Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
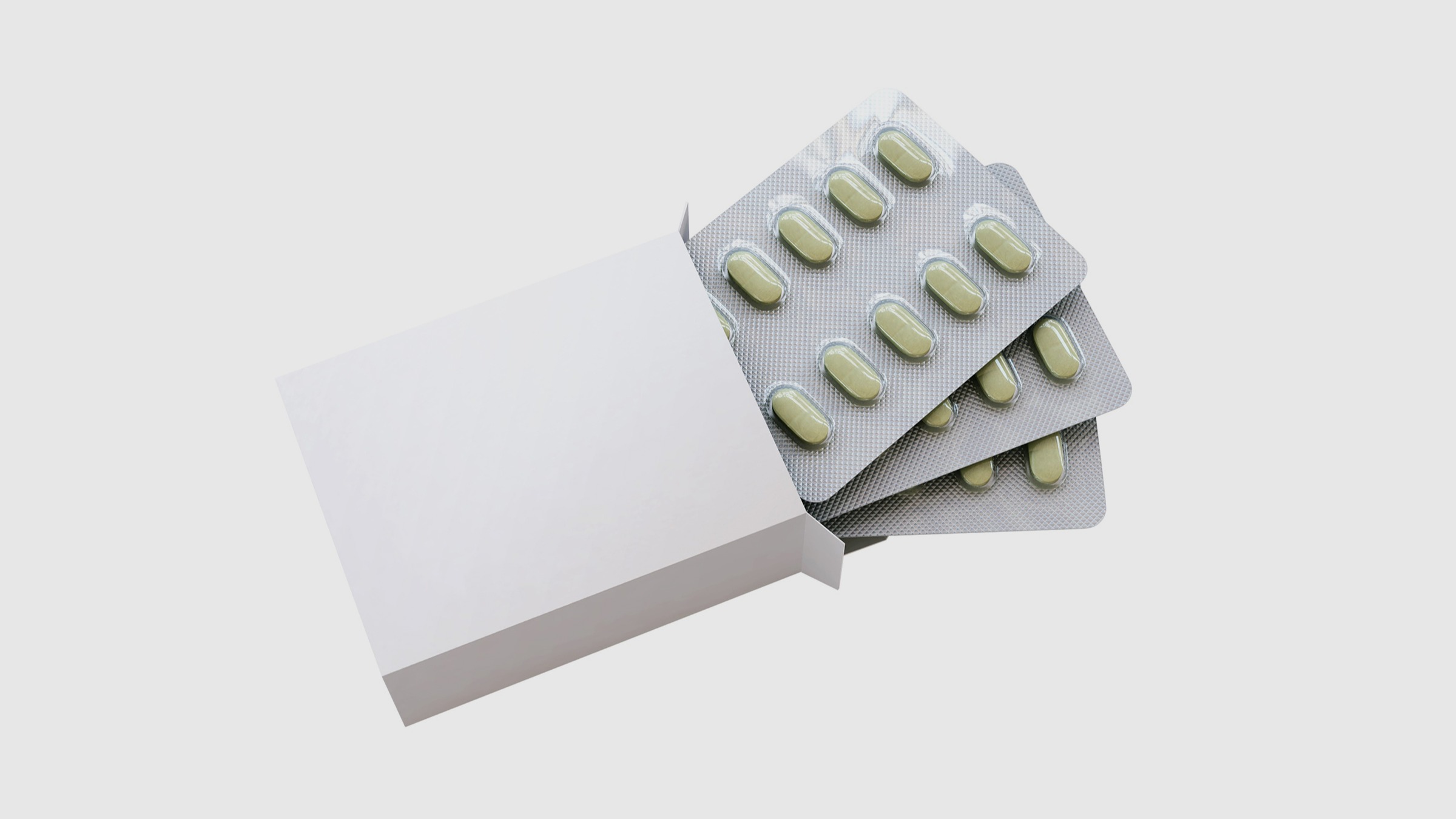
Gabapentin, sold under the brand name Neurontin among others, is an anticonvulsant medication primarily used to treat neuropathic pain and also for partial seizures [10][7] of epilepsy. It is a commonly used medication for the treatment of neuropathic pain caused by diabetic neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia, and central pain. [11] It is moderately effective: about 30–40% of those given Frequent use of gabapentin for back pain may raise the risk of dementia by 29% and mild cognitive impairment by 85%, new study finds. Neurontin (gabapentin) is used to treat seizures and nerve pain caused by the herpes virus. Includes Neurontin side effects, interactions and indications. Gabapentin drug interactions: Along with side effects, gabapentin has possible interactions to know about. Gabapentin FAQs: Experts answer common questions about taking gabapentin, from if you should take it with food to what to do if you miss your dose. Receiving six or more prescriptions of the drug gabapentin for low back pain is associated with significantly increased risks of developing dementia and mild cognitive impairment (MCI)—29% and Gabapentin is a prescription drug used to treat seizure disorders and nerve damage from shingles. Off label uses (non-FDA approved) include fibromyalgia, headaches, and hot flashes. Common side effects are fatigue, nausea, hostility, dizziness, and tremors. Gabapentin is not an opioid narcotic, but it does have signs and symptoms associated with drug misuse, addiction, and withdrawal symptoms Gabapentin is an anti-epileptic drug, also called an anticonvulsant. It is used to treat some types of seizures and nerve pain caused by shingles. Learn about the side effects of gabapentin, from common to rare, for consumers and healthcare professionals. Easy-to-read patient tips for gabapentin covering how it works, benefits, risks, and best practices. Gabapentin is an anti-seizure drug that is used to treat nerve pain, epilepsy after shingles and restless legs syndrome by affecting the chemical messengers in the brain and nerves. With every A large U.S. medical records study has found that adults prescribed gabapentin six or more times for chronic low back pain face significantly higher risks of dementia (29%) and mild cognitive impairment (85%) within 10 years. Gabapentin works in the brain to prevent seizures and relieve pain for certain conditions in the nervous system. It is not used for routine pain caused by minor injuries or arthritis. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant. This medicine is available only with your doctor's prescription. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication prescribed for a variety of conditions. Learn about its uses, side effects, and what you should know if you've been prescribed this medication. Gabapentin is approved to prevent and control partial seizures, relieve postherpetic neuralgia after shingles and moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome. Learn what side effects to watch for, drugs to avoid while taking gabapentin, how to take gabapentin and other important questions and answers. Gabapentin is available in both branded and generic forms. The anti-seizure drug gabapentin is used to treat epilepsy, nerve pain after shingles and restless legs syndrome by affecting chemical messengers in the brain and nerves. Common side effects Doctors prescribe gabapentin to treat epilepsy, restless legs syndrome, and some types of nerve pain. Learn more the drug's uses, risks, and safety here. Read the Medication Guide before you start taking gabapentin and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking to your healthcare provider about your medical condition or treatment. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsive medication that received approval from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1993 and has been available in generic form in the USA since 2004. Gabapentin was originally used as a muscle relaxant and an anti-spasmodic. However, it was later discovered that gabapentin has the potential of an anticonvulsive medication and can be used as an adjunct to more Find patient medical information for Gabapentin (Gralise, Neurontin) on WebMD including its uses, side effects and safety, interactions, pictures, warnings, and user ratings If you suddenly stop taking gabapentin tablets, capsules, or oral solution, you may experience withdrawal symptoms such as anxiety, difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep, nausea, pain, and sweating. If you are taking gabapentin to treat seizures and you suddenly stop taking the medication, you may experience seizures more often.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |