Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
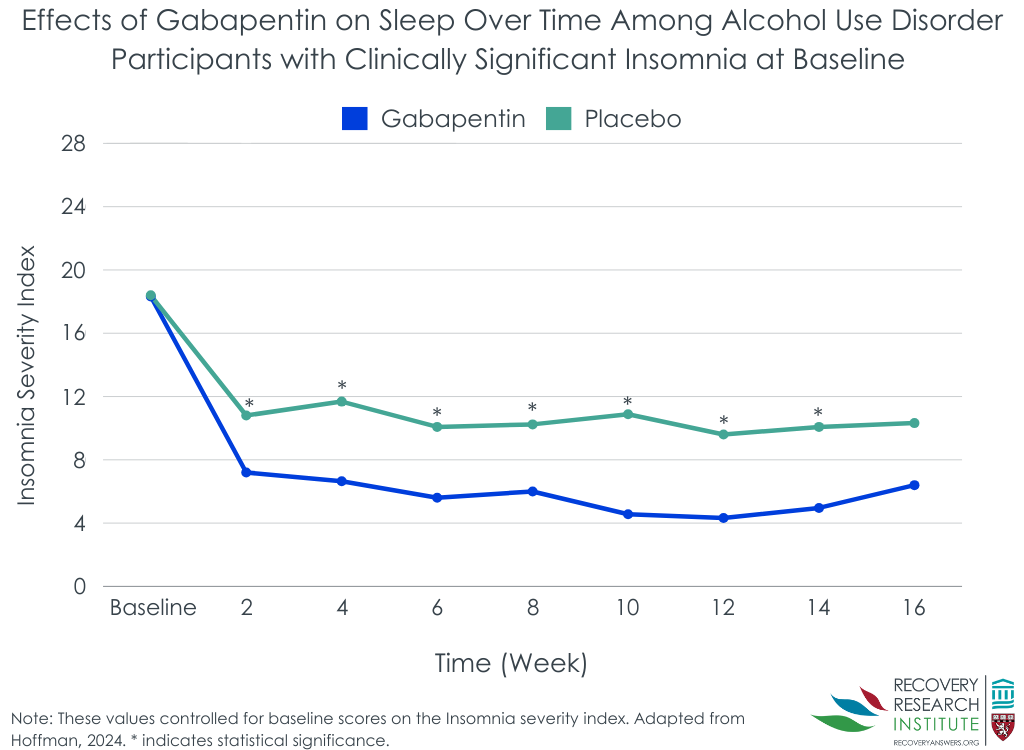
Sleep Aid and Gabapentin: Combining Medications Safely is a crucial topic to discuss with a healthcare provider to ensure safe and effective treatment. Withdrawal symptoms and tapering off gabapentin are important considerations for those who have been using the medication long-term. Gabapentin is safe and effective in improving the sleep quality of patients with sensory nervous-system diseases. Due to the limitations of sample size and types of diseases in the current study, the field needs multicenter, large-sample, and high-quality RCTs for further validation in the future. Gabapentin is a prescription medication that is FDA-approved to treat epilepsy and neuropathic pain caused by shingles. Healthcare providers often prescribe it for other off-label uses as well, including anxiety, bipolar disorder, and fibromyalgia. One of gabapentin’s most common side effects is drowsiness. Therefore, doctors may also prescribe it for sleep. Read on to learn more about Gabapentin (Neurontin) is prescribed for epilepsy and nerve pain, but some people may take gabapentin for sleep. Learn about whether off-label gabapentin works for sleep disorders. This study revealed that without consideration of the type of sleep outcomes, gabapentin was significantly superior to placebos for the treatment for sleep disorders secondary to RLS, neuropathic pain, alcohol dependence, hot flashes in menopause, fibromyalgia, phantom limb pain, HIV-associated sensory neuropathies, and bipolar disorder. Intro Gabapentin is a medication that has garnered attention for its potential role in sleep disorders. Initially developed to treat epilepsy, it has found varied applications, including pain management and anxiety relief. An increasing number of individuals are exploring its efficacy for sleep-related issues. This article aims to provide a comprehensive analysis of gabapentin dosage Gabapentin, initially developed for seizure management, has found its niche in the realm of sleep aids. Its influence on neuropathic pain and anxiety suggests a potential benefit for those struggling with sleep issues as well. Types of Sleep Disorders Treated Gabapentin has been used to treat a variety of sleep disorders. Study Objectives:To evaluate the effects of single doses of gabapentin 250 and 500 mg on polysomnographic (PSG) and participant-reported sleep measures in a 5-h phase advance insomnia model.Methods:Adults reporting occasional disturbed sleep received Gabapentin enhances slow-wave sleep in patients with primary insomnia. It also improves sleep quality by elevating sleep efficiency and decreasing spontaneous arousal. The results suggest that gabapentin may be beneficial in the treatment of primary insomnia. The optimal use of gabapentin for sleep involves careful consideration of timing, dosage, and integration with good sleep hygiene practices. Typically, taking gabapentin 1-2 hours before bedtime allows for its sleep-promoting effects to align with the desired sleep onset. Explore gabapentin's uses, effectiveness, and risks for treating sleep disorders and anxiety in this comprehensive guide. By weighing the benefits against the potential risks, individuals can make informed decisions about using gabapentin for sleep. This ensures that it is utilized safely and appropriately in their treatment plans, addressing their specific sleep concerns while minimizing any adverse effects on their overall health and well-being. Have you used Gabapentin for sleep or insomnia? If you’ve used gabapentin to treat a sleep disorder such as insomnia or to enhance sleep, be sure to share your experience in the comments section below. Intro The relationship between gabapentin and insomnia is a topic of great importance in the medical community. Gabapentin, originally developed to treat seizures, has found a place in the management of neuropathic pain. However, the off-label usage of gabapentin for sleep disorders, including insomnia, raises questions about its effectiveness and safety. This article seeks to provide a Gabapentin is a prescription medication that may help you sleep. That may be why it has been prescribed for people with insomnia, even though it is not approved for that use. However, gabapentin enacarbil (Horizant) has been approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to treat a sleep disorder called restless legs syndrome (RLS). One of the most common side effects of gabapentin is What is Insomnia? Insomnia is a sleep disorder that can make it difficult to fall asleep, stay asleep, or both. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including stress, anxiety, depression, and certain medications. How Does Gabapentin Cause Insomnia ? The exact mechanism by which gabapentin can cause insomnia is not fully understood. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant that is primarily used to treat seizures, but it can be used off-label as a sleep aid. Gabapentin can reduce nighttime awakenings and promote more slow-wave sleep. There is a risk of misuse and dependence on gabapentin, which leads to potential concerns regarding its long-term use. Gabapentin vs Doxepin for Sleep: Comparing Effectiveness and Side Effects provides a comparative analysis that can be helpful in understanding these options. For individuals with specific sleep-related conditions, such as sleep apnea, the relationship between gabapentin and their condition requires careful consideration. The aim of this study was to systematically review the efficacy and tolerability of gabapentin in the treatment of sleep disturbance in patients with medical illness. PubMed was searched for randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trials that Insomnia is common and frequently occurs with other disorders. First-line cognitive behavioral therapy with or without medication can produce rapid, sustained alleviation of insomnia symptoms.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |