Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
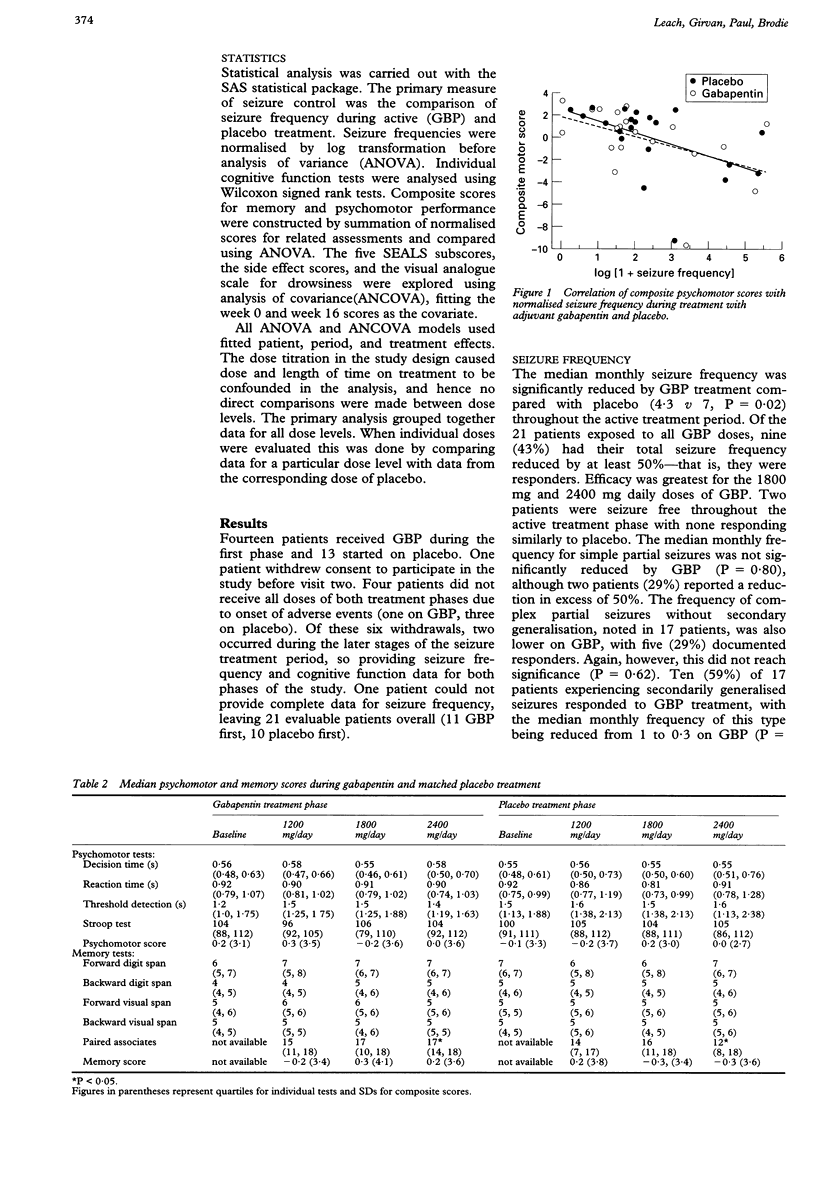
Abstract Background: There is a great need in the treatment of schizophrenia for a drug, or drug combinations, to improve clinical response with fewer serious side effects. The objective of this study was to explore the therapeutic effects and tolerability of the anticonvulsant gabapentin as an adjunctive in the treatment of patients with partially responsive schizophrenia. 4. Jablonowski K, Margolese HC, Chouinard G. Gabapentin-induced paradoxical exacerbation of psychosis in a patient with schizophrenia. Can J Psychiatry 2002; 47: 975–976. FROM THE EDITOR To keep up-to-date with the voluminous psychiatric literature, I scan many psychiatric and neuroscience publications in search of articles that pull me in for a deeper look. Recently, I skimmed the titles of a weekly email newsletter I receive and was immediately drawn to the first article: “Before You Prescribe Gabapentin, Consider These Risks.” 1 The first sentence of the Gabapentin is commonly used off-label in the treatment of psychiatric disorders with success, failure, and controversy. A systematic review of the literature was performed to elucidate the evidence for clinical benefit of gabapentin in psychiatric disorders. 2 There are vari- ous reports where gabapentin is found efficacious in patients with schizophrenia for treatment augmentation and management of aggressive and impulsive This article reviews evidence-based psychiatric uses of gabapentin, along with associated risks. An extensive literature review was conducted, primarily of articles searchable in PubMed, relating to psychiatric uses, safety, and adverse effects of Exploring the potential benefits and drawbacks of using gabapentin as a treatment for schizophrenia. Abstract Despite its prevalence and disease burden, several chasms still exist with regard to the pharmacotherapy of bipolar disorder (BD). Polypharmacy is commonly encountered as a significant proportion of patients remain symptomatic, and the management of the depressive phase of the illness is a particular challenge. Gabapentin and pregabalin have often been prescribed off-label in spite of These reports illustrate the breadth of GABA-related abnormalities in schizophrenia, with alterations identified in multiple brain regions using a variety of techniques. Thus, it appears timely to comment on certain aspects of what we currently know, and do not know, about GABA neurotransmission in the disease process of schizophrenia. Abstract Background There is a great need in the treatment of schizophrenia for a drug, or drug combinations, to improve clinical response with fewer serious side effects. The objective of this study was to explore the therapeutic effects and tolerability of the anticonvulsant gabapentin as an adjunctive in the treatment of patients with partially responsive schizophrenia. Methods Ten The most common side effects of gabapentin include somnolence, ataxia, and fatigue. However, no studies have reported gabapentin induced psychotic disorder. Gabapentin is commonly used off-label in the treatment of psychiatric disorders with success, failure, and controversy. A systematic review of the literature was performed to elucidate the evidence for clinical benefit of gabapentin in psychiatric Gabapentin-Induced Paradoxical Exacerbation of Psychosis in a Patient With Schizophrenia Dear Editor: Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant that is in-creasingly prescribed to patients with schizophrenia (1). Uses of anticonvul-sants in this population have traditionally included antipsychotic augmentation and control of aggression and impulsivity (1). This article presents the negative side effects of gabapentin such as psychotic and depressive symptoms, which occur shortly after its use. The use of gabapentin in mood disorders is discussed through these side effects. We study how severe was Schizophrenia, when it was recovered, drug effectiveness, race, and more among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin) - Gabapentin adjunctive to risperidone or olanzapine in partially responsive schizophrenia: an open-label pilot study Adel GabrielDepartments of Psychiatry and Community Health Sciences, University of Calgary, Alberta, CanadaBackground: There is a great need in the treatment of schizophrenia for a drug, or drug ­combinations, to improve clinical response with fewer serious side effects. The Summary: Schizophrenia is reported as a side effect among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin), especially for people who are female, 30-39 old, have been taking the drug for 1 - 6 months also take Sertraline, and have Hair loss. The phase IV clinical study analyzes which people have Schizophrenia when taking Gabapentin, including time on the drug, (if applicable) gender, age, co-used drugs In addition to being used to treat pain, gabapentin is used off label to treat anxiety, alcohol use disorder (AUD), alcohol withdrawal, depression, substance use disorders (SUDs), sleep problems, and more. However, the data to support these off-label uses of gabapentin are mixed, especially for long-term use. This article examines the role of gabapentin in antipsychotic treatment, discussing its effectiveness, potential side effects, and how it can be used in conjunction with other medications to manage symptoms of schizophrenia and other psychiatric disorders. Cyclohexanecarboxylic Acids / therapeutic use* Drug Administration Schedule Drug Resistance Drug Therapy, Combination Gabapentin Haloperidol / therapeutic use Humans Male Schizophrenia / drug therapy* Schizophrenic Psychology Treatment Outcome Violence / prevention & control Violence / psychology gamma-Aminobutyric Acid / therapeutic use*
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |