Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
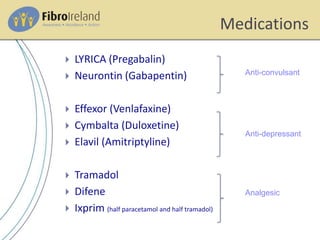
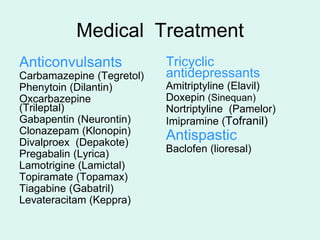
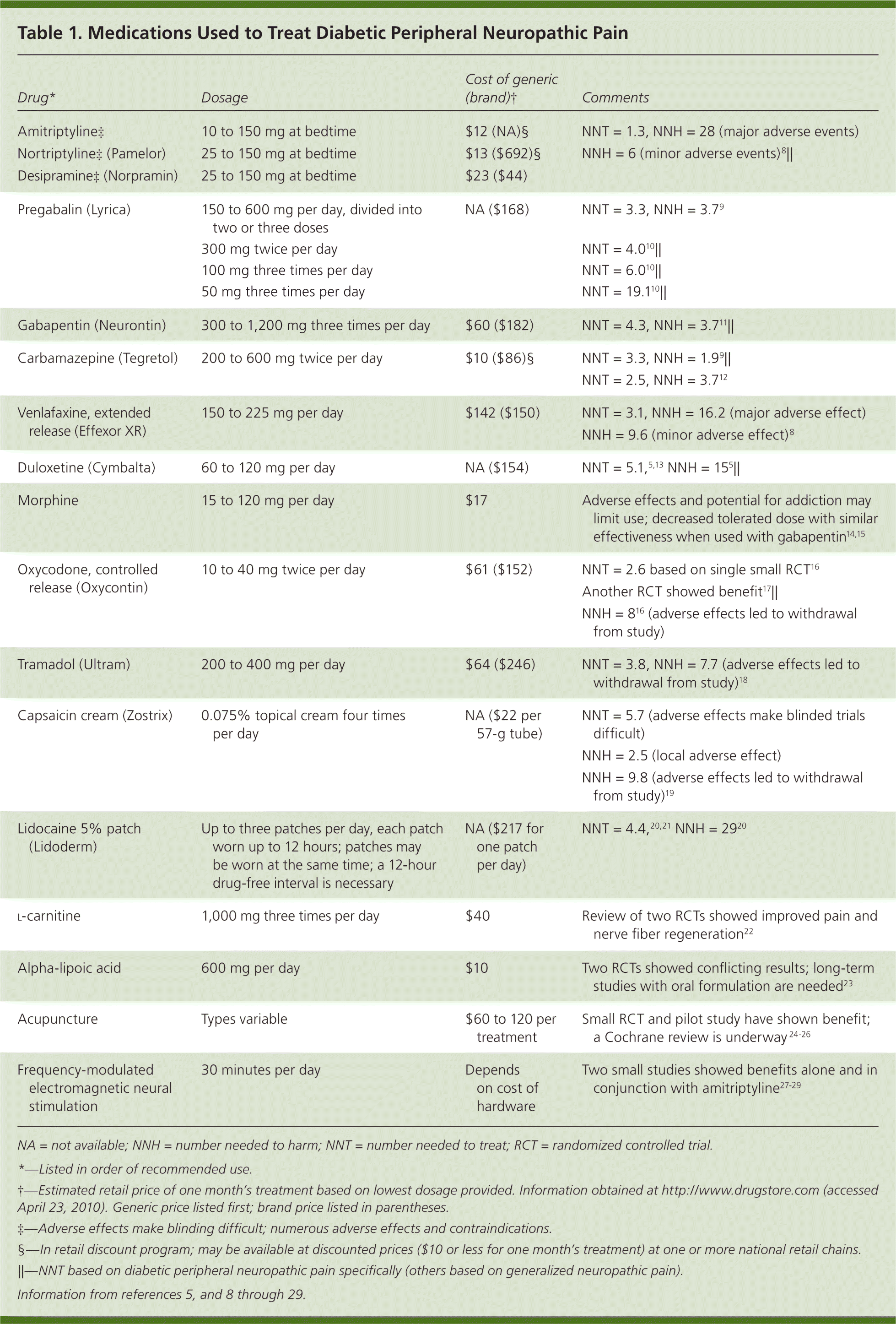
In a clinical study conducted by Chakrabarty and colleagues, the efficacy of pregabalin (150 mg) monotherapy, amitriptyline (25 mg) monotherapy, and low-dose pregabalin (75 mg) plus amitriptyline (10 mg) as combination therapy for reducing NP symptoms was investigated [110]. Amitriptyline is in the tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) drug classification and acts by blocking the reuptake of both serotonin and norepinephrine neurotransmitters. Amitriptyline is an FDA-approved medication to treat depression in adults. The non-FDA approved indications are anxiety, post-traumatic stress disorder, insomnia, chronic pain (diabetic neuropathy, fibromyalgia), irritable bowel Commonly prescribed drugs for management of neuropathic pain, such as amitriptyline, pregabalin, and gabapentin are preferred at lower doses in Indian clinical settings. Acceptable efficacy and low tolerance to the standard dosage is believed to be the reason behind the prescribed dose. Diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain (DPNP) is common and often distressing. Most guidelines recommend amitriptyline, duloxetine, pregabalin, or gabapentin as initial analgesic treatment for DPNP, but there is little comparative evidence on which one is best or whether they should be combined. We aimed to assess the efficacy and tolerability of different combinations of first-line drugs for Amitriptyline is used to treat symptoms of depression. Amitriptyline is in a class of medications called tricyclic antidepressants. It works by increasing the amounts of certain natural substances in the brain that are needed to maintain mental balance. This page from Great Ormond Street Hospital (GOSH) explains about medicines used to treat neuropathic pain – pain caused by the nerves sending wrong signals to and from the brain. At GOSH, we mainly use amitriptyline, gabapentin and pregabalin, although o TCAs with gabapentin, pregabalin and commonly used antidepressants Amitriptyline or nortriptyline (at doses recommended in this guideline) may safely be added to the following: Pregabalin outperforms Gabapentine and Amitriptyline in terms of the Numeric Pain Rating Scale (NPRS) score. Gabapentine has fewer reported side effects, resulting in higher long-term patient compliance. Amitriptyline alleviates painful diabetic neuropathy. It is recommended by a variety of guidelines as a first or second-line treatment. [13] It is as effective for this indication as gabapentin or pregabalin but less well tolerated. [28] Amitriptyline is as effective at relieving pain as duloxetine. Combination treatment of amitriptyline and pregabalin offers additional pain relief for people NICE found consistent evidence showing that compared with placebo, amitriptyline, duloxetine, gabapentin, and pregabalin are effective at reducing neuropathic pain and are safe and cost-effective. The main objective is to compare efficacy and safety of pregabalin and amitriptyline monotherapy with their low-dose combination in patients of neuropathic pain (NeuP). In this parallel-group, open-label interventional study at the Neurology We aim to compare the effects of pregabalin with low-dose amitriptyline and gabapentin with low-dose amitriptyline in managing neuropathic pain in cancer patients undergoing palliative care. Gabapentin and pregabalin are similar drugs but differ in several distinct ways. The main differences are their indications—specific uses that the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved them to treat—and their dosages. Neuropathic pain is difficult to diagnose and difficult to treat with certainty. So the aim of the study was to evaluate comparative clinical efficacy of pregabaline with amitriptyline and gabapentin in neuropathic cancer pain. Find patient medical information for Amitriptyline (Amitid, Elavil, Endep) on WebMD including its uses, side effects and safety, interactions, pictures, warnings, and user ratings Amitriptyline is an effective antidepressant but it may cause drowsiness initially and a withdrawal syndrome with abrupt discontinuation. It may be used off-label to treat other conditions such as more. Pregabalin is used in the treatment of nerve pain and also to prevent seizures. Gabapentin, pregabalin, and amitriptyline demonstrate similar effectiveness in alleviating neuropathic (NeP) pain. The study concludes that gabapentin is superior to both pregabalin and amitriptyline with fewer adverse effects, leading to improved patient adherence for long-term use. Amitriptyline is a tricyclic antidepressant used to treat depression and, off-label, conditions like insomnia, anxiety, migraines, and chronic pain. Common side effects of Amitriptyline include: drowsiness, dizziness, dry mouth, blurred vision, constipation, weight gain, and trouble urinating Serious side effects of Amitriptyline include: easy bruising, unusual bleeding, persistent heartburn, shaking, mask-like facial expressions, muscle spasms, severe stomach pain, decreased sexual ability or desire, enlarge or painful breasts, black Both gabapentin and amitriptyline are good nerve pain relievers. Amitriptyline can be better for some patients because of the convenient dosing schedule. On the other hand, most patients prefer gabapentin (the relatively newer medication) over amitriptyline due to less anticholinergic effects (dry mouth, constipation) and less sedation.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |