orthostatic hypotension is easily confirmed at the bedside with orthostatic vitals. Neurogenic orthostatic hypotension, postprandial hypotension and exercise-induced hypotension are common features of cardiovascular autonomic failure. Despite the serious impact on patient’s quality of life, evidence-based guidelines for Chronic orthostatic hypotension (OH) is a common, often underdiagnosed, disorder, defined by an excessive fall in blood pressure (BP) with standing. OH can be associated with postural lightheadedness, dizziness, fatigue, coat hanger pain, and, in extreme situations, syncope, falls, and injuries. OH is associated with increased risk of cardiovascular and total mortality. 1–4 Management Cini Bhanu and colleagues evaluate the extent to which different drug groups are associated with orthostatic hypertension in this systematic review and meta-analysis. View gabapentin information, including dose, uses, side-effects, renal impairment, pregnancy, breast feeding, monitoring requirements and important safety information. Do you take Gabapentin and are concerned about Orthostatic hypotension? eHealthMe's data-driven phase IV clinical trials have been referenced on 800+ peer-reviewed medical publications including The Lancet, Mayo Clinic Proceedings, and Nature. Check whether Orthostatic hypotension is associated with a drug or a condition. Data on chronic opioid treatment are limited, but hypotension, orthostatic hypotension, and syncope are commonly reported among potential adverse effects of most opioid analgesics, such as morphine, buprenorphine, fentanyl, oxycodone, and tapentadol [55 •]. Yet, the mechanism underlying opioid-mediated hypotension still remains a matter of Oral and intravenous gabapentin can markedly attenuate blood pressure (BP) in hypertensive rats. The nucleus tractus solitarii (NTS) is the primary integrative center for cardiovascular control and other autonomic functions in the central nervous Orthostatic hypotension is a frequent cause of falls and syncope, impairing quality of life. It is an independent risk factor of mortality and a common cause of hospitalizations, which exponentially increases in the geriatric population. We present a management plan based on a systematic literature review and understanding of the underlying pathophysiology and relevant clinical pharmacology
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |