Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
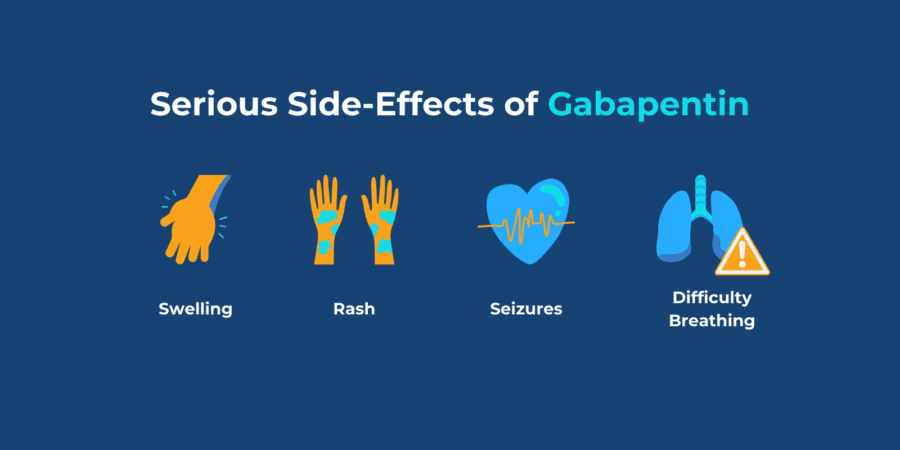
What are the side-effects of gabapentin (Neurontin)? Pharmacologic class: gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) analogue. Therapeutic class: anticonvulsant, antineuralgic. Pregnancy category: C. Epilepsy dosage. Adults: PO: 300mg TDS. Maintenance dose: 900 – 1800mg/day in 2 to 3 divided doses. Children (3-12yrs): PO: 10 – 15mg/day in 3 divided doses. What is Gabapentin? Gabapentin is a medication primarily used to treat neuropathic pain and epilepsy. It is also known under the brand names Neurontin and Gralise. As a nurse, understanding the uses, dosages, side effects, and patient education related to gabapentin is crucial for providing optimal care. Gabapentin (Neurontin) MoA: Increases release of GABA into the synapse. Indications: Seizures Side Effects: Fatigue, Xerostomia, Dizziness Drug Interactions: Antacids Nursing Implications: Monitor for possible suicidal ideation. Educate Patient on reporting changes in vision, hallucinations, and fever to their healthcare provider. Gabapentin Medication GridNCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health. Open Resources for Nursing (Open RN); Ernstmeyer K, Christman E, editors. Nursing Pharmacology [Internet]. 2nd edition. Eau Claire (WI): Chippewa Valley Technical College; 2023. Therapeutic Effects: Decreased incidence of seizures. Decreased postherpetic pain. CNS: confusion, depression, drowsiness, sedation, anxiety, concentration difficulties (children), dizziness, emotional lability (children), hostility, hyperkinesia (children), malaise, vertigo, weakness. EENT: abnormal vision, nystagmus. CV: hypertension. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsive medication that received approval from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1993 and has been available in generic form in the USA since 2004. Gabapentin was originally used as a muscle relaxant and an anti-spasmodic. However, it was later discovered that gabapentin has the potential of an anticonvulsive medication and can be used as an adjunct to more Advice for mothers using Gabapentin while breastfeeding. Includes possible effects on breastfed infants and lactation. Inform the patient this drug may cause joint, muscle, or bone pain. Immediately report signs of depression, suicidal thoughts, or unusual behavior. Advise avoiding alcohol intake. Recommend to always carry identification noting seizure disorder/anticonvulsant therapy. Potential Side Effects of Gabapentin: 1. Drowsiness: Gabapentin can cause drowsiness and impair cognitive function. Nurses should assess patients for any signs of excessive sedation and advise them to avoid activities that require mental alertness. 2. Dizziness: Patients taking Gabapentin may experience dizziness. Patient/caregiver was educated on side effects of gabapentin as follows: General allergic reactions: Gabapentin use can result in general allergic reactions, such as, skin rashes, hives, and itching. Educate the patient about potential side effects of gabapentin, such as drowsiness, dizziness, or coordination difficulties. By providing information about potential side effects, patients can make informed decisions about their treatment. Check with your doctor immediately if any of the following side effects occur while taking gabapentin: More common in children. Some side effects of gabapentin may occur that usually do not need medical attention. These side effects may go away during treatment as your body adjusts to the medicine. Gabapentin is generally well-tolerated, but it can cause a range of side effects that nurses must monitor. Mood Changes: Including depression, anxiety, and suicidal thoughts. Severe Allergic Reactions: Such as rash, itching, or anaphylaxis. Respiratory Depression: Particularly when combined with other CNS depressants. Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center Gabapentin administration requires meticulous nursing care. Nurses ensure proper medication administration, closely monitor side effects such as drowsiness and dizziness, and assess for drug interactions. Patient education is crucial to promote adherence and minimize adverse effects. Nurses vigilantly monitor patients for respiratory depression, especially when gabapentin is used with other Gabapentin is approved to prevent and control partial seizures, relieve postherpetic neuralgia after shingles and moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome. Learn what side effects to watch for, drugs to avoid while taking gabapentin, how to take gabapentin and other important questions and answers. Evaluation The nurse promotes safe and effective relief of pain through assessment, patient education, and monitoring for therapeutic and adverse effects of gabapentin. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication commonly prescribed for epilepsy, neuropathic pain, and various off-label uses. Understanding proper nursing considerations is crucial for safe and effective patient care. We use Gabapentin for the prevention of seizures for peripheral neuropathy, for neuropathic pain and for the prevention of migraines. So some of the side effects that we see with Gabapentin are things like drowsiness, facial edema, hypertension, and confusion. So let's take a look at a few nursing considerations. You may experience these side effects: Dizziness, blurred vision (avoid driving or performing other tasks requiring alertness or visual acuity); GI upset (take drug with food or milk, eat frequent small meals); headache, nervousness, insomnia; fatigue (periodic rest periods may help).
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |