Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
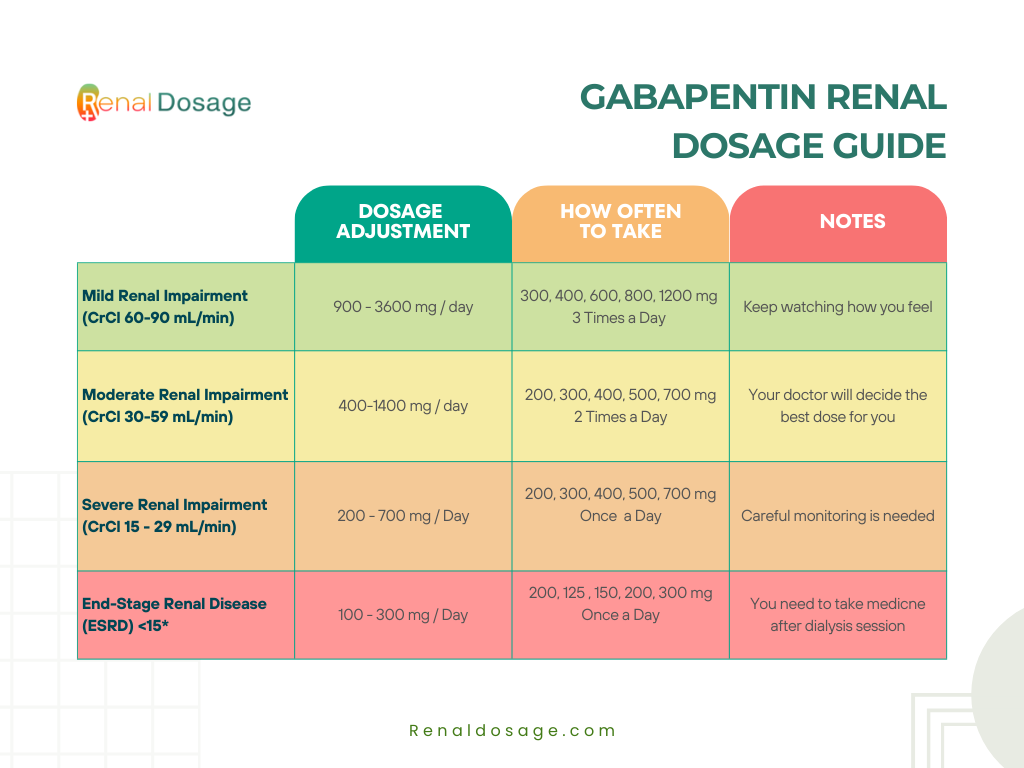
Below are the general guidelines for dosing gabapentin. Note that these dosages may be adjusted on a case-by-case basis for individual patients by provider. Gabapentin is increasingly prescribed to elderly patients for various conditions, but its safety profile in this age group requires special attention. This article explores the benefits, risks, and considerations for gabapentin use in older adults. The starting dose range is 10 mg/kg/day to 15 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses, and the recommended maintenance dose reached by upward titration over a period of approximately 3 days. The recommended maintenance dose of gabapentin capsules in patients 3 to 4 years of age is 40 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses. Gabapentin is a drug used to treat epilepsy and neuropathic pain. It also has some effect on spasticity and can be used in combination with other drugs as an off-label use; it is particularly useful if pain and spasticity co-exist. The maximum dose is 3600 mg per day in divided doses. Slow titration (suitable if the person is elderly, frail, or has experienced adverse effects with higher doses). Start with 100 mg at night, increasing by 100 mg a day until pain is significantly reduced, intolerable adverse effects occur, or a maximum daily dosage of 3600 mg (1200 mg three times a day) is reached [Dworkin, 2007]. Detailed Gabapentin dosage information for adults and children. Includes dosages for Restless Legs Syndrome, Epilepsy and Postherpetic Neuralgia; plus renal, liver and dialysis adjustments. d sedation, which could increase the occurrence of accidental injury (fall) in the elderly popu ose or dosing regimen are necessary in patients at higher risk of respiratory depression, includ ical disease, or renal im taking other CNS depressants (including opioid-containing medicines). aged older than 65 years. A titrated approach for initiation of both gabapentin and pregabalin is recommended, Titration of doses should be managed according to side effects and clinical effectiveness. taking into consideration patient characteristics, e.g. elderly, renal impairment, breast feeding which may affect the suitability for prescribing or the dosage. Gabapentin is an effective treatment for chronic neuropathic pain but may cause dizziness, drowsiness, and confusion in some older adults. The goal of this study was to assess the association between gabapentin dosing and adverse outcomes by Gabapentin is a safe and well-tolerated anticonvulsant with a wide therapeutic index, and it is used for neuropathic pain. The aim of this study was to compare previous dosing methods with the administration of four different doses of gabapentin The starting dose range is 10 mg/kg/day to 15 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses, and the recommended maintenance dose reached by upward titration over a period of approximately 3 days. The recommended maintenance dose of gabapentin in patients 3 to 4 years of age is 40 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses. The recommended maintenance dose of gabapentin in patients 5 to 11 years of age For frail, elderly patients, only titrate up to 300 mg PO three times daily prior to referral. For younger, fitter patients, titrate up to 600 mg three times daily. QUANTITY to prescribe for the first 28 to 30 days: FAST up-titration: 140 x 300 mg capsules; LOW up-titration: 140 x 100 mg capsules. The starting dose range is 10 mg/kg/day to 15 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses, and the recommended maintenance dose reached by upward titration over a period of approximately 3 days. The recommended maintenance dose of gabapentin capsules in patients 3 to 4 years of age is 40 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses. Neuropathic pain due to a lesion or a disease of the somatosensory system often affects older people presenting several comorbidities. Moreover, elderly patients are often poly-medicated, hospitalized and treated in a nursing home with a growing Key Takeaway While gabapentin can be effective for treating certain conditions in elderly patients, it requires careful dosing and monitoring due to potential side effects and interactions with other medications. Gabapentin dosing information - GabapentinGabapentin comes as: 100 mg, 300 mg, and 400 mg capsules 300 mg, 600 mg, and 800 mg tablets a 250 mg/5 mL oral (by mouth) solution. Inactive ingredients in the capsules include lactose, cornstarch, and talc. The 100-mg capsule shell also contains: gelatin and titanium dioxide. The 300-mg capsule shell also contains: gelatin, titanium dioxide, and Gabapentin should be started slowly according to the regimen below. In renal impairment, the elderly or drug sensitive patients, this titration may need to be done in 100mg increments. The dose can be increased further if necessary. Slow titration table for elderly patients or patients who are sensitive to Gabapentin Stay on this dose for a few days and if pain relief is adequate remain at this, but if pain is still a problem, try increasing the tablets as follows (see overleaf). Learn about common and serious gabapentin side effects in elderly patients. Understand risks, precautions, and when to seek medical help. Key Takeaway Gabapentin can be an effective treatment for various conditions in elderly patients, but requires careful dosing and monitoring due to age-related changes in pharmacokinetics and potential side effects.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |